Regulation Of Citric Acid Cycle
Regulation Of Citric Acid Cycle
The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle or the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a key metabolic pathway that takes place within the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role in the generation of ATP, the energy currency of the cell. The citric acid cycle is a series of chemical reactions that break down acetyl-CoA and produce energy-rich molecules such as NADH and FADH2, which are then used in the electron transport chain to generate ATP. This article will explore the regulation of the citric acid cycle and highlight its importance in cellular metabolism.
Regulation of Citric Acid Cycle
The citric acid cycle is tightly regulated through various mechanisms to ensure efficient energy production and to maintain cellular homeostasis. Several key regulatory steps exist within the cycle, and these steps are primarily regulated by substrate availability, product inhibition, and allosteric regulation. Let's explore these regulatory mechanisms in more detail.
1. Substrate Availability
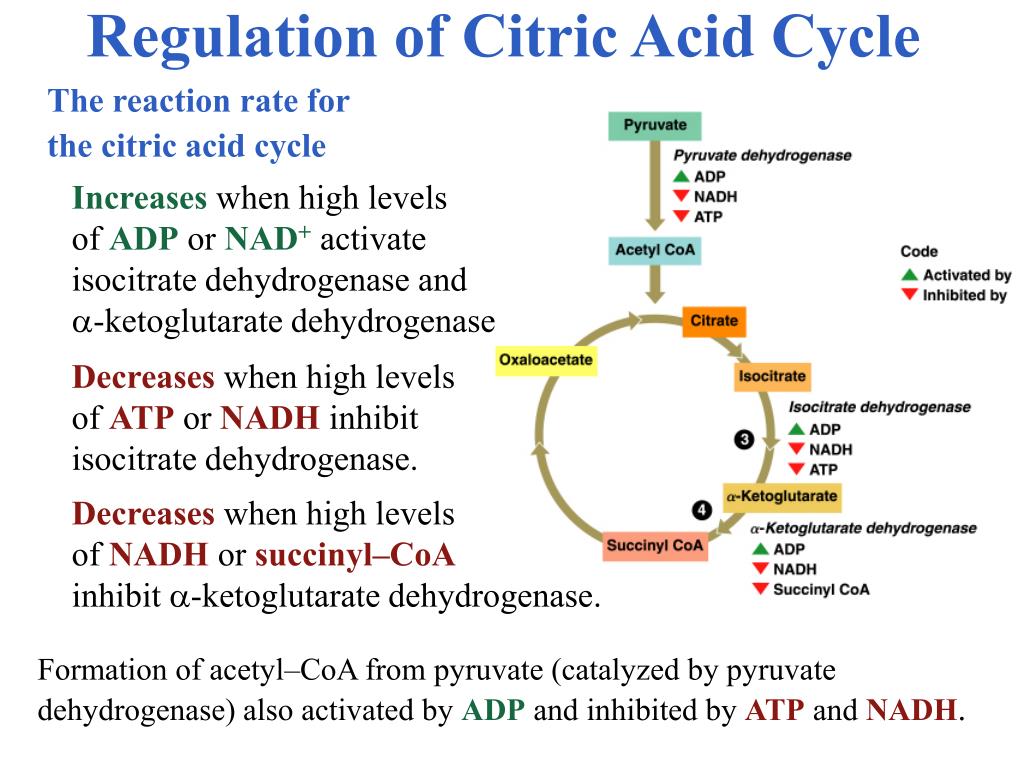
The availability of substrates such as acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate directly influences the rate of the citric acid cycle. Acetyl-CoA is derived from the breakdown of carbohydrates, fatty acids, or amino acids, and its concentration is regulated by the activity of various metabolic pathways. Oxaloacetate, on the other hand, is produced from pyruvate, which is the end product of glycolysis. The levels of these substrates are tightly regulated to maintain proper functioning of the cycle.
