Positive Regulation : What it is
What is Positive Regulation in Gene Expression?
Positive regulation is a mechanism in gene expression that enhances the production of specific proteins or RNA molecules within a cell. It involves the activation of gene transcription, allowing the genetic information stored in DNA to be translated into functional products.
1. Importance of Positive Regulation in Gene Expression
Positive regulation plays a crucial role in various biological processes, ensuring the proper functioning and development of organisms. Some of the key reasons why positive regulation is significant are:
- Enhanced Protein Production: Positive regulation stimulates the production of proteins that are essential for the cell's normal activities and responses to environmental changes. This allows cells to efficiently carry out their functions and maintain homeostasis.
- Better Adaptation to Stress: Positive regulation enables cells to adapt and respond effectively to internal and external stressors. Through the upregulation of specific genes, cells can produce proteins that counteract stress-induced damage or promote survival.
- Developmental Processes: Positive regulation is critical during various developmental stages. It controls the expression of genes involved in cell differentiation, tissue formation, and organ development, ensuring the correct structure and function of different body parts.
2. Mechanisms of Positive Regulation
Positive regulation can be achieved through different mechanisms, including:
- Activator Proteins: Activator proteins bind to specific DNA sequences near the target gene, promoting transcription by interacting with RNA polymerase and other transcription factors. This interaction leads to the initiation of gene expression.
