Fructose 2 6 Bisphosphatase Regulation
Fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase, also known as PFK-2/FBPase-2, plays a significant role in the regulation of glycolysis and gluconeogenic pathways. This enzyme acts as a key control point, ensuring a delicate balance between the breakdown and synthesis of glucose within the body. Understanding the intricate mechanisms by which fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase operates is crucial for comprehending the metabolic processes that contribute to overall homeostasis.
Regulating Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis
Glycolysis is a central pathway that facilitates the breakdown of glucose into pyruvate. This process generates energy in the form of ATP and NADH, which are essential for various cellular functions. On the other hand, gluconeogenesis is responsible for the synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources, such as amino acids and glycerol.

The interplay between these two pathways is precisely regulated by fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase. Under normal physiological conditions, the enzyme catalyzes the conversion of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate (F2,6BP) into fructose 6-phosphate (F6P), effectively inhibiting glycolysis and promoting gluconeogenesis.
Fructose 2,6-Bisphosphatase: A Balancing Act
Fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase is part of a family of enzymes known as phosphofructokinase (PFK) regulators. Its primary function is to adjust the activity of phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1), a key enzyme in the glycolytic pathway.
By controlling the levels of F2,6BP, fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase indirectly regulates the activity of PFK-1. When F2,6BP levels are low, fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase is active, leading to increased levels of F6P. Consequently, this inhibits PFK-1, effectively suppressing glycolysis.
On the flip side, when F2,6BP levels are high, fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase is inhibited, and glycolysis is promoted through the activation of PFK-1. This balancing act ensures that the body adapts to varying energy demands and maintains glucose homeostasis.
The Intricacies of Fructose 2,6-Bisphosphatase Regulation
Fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase regulation is a highly complex process that involves multiple factors and intricate feedback loops. One of the key players in this regulation is the hormone insulin, which acts as a powerful modulator of fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase activity.
Insulin, secreted by the pancreas in response to elevated blood glucose levels, stimulates the production of a protein called phosphofructokinase-2 (PFK-2). PFK-2 possesses both kinase and phosphatase activities, allowing it to control the levels of F2,6BP dynamically.

When insulin levels are high, PFK-2 is activated, leading to the production of F2,6BP. This, in turn, stimulates glycolysis and promotes glucose utilization. Conversely, when insulin levels drop, PFK-2 is inhibited, resulting in reduced F2,6BP levels. As a consequence, gluconeogenesis is favored and glucose production is increased.
Implications in Disease and Therapeutics
Alterations in fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase regulation have been associated with various metabolic disorders. For example, the overexpression of a protein called TIGAR, which functions as a fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase, has been implicated in cancer development and progression.
TIGAR, originally identified for its ability to protect cells against oxidative stress, plays a role in the redirection of glucose from glycolysis to the pentose phosphate pathway. By inhibiting fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase activity and promoting the production of ribose-5-phosphate, TIGAR supports nucleotide synthesis and counters the damaging effects of reactive oxygen species.
FAQ
1. How does fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase affect glycolysis and gluconeogenesis?
Fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase acts as a key control point in regulating the balance between glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. When active, it inhibits glycolysis by reducing fructose 2,6-bisphosphate levels and promotes gluconeogenesis by increasing fructose 6-phosphate levels.
2. What is the role of insulin in fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase regulation?
Insulin stimulates the production of phosphofructokinase-2 (PFK-2), a protein that plays a crucial role in fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase regulation. PFK-2 controls the levels of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, thereby influencing the balance between glycolysis and gluconeogenesis.
3. How does TIGAR affect fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase activity?
TIGAR functions as a fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase and inhibits its activity. By redirecting glucose metabolism towards the pentose phosphate pathway, TIGAR promotes nucleotide synthesis and protects cells from oxidative stress.
Understanding the intricate regulation of fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase is paramount for comprehending the complexities of glucose metabolism and its implications in various diseases. Further research in this field holds great promise for uncovering potential therapeutic targets and interventions to modulate these metabolic processes effectively.