2. Product Inhibition
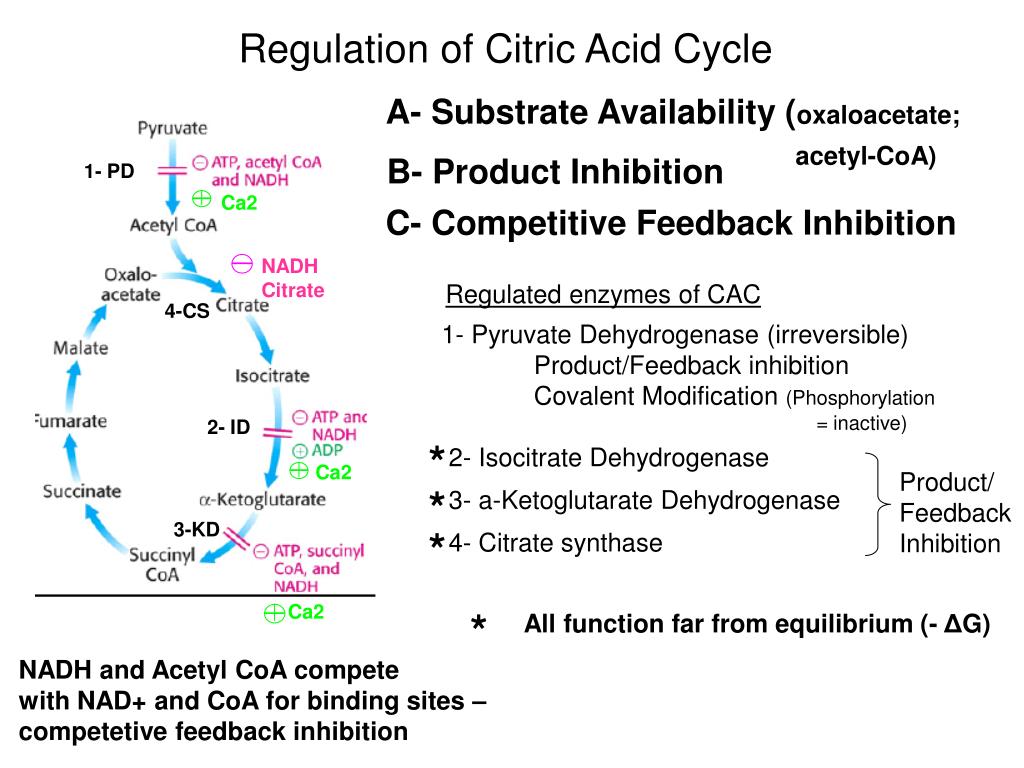
Certain intermediates within the citric acid cycle act as allosteric inhibitors, regulating the rate of the cycle. For example, ATP is a negative allosteric regulator of citrate synthase, the enzyme that catalyzes the first step of the cycle. An increase in ATP levels inhibits the activity of citrate synthase, thereby slowing down the citric acid cycle. Similarly, high levels of NADH and succinyl-CoA act as negative regulators of key enzymes in the cycle, ensuring a balanced metabolic state.
3. Allosteric Regulation
Allosteric regulation, which involves the binding of molecules to a site on an enzyme other than the active site, also plays a significant role in regulating the citric acid cycle. For instance, when the concentration of NADH and ATP is high, they bind to specific sites on isocitrate dehydrogenase, an enzyme involved in the cycle. This binding inhibits the enzyme's activity and slows down the cycle, ensuring that ATP production matches the energy demands of the cell.
FAQs
Q: What is the significance of the citric acid cycle?
The citric acid cycle is vital for cellular respiration as it is the primary pathway through which energy-rich molecules, such as NADH and FADH2, are generated. These molecules are then used in the electron transport chain to produce ATP, which fuels various cellular processes. Additionally, the cycle serves as a hub for the integration of different metabolic pathways, allowing the cell to efficiently utilize different substrates for energy production.
Q: How is the citric acid cycle regulated in response to changes in energy demand?
When energy demand is high, the levels of ADP and NAD+ are elevated, signaling the need for increased ATP production. This, in turn, activates key enzymes in the citric acid cycle, leading to a higher flux through the pathway. Conversely, when ATP levels are high, allosteric inhibitors, such as ATP and NADH, reduce the cycle's activity, preventing ATP overproduction and waste of cellular resources.
Q: Can dysregulation of the citric acid cycle lead to metabolic disorders?
Yes, dysregulation of the citric acid cycle can result in various metabolic disorders. Mutations in enzymes involved in the cycle can lead to a buildup of toxic intermediates or a decrease in ATP production. For example, deficiencies in enzymes like succinate dehydrogenase or fumarate hydratase have been associated with hereditary cancer syndromes. Understanding the regulation of the citric acid cycle is crucial for diagnosing and treating such disorders.