- Enhancer Elements: Enhancer elements are DNA sequences located thousands of base pairs away from the target gene. When bound by activator proteins, enhancer elements physically interact with the gene's promoter region. This interaction enhances the recruitment and activity of transcription machinery, resulting in increased gene expression.
- Signal Transduction Pathways: Positive regulation can also occur through signal transduction pathways. External signals, such as hormones or growth factors, activate cell surface receptors, triggering a cascade of intracellular events that ultimately lead to enhanced gene expression.
3. Diseases Associated with Dysregulated Positive Regulation
When positive regulation mechanisms malfunction, it can have profound effects on cellular processes, potentially leading to various diseases and disorders. Some examples include:
- Cancer: In cancer cells, positive regulation pathways related to cell division and growth become dysregulated. This results in uncontrolled cell proliferation and the formation of tumors.
- Neurological Disorders: Dysregulation of positive regulation mechanisms can influence the production of proteins essential for proper brain function. This may contribute to neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and Huntington's disease.
- Metabolic Disorders: Positive regulation dysfunction can disrupt the regulation of metabolic pathways, leading to conditions like diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How does positive regulation differ from negative regulation?
A: Positive regulation enhances gene expression, while negative regulation suppresses or inhibits it. Both mechanisms work in balance to ensure precise control of gene activity.
Q: Can positive regulation be targeted for therapeutic interventions?
A: Yes, understanding positive regulation mechanisms is vital for developing potential therapeutic strategies. Modulating positive regulation pathways can help treat diseases characterized by insufficient gene expression or aberrant protein production.
Q: Are there any drugs targeting positive regulatory pathways?
A: Yes, several drugs have been developed to target positive regulation pathways. For example, drugs targeting specific activator proteins or signal transduction cascades have shown promise in cancer treatment and other disease areas.
Images
1. Positive and Negative Regulation
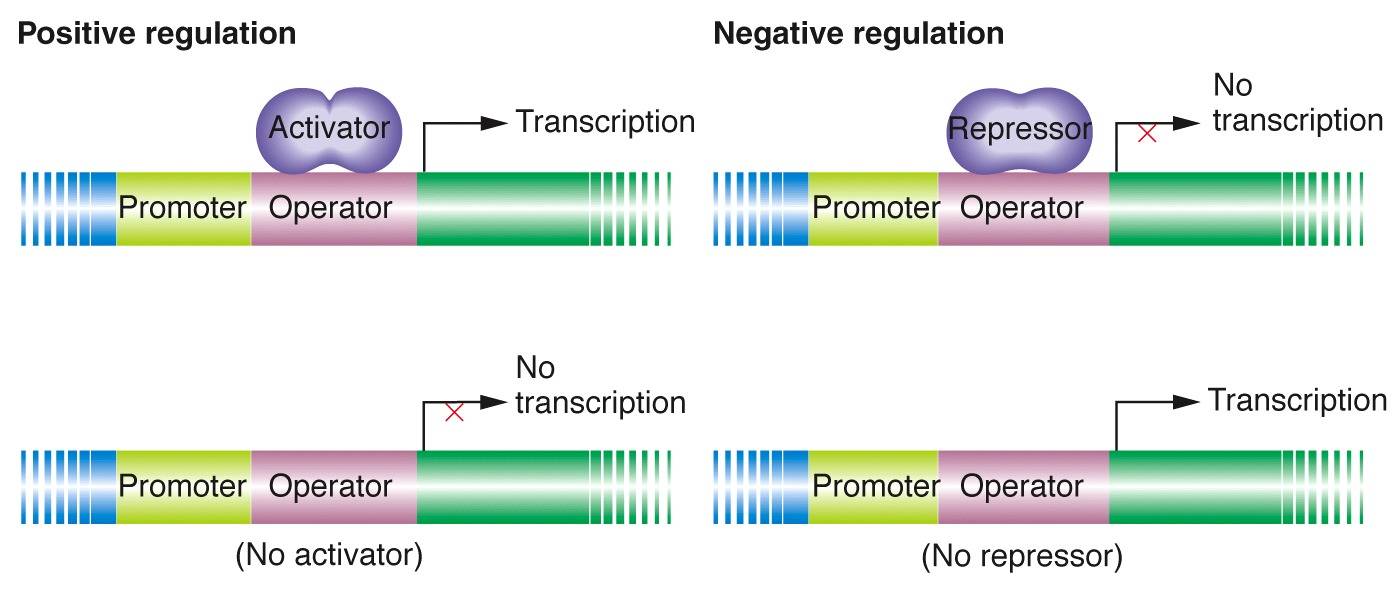
This image illustrates the concepts of positive and negative regulation in gene expression. It visually represents how these regulatory mechanisms influence the production of proteins from specific genes.
2. Positive & Negative Regulation of Gene Expression Diagram

This diagram provides a clear depiction of the positive and negative regulation of gene expression. It highlights the different molecular interactions and processes involved in controlling gene activity.
By exploring positive regulation in gene expression, we gain insights into the intricacies of gene control mechanisms and their implications in various biological processes. This understanding paves the way for advancements in both basic science and clinical applications.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. Please consult with a qualified healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
