Phosphofructokinase 2 Regulation
Phosphofructokinase 2 (PFK-2) is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in regulating glycolysis, the metabolic pathway that converts glucose into energy. It is a fascinating enzyme that has caught the attention of many researchers in the field of biochemistry. In this post, we will explore the regulation of Phosphofructokinase 2 and its importance in cellular metabolism.
What is Phosphofructokinase 2?
To understand the regulation of Phosphofructokinase 2, we first need to know what it is and how it functions. Phosphofructokinase 2 is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-2,6-bisphosphate, a key regulator of glycolysis. It is part of a larger enzyme complex called 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase (PFK-2/FBPase-2) complex. PFK-2 is responsible for the synthesis of fructose-2,6-bisphosphate, which allosterically activates the glycolytic enzyme, phosphofructokinase 1 (PFK-1).
Regulation of Phosphofructokinase 2
Phosphofructokinase 2 is tightly regulated by various factors to maintain the balance between glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, the opposing metabolic pathway. One of the key factors that regulate PFK-2 activity is the hormone insulin. Insulin stimulates the activation of PFK-2 through a signaling cascade involving protein kinase B (PKB), also known as Akt. Activation of PFK-2 leads to an increase in fructose-2,6-bisphosphate levels, which in turn enhances glycolysis by activating PFK-1. This regulation ensures that glucose is efficiently converted into energy when it is available in abundance.
Another important regulator of PFK-2 is the enzyme AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). AMPK serves as an energy sensor in cells and becomes activated when ATP levels are low. Activated AMPK phosphorylates and inhibits PFK-2, reducing the levels of fructose-2,6-bisphosphate and preventing excessive glycolysis. This mechanism allows cells to conserve energy during times of energy deprivation.
Importance of Phosphofructokinase 2 in Cellular Metabolism
Phosphofructokinase 2 plays a vital role in cellular metabolism by controlling the flux of glucose through the glycolytic pathway. Its regulation allows cells to respond to changes in nutrient availability and energy demands. Here are three key aspects highlighting the importance of Phosphofructokinase 2:
1. Control of Glycolysis-Gluconeogenesis Switch
Phosphofructokinase 2 acts as a key player in the glycolysis-gluconeogenesis switch, which determines whether glucose is utilized as an energy source or stored as glycogen. During times of high glucose levels, insulin activates Phosphofructokinase 2, promoting glycolysis and energy production. Conversely, during fasting or in conditions of low glucose, Phosphofructokinase 2 is inhibited, leading to the activation of gluconeogenesis, the process of glucose synthesis. This fine-tuned regulation allows cells to maintain glucose homeostasis and adapt to different metabolic states.
2. Integration of Glycolysis and Lipogenesis
Phosphofructokinase 2 also plays a crucial role in the integration of glycolysis and lipogenesis, the process of fatty acid synthesis. Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate, the product of PFK-2 activity, not only activates PFK-1 to enhance glycolysis but also inhibits fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase-1), an enzyme involved in gluconeogenesis. This inhibition of FBPase-1 ensures that glucose carbon is directed towards fatty acid synthesis rather than being used for glucose production. In this way, Phosphofructokinase 2 influences the balance between carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
3. Regulation of ATP Production
By controlling the flux of glucose through the glycolytic pathway, Phosphofructokinase 2 indirectly regulates ATP production. Glycolysis is a major source of ATP in cells, and the activation of PFK-2 by insulin ensures efficient energy production during periods of high-energy demand. In contrast, the inhibition of PFK-2 by AMPK during energy deprivation conserves ATP by reducing glycolytic flux. This dynamic regulation allows cells to maintain ATP levels and meet their energy requirements under varying conditions.
FAQs about Phosphofructokinase 2 and Regulation
Q1: What happens if Phosphofructokinase 2 is overactivated?
If Phosphofructokinase 2 is overactivated, there could be an excessive stimulation of glycolysis, leading to an increased production of lactate. This phenomenon, known as aerobic glycolysis or the Warburg effect, is often observed in cancer cells and can promote tumor growth and progression.
Q2: Are there any diseases associated with abnormalities in Phosphofructokinase 2 regulation?
Yes, there are diseases associated with abnormalities in Phosphofructokinase 2 regulation. For example, deficiencies in PFK-2 have been linked to glycogen storage disease type VII (also known as Tarui disease), a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by muscle weakness and exercise intolerance.
Q3: Can targeting Phosphofructokinase 2 be a therapeutic strategy?