In conclusion, the regulation of the citric acid cycle involves complex mechanisms that ensure optimal energy production and maintain cellular homeostasis. Substrate availability, product inhibition, and allosteric regulation play significant roles in governing the activity of key enzymes within the cycle. Dysregulation of the citric acid cycle can have severe consequences and lead to various metabolic disorders. By understanding the regulation of this crucial metabolic pathway, researchers can better comprehend the underlying mechanisms of diseases and develop targeted therapeutic interventions.Regulation Of Citric Acid Cycle - Bioscience Notes
 Image Source : www.biosciencenotes.com
Image Source : www.biosciencenotes.com cycle acid regulation citric tca
Citric Acid Cycle Regulation - YouTube
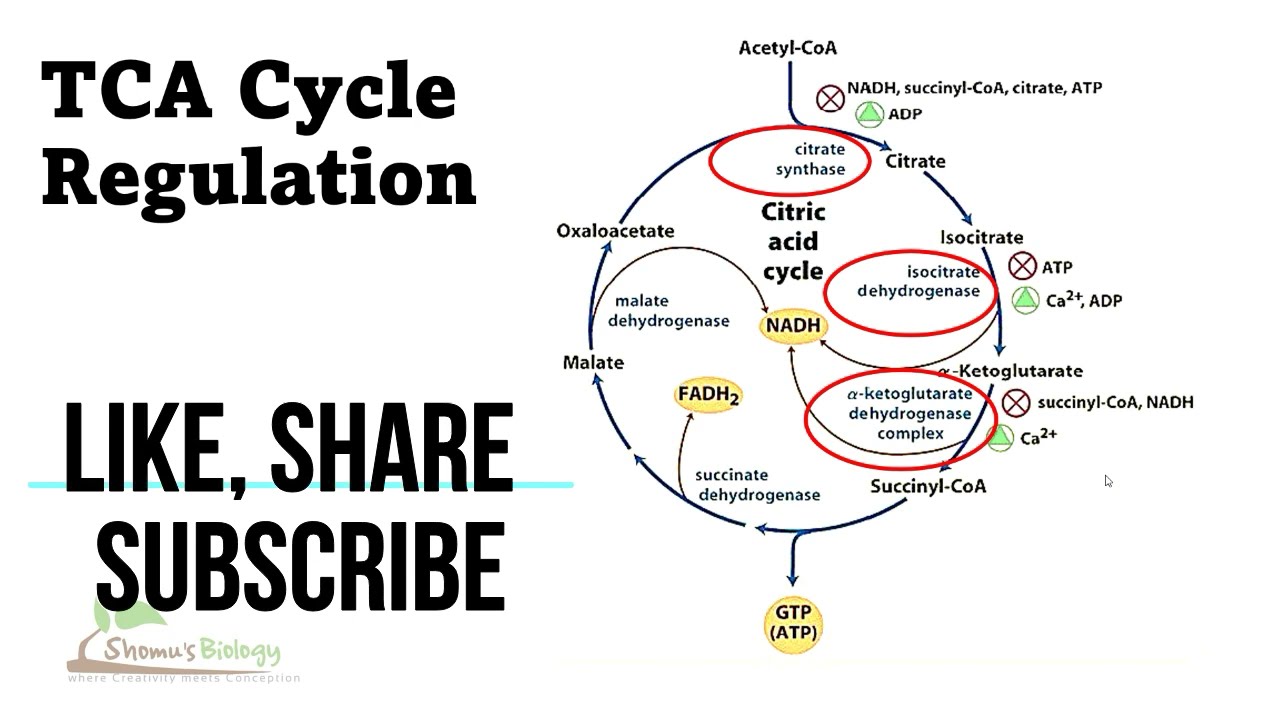 Image Source : www.youtube.com
Image Source : www.youtube.com PPT - Stages Of Metabolism PowerPoint Presentation, Free Download - ID
 Image Source : www.slideserve.com
Image Source : www.slideserve.com cycle acid citric regulation stages ppt dehydrogenase metabolism isocitrate powerpoint presentation rate slideserve
PPT - Regulation Of Glycolysis/Gluconeogenesis Citric Acid Cycle / TCA
 Image Source : www.slideserve.com
Image Source : www.slideserve.com cycle regulation acid citric tca gluconeogenesis kreb glycolysis ca2 ppt powerpoint presentation
Regulation Of The Cycle - Citric Acid Cycle - MCAT Content
 Image Source : jackwestin.com
Image Source : jackwestin.com Citric Acid Cycle Regulation
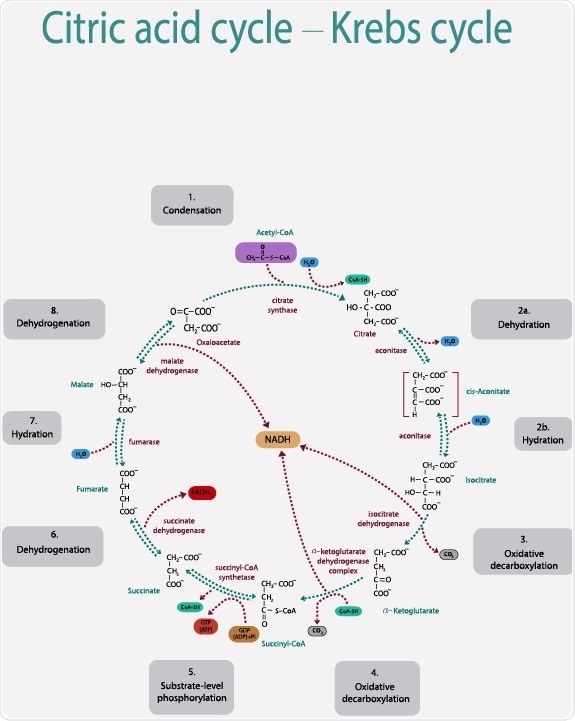 Image Source : klickhealth.ath.cx
Image Source : klickhealth.ath.cx The Citric Acid Cycle: Functions, Reactions, Regulation, Inhibitors
 Image Source : notesmed.com
Image Source : notesmed.com citric acid inhibitors biochemistry
Schematic Diagram Of The Citric Acid Cycle Showing The Trend Of
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net citric acid regulation
Citric acid cycle regulation. Regulation of citric acid cycle. Citric acid inhibitors biochemistry. Citric acid cycle regulation. Schematic diagram of the citric acid cycle showing the trend of