Positive And Negative Regulation
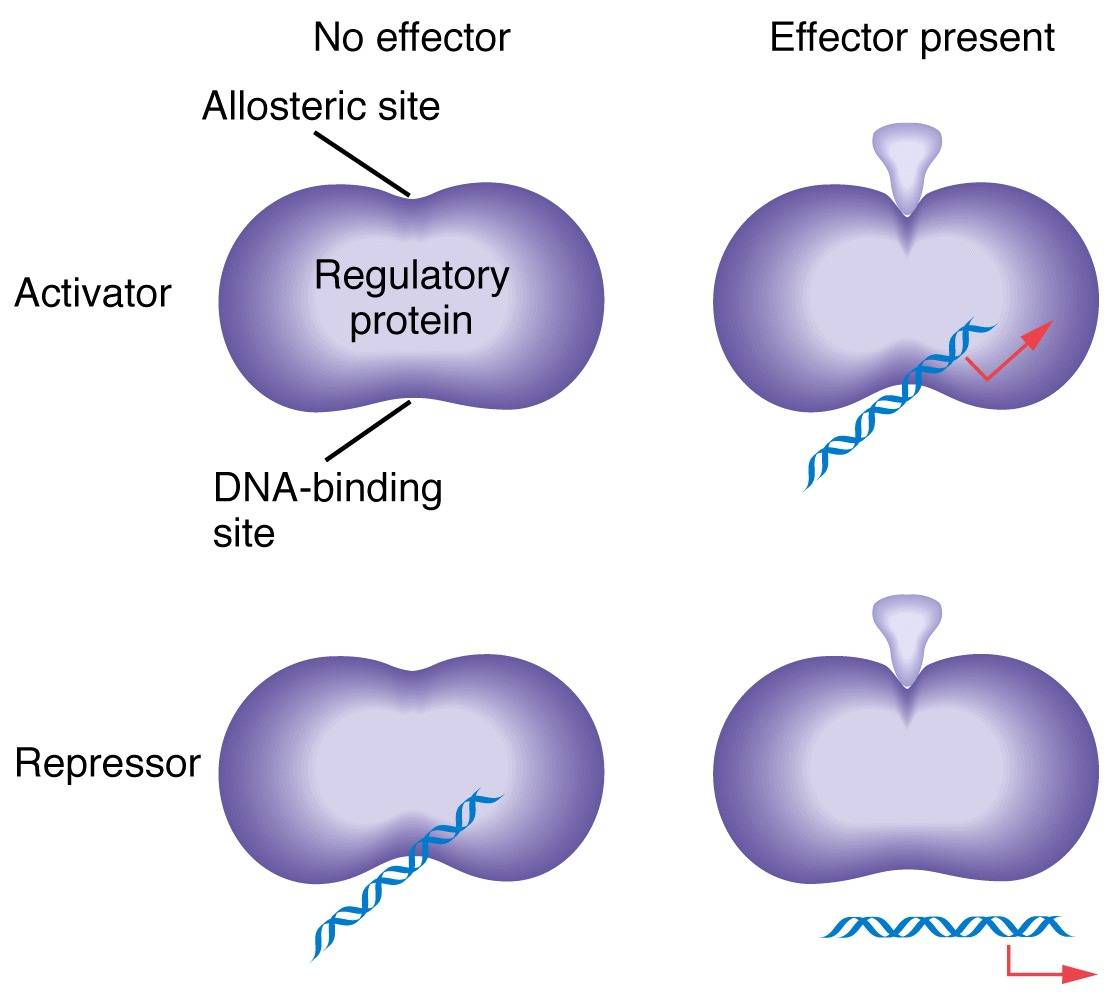 Image Source : www.mun.ca
Image Source : www.mun.ca allosteric negative molecules
Positive And Negative Regulation
 Image Source : www.mun.ca
Image Source : www.mun.ca biology regulation regulatory
What Is The Difference Between Positive And Negative Gene Regulation
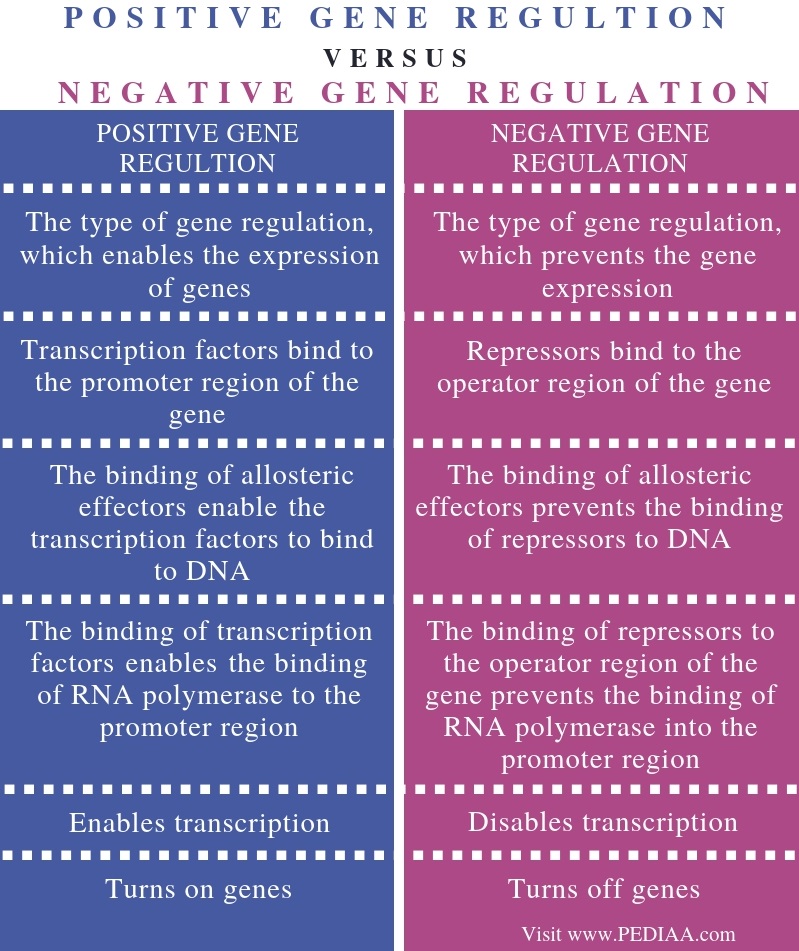 Image Source : pediaa.com
Image Source : pediaa.com positive regulation gene negative difference between pediaa
PPT - Regulation Of Gene Expression In Prokaryotes PowerPoint
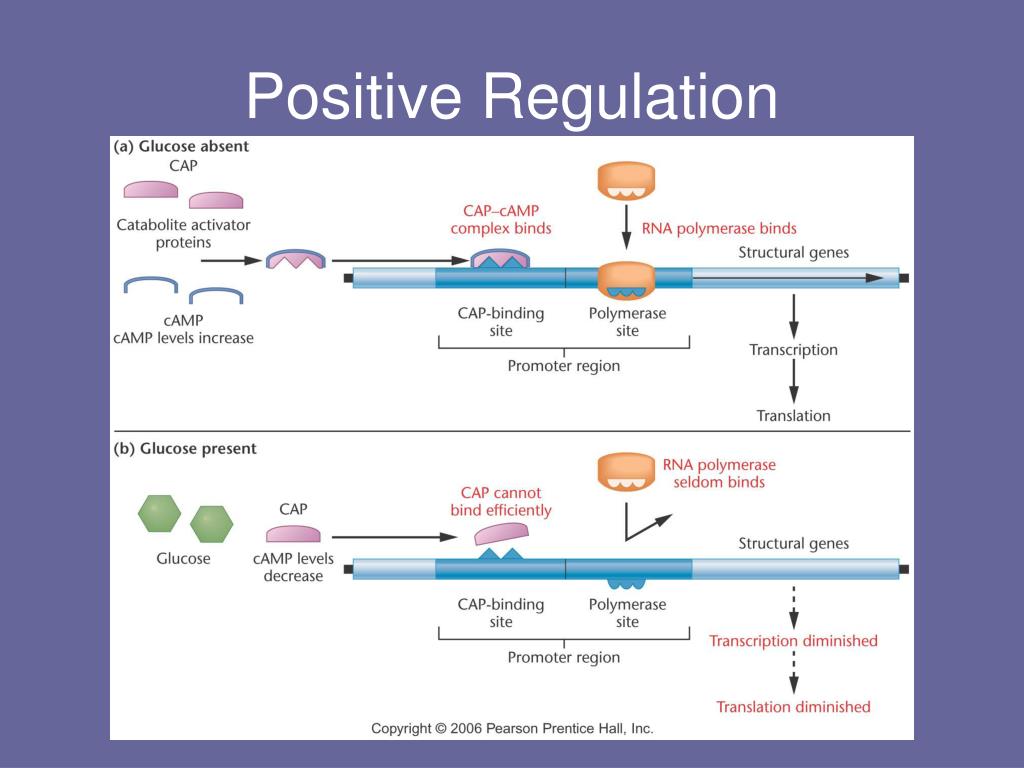 Image Source : www.slideserve.com
Image Source : www.slideserve.com regulation positive gene expression prokaryotes ppt powerpoint presentation
Positive Regulation - YouTube
 Image Source : www.youtube.com
Image Source : www.youtube.com positive regulation
***All Or None - Identify Transcription Factors | Chegg.com
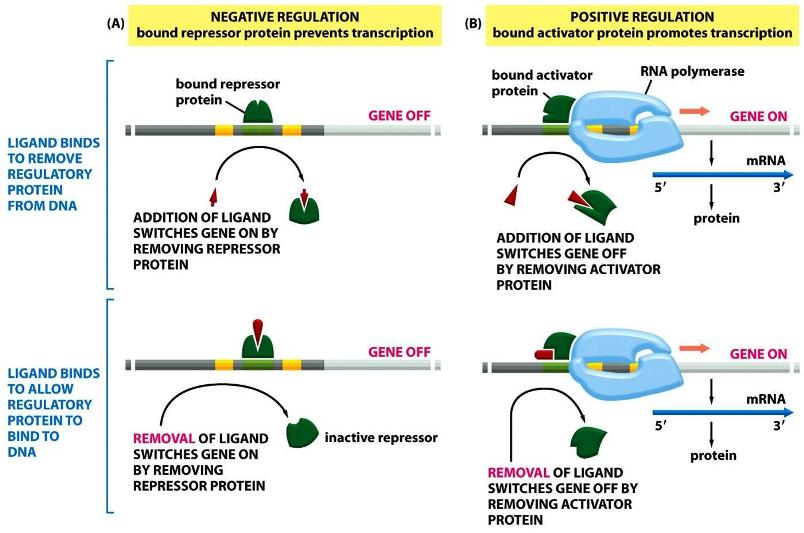 Image Source : www.chegg.com
Image Source : www.chegg.com transcription regulation activator repressor regulatory rna satisfying example polymerase
Positive & Negative Regulation Of Gene Expression Diagram | Quizlet
 Image Source : quizlet.com
Image Source : quizlet.com Lecture Notes
 Image Source : www.discoveryandinnovation.com
Image Source : www.discoveryandinnovation.com regulation positive operon prokaryotic
Biology regulation regulatory. Allosteric negative molecules. Transcription regulation activator repressor regulatory rna satisfying example polymerase. Positive regulation. ***all or none