Targeting Phosphofructokinase 2 has shown potential as a therapeutic strategy, particularly in the context of cancer. Inhibiting PFK-2 can help disrupt the metabolic rewiring seen in cancer cells, thereby limiting their ability to proliferate and survive. However, further research is needed to develop effective and specific inhibitors of PFK-2 that can be utilized in clinical settings.
Phosphofructokinase 2 is a fascinating enzyme that lies at the heart of glycolysis regulation. Its tight control allows cells to adapt to changing energy demands, maintain glucose homeostasis, and integrate carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Understanding the regulation of Phosphofructokinase 2 provides valuable insights into the intricate workings of cellular metabolism and may have implications for the development of novel therapeutic approaches.
Role Of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase (PFK-2)/fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net fructose pfk kinase bisphosphatase fbpase metabolism glycolytic
Phosphofructokinase 2 - Alchetron, The Free Social Encyclopedia
The Bifunctional Enzyme
 Image Source : laproteinadealex.blogspot.com
Image Source : laproteinadealex.blogspot.com enzyme bifunctional pfk allosteric activator does applicable relevant
Phosphofructokinase 2 - Alchetron, The Free Social Encyclopedia
 Image Source : alchetron.com
Image Source : alchetron.com Glycolysis - USMLE Strike
 Image Source : usmlestrike.com
Image Source : usmlestrike.com Phosphofructokinase 1 - Alchetron, The Free Social Encyclopedia
phosphofructokinase regulation allosteric pfk kegg biochemistry
Phosphofructokinase 2 - Alchetron, The Free Social Encyclopedia
PPT - CHAPTER 15 Principles Of Metabolic Regulation PowerPoint
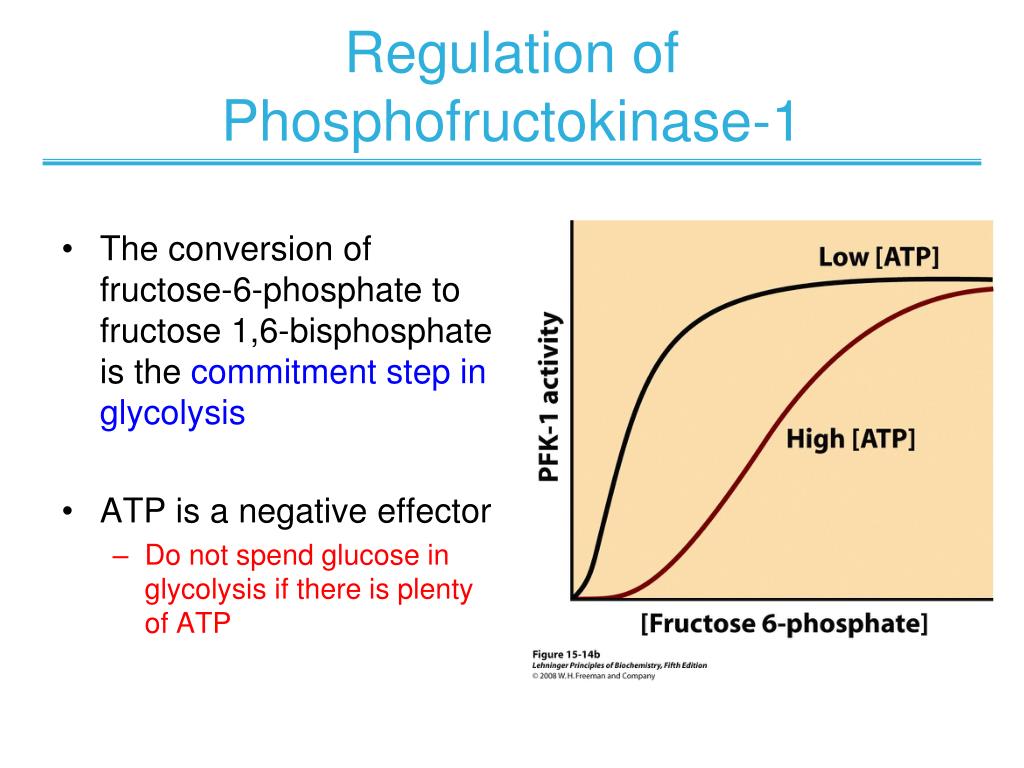 Image Source : www.slideserve.com
Image Source : www.slideserve.com regulation phosphofructokinase metabolic principles chapter atp ppt powerpoint presentation fructose
Enzyme bifunctional pfk allosteric activator does applicable relevant. The bifunctional enzyme. Phosphofructokinase regulation allosteric pfk kegg biochemistry. Fructose pfk kinase bisphosphatase fbpase metabolism glycolytic. Role of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase (pfk-2)/fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase