Heart Rate Regulation : What it is
Heart Rate Regulation: What It Is The heart is a vital organ in the human body responsible for pumping blood and delivering oxygen and nutrients to various tissues and organs. One of its essential functions is to regulate the heart rate, which refers to the number of times the heart beats per minute. Heart rate regulation is a complex physiological process influenced by various factors, including exercise, emotions, environmental conditions, and overall health. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of heart rate regulation, its significance, and how it is affected during exercise. So, let's dive in! 1. Understanding Heart Rate Regulation Heart rate regulation is controlled by the autonomic nervous system, which consists of two branches: the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. These branches work in balance to maintain heart rate within a healthy range, depending on the body's needs. a) The Role of the Sympathetic Nervous System The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for accelerating heart rate. It releases hormones like adrenaline, which increases the heart rate in response to stress, exercise, or other stimuli. To better understand heart rate regulation, let's consider an example. Imagine you are walking in a dark alley, and suddenly, you sense something following you. In response to this threat, your brain signals the sympathetic nervous system to release adrenaline, increasing your heart rate. This physiological response prepares your body for a "fight or flight" situation, providing extra oxygen and nutrients to your muscles to enhance your performance. b) The Role of the Parasympathetic Nervous System On the other hand, the parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for decelerating heart rate, bringing it back to a relaxed state. This branch of the autonomic nervous system is active during resting periods, ensuring that the heart rate remains at a healthy level and conserving energy. 2. Heart Rate Regulation During Exercise Physical activity is one of the most significant factors influencing heart rate regulation. When we exercise, our body demands more oxygen and nutrients to fuel the muscles, leading to an increased heart rate. This increase in heart rate is essential to meet the increased oxygen requirements of the body during exercise. a) Target Heart Rate During exercise, it is crucial to reach and maintain a target heart rate to achieve optimal cardiovascular benefits. The target heart rate varies based on age, fitness level, and exercise intensity. It is generally recommended to aim for a heart rate that falls within 50-85% of your maximum heart rate. To calculate your maximum heart rate, subtract your age from 220. For example, if you are 30 years old, your maximum heart rate would be 220 - 30 = 190 beats per minute (bpm). Therefore, your target heart rate during exercise should be between 95 bpm (50% of 190) and 162 bpm (85% of 190). b) Factors Affecting Heart Rate During Exercise Several factors influence heart rate regulation during exercise, including: i. Exercise Intensity: The more intense the exercise, the higher the heart rate response. High-intensity activities like sprinting will significantly increase heart rate compared to moderate activities like brisk walking. ii. Fitness Level: Individuals who are physically fit tend to have lower resting heart rates and a more efficient cardiovascular system. As a result, their heart rates rise less during exercise compared to individuals who are less fit. iii. Environment: Factors like temperature and humidity can affect heart rate regulation during exercise. In hot and humid conditions, the heart rate tends to increase to dissipate heat and maintain a stable body temperature. iv. Emotional State: Emotions such as stress, anxiety, and excitement can influence heart rate regulation during exercise. For example, feeling anxious before a competition or excited about a sporting event can cause an increase in heart rate. 3. The Effects of Heart Rate Regulation on Health Maintaining a healthy heart rate is crucial for overall cardiovascular health. Chronically elevated heart rates, especially at rest, can be a sign of an underlying health condition or poor fitness level. Conversely, a very low heart rate can indicate a problem with the heart's electrical conduction system. a) Resting Heart Rate Resting heart rate refers to the number of times your heart beats per minute while at complete rest. A normal resting heart rate range for adults is between 60 and 100 bpm. Lower resting heart rates are usually observed in individuals who are physically fit, while higher resting heart rates may indicate a higher risk of heart disease or other health issues. b) Heart Rate Variability Heart rate variability (HRV) refers to the variation in time intervals between consecutive heartbeats. A healthy heart has naturally occurring fluctuations in heart rate intervals, indicating a flexible and adaptive cardiovascular system. Reduced HRV is associated with various health conditions, including stress, anxiety, depression, and heart disease. 4. FAQs Here are some frequently asked questions about heart rate regulation: Q1: Can medications affect heart rate? A: Yes, certain medications, such as beta-blockers, can lower heart rate by blocking the effects of adrenaline on the heart. Other medications, like stimulants, can increase heart rate. Q2: Does age affect heart rate regulation? A: Yes, as individuals age, their maximum heart rate decreases, and the heart rate response to exercise may be slower. However, regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy heart rate even as we age. Q3: How can I improve my heart rate regulation during exercise? A: Regular aerobic exercise, such as running, swimming, or cycling, can improve heart rate regulation. Gradually increasing exercise intensity and duration over time can help enhance cardiovascular fitness and efficiency. Conclusion Heart rate regulation is a complex process influenced by various factors, including exercise, emotions, and overall health. Understanding how heart rate is regulated and the significance of maintaining a healthy heart rate can help individuals make informed decisions about their lifestyle and exercise choices. By incorporating regular physical activity and adopting a balanced approach to stress management, we can support our heart's health and overall well-being. Remember, consult with a healthcare professional before starting any exercise program or making significant changes to your lifestyle.  Image Source : www.youtube.com
Image Source : www.youtube.com  Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net  Image Source : www.brainkart.com
Image Source : www.brainkart.com  Image Source : www.youtube.com
Image Source : www.youtube.com 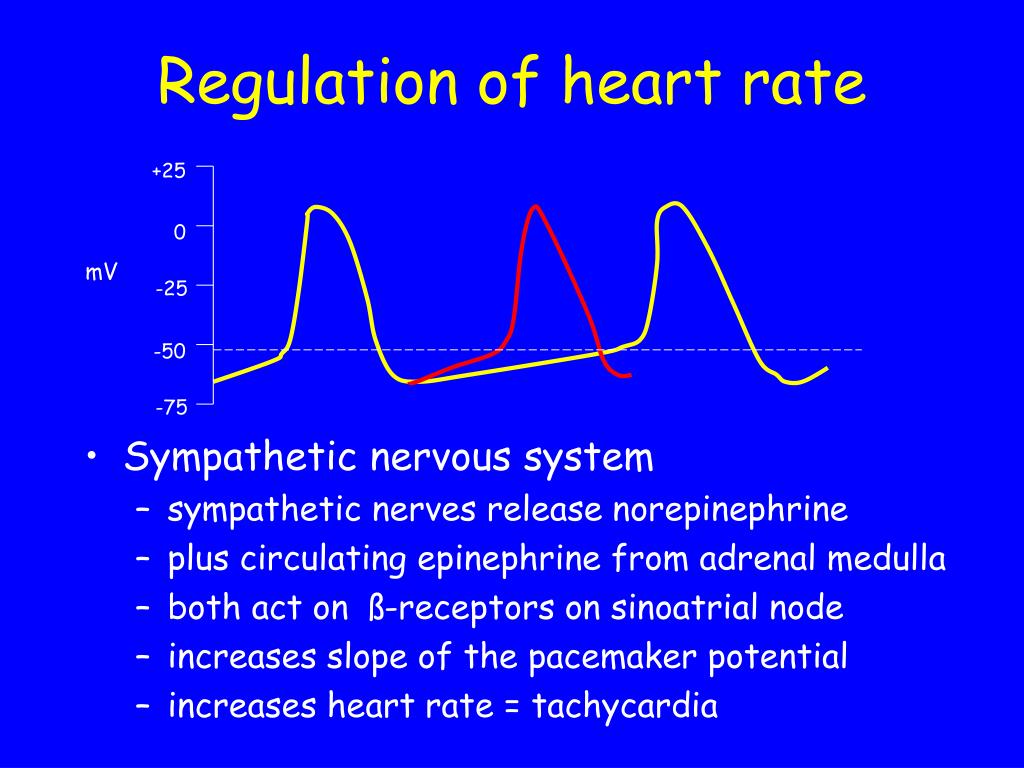 Image Source : www.slideserve.com
Image Source : www.slideserve.com  Image Source : www.physoc.org
Image Source : www.physoc.org  Image Source : prezi.com
Image Source : prezi.com  Image Source : studylib.net
Image Source : studylib.net
Heart Rate Regulation - Neural, Hormonal And Intrinsic - YouTube
 Image Source : www.youtube.com
Image Source : www.youtube.com regulation neural hormonal intrinsic
A Simplified Schematic For The Mechanism Of Heart Rate Regulation By
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net regulation vagus nerve schematic simplified acetylcholine inhibitory receptor camp potassium signaling pathway
Regulation Of Heart Rate
 Image Source : www.brainkart.com
Image Source : www.brainkart.com heart rate regulation anatomy beat
Regulation Of Heart Rate (Cardiovascular Variables Part 2) - YouTube
 Image Source : www.youtube.com
Image Source : www.youtube.com regulation cardiovascular
PPT - Regulation Of Stroke Volume & Heart Rate PowerPoint Presentation
 Image Source : www.slideserve.com
Image Source : www.slideserve.com heart regulation rate stroke volume ppt powerpoint presentation cardiac output system
Heart Rate Regulation During Exercise - The Physiological Society
 Image Source : www.physoc.org
Image Source : www.physoc.org regulation physiological cardiovascular physiology
Heart Rate Regulation By Kerry Adele
 Image Source : prezi.com
Image Source : prezi.com regulation rate heart
Heart Rate Regulation And Control.
 Image Source : studylib.net
Image Source : studylib.net Heart rate regulation anatomy beat. Regulation neural hormonal intrinsic. Heart rate regulation and control.. Heart rate regulation by kerry adele. Regulation of heart rate