5. Coordinated Regulation Of Carbohydrate Metabolism – Greek.doctor
 Image Source : greek.doctor
Image Source : greek.doctor fructose pfk bisphosphate carbohydrate metabolism fbpase coordinated glycolysis
Schematic Representation Of The Regulatory Mechanism Of Fructose
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net fructose mechanism bisphosphate regulatory representation
Balancing Glycolytic Flux: The Role Of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase
 Image Source : cancerandmetabolism.biomedcentral.com
Image Source : cancerandmetabolism.biomedcentral.com fructose role pfk kinase glycolytic metabolism cancer figure control balancing flux
PPT - Carbohydrate Anabolism PowerPoint Presentation - ID:611281
fructose bisphosphate regulation formation bisphosphatase carbohydrate anabolism ppt powerpoint presentation slideserve but generated polypeptide pfk broken note single down glycolysis
PFK-2/FBPase-2 Control Of Glycolysis And Gluconeogenic Pathways
 Image Source : www.pinterest.com
Image Source : www.pinterest.com glycolysis pfk fbpase fructose pathways gluconeogenesis regulation phosphofructokinase gluconeogenic enzymes bisphosphate mechanism bisphosphatase pyruvate biochemistry allosteric inhibitor kinase activator cofactors
Biomolecules | Free Full-Text | New Insights To Regulation Of Fructose
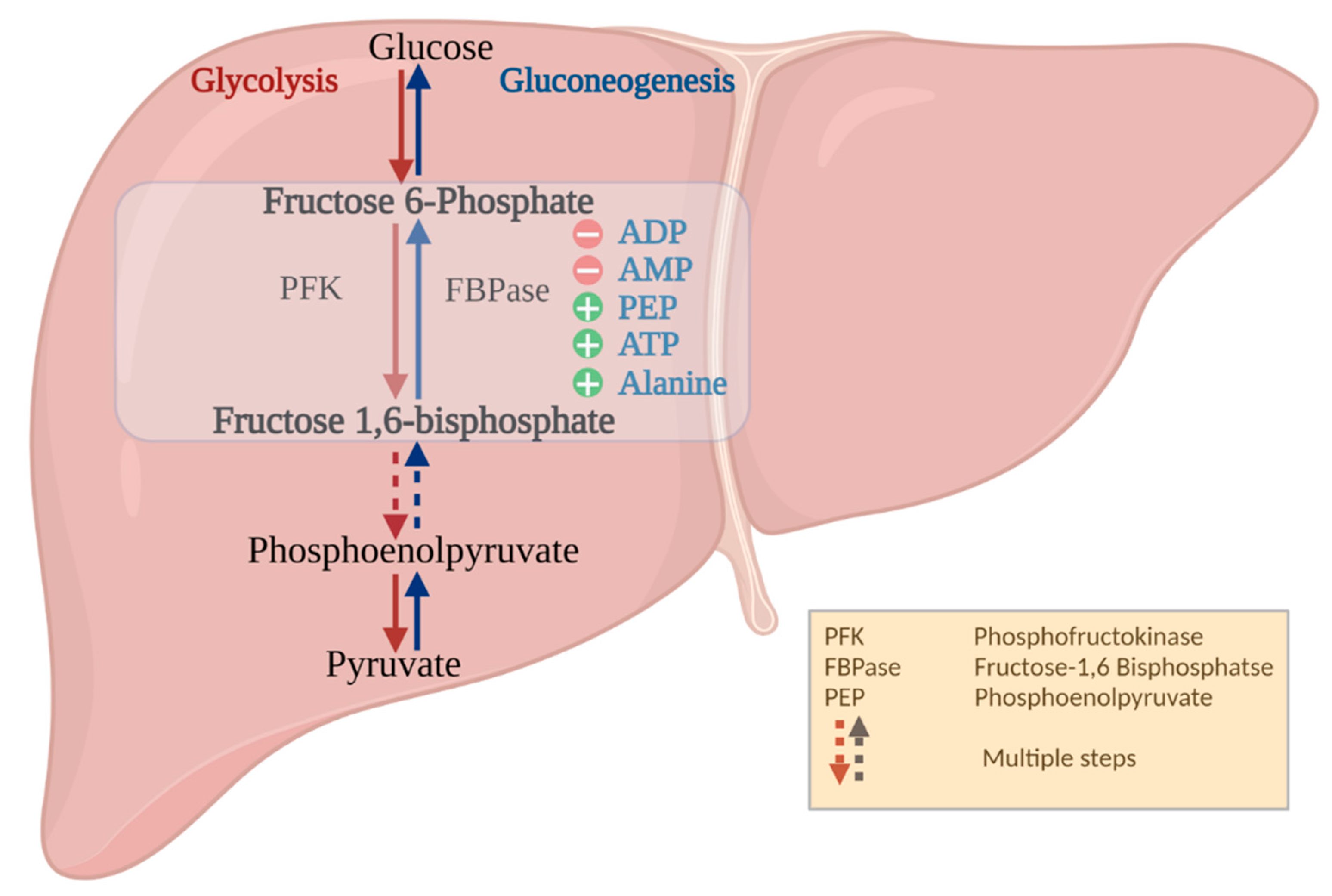 Image Source : www.mdpi.com
Image Source : www.mdpi.com ¿La Insulina Activa La Fosfofructoquinasa? – Solo Preguntas Frecuentes!!
 Image Source : solofaq.com
Image Source : solofaq.com TIGAR Functions As A Fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. Schematic Of
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net Tigar functions as a fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. schematic of. Balancing glycolytic flux: the role of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase. Fructose mechanism bisphosphate regulatory representation. Schematic representation of the regulatory mechanism of fructose. Fructose pfk bisphosphate carbohydrate metabolism fbpase coordinated glycolysis