Regulation Examples Biology
Regulation plays a crucial role in maintaining the proper functioning of biological systems. In the field of biology, regulation refers to the control of gene expression and cellular processes. Understanding the mechanisms of regulation is key to comprehending how organisms function. In this article, we will explore some examples of regulation in biology and delve into the fascinating world of gene expression and cellular control.
1. Gene Regulation: An Overview

Gene regulation is the process through which genes are turned on or off, enabling cells to respond to their environment and perform their specialized functions. This regulation occurs at multiple levels, including transcription, translation, and post-translational modifications.
Transcriptional regulation, the most common form of gene regulation, involves the control of gene expression at the level of transcription. This process ensures that only the necessary genes are transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA) for protein synthesis. Transcription factors and other regulatory molecules are responsible for initiating or repressing the transcription of specific genes.
Another level of gene regulation is post-transcriptional regulation, which occurs after the mRNA has been transcribed. This regulation includes processes such as alternative splicing, mRNA stability control, and regulation by noncoding RNAs. These processes enable cells to fine-tune gene expression and produce diverse proteins from a single gene.
2. Allosteric Regulation: Controlling Enzyme Activity

Allosteric regulation is a mechanism by which the activity of an enzyme is controlled by the binding of an effector molecule at a site other than the enzyme's active site. This type of regulation allows cells to regulate metabolic pathways and respond to changes in their environment.
The binding of an effector molecule to the allosteric site can either activate or inhibit the enzyme's activity. This regulation ensures that metabolic reactions occur at the right time and in the appropriate quantities. Additionally, allosteric regulation allows cells to respond to feedback signals and maintain homeostasis.
3. Feedback Inhibition: Maintaining Balance
Feedback inhibition is a form of allosteric regulation that enables cells to maintain balance in metabolic pathways. It works by using the end-product of a pathway to inhibit an earlier enzyme in the pathway.
For example, in the biosynthesis of amino acids, each step of the pathway is catalyzed by a specific enzyme. The end-product of the pathway acts as an allosteric inhibitor of the first enzyme in the pathway. This feedback inhibition prevents the overproduction of amino acids and ensures that they are synthesized only when needed.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q: What is gene expression?
A: Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used to synthesize a functional gene product, such as a protein.
Q: How do transcription factors regulate gene expression?
A: Transcription factors are proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences and control the rate of transcription. They can either activate or repress the transcription of target genes.
Q: Can gene regulation be influenced by the environment?
A: Yes, gene regulation can be influenced by environmental factors such as temperature, light, nutrients, and stress. Environmental cues can trigger specific signaling pathways that ultimately impact gene expression.
Q: What is the significance of post-transcriptional regulation?
A: Post-transcriptional regulation allows cells to control gene expression after the mRNA has been transcribed. This regulation plays a vital role in generating protein diversity, fine-tuning gene expression levels, and responding to changing cellular conditions.
Regulation in biology is a fascinating and intricate process that ensures the proper functioning of living organisms. From controlling gene expression to maintaining metabolic balance, these examples of regulation provide a glimpse into the complex world of cellular control. By understanding these mechanisms, scientists can unravel the mysteries of life and develop innovative solutions in various fields of biology.
Disclaimer: The content above is for informational purposes only and is not intended to substitute professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Sources:
- Regulation of Gene - Gene Expression and Transcription of Cell. Retrieved from: http:\/\/s3-ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com\/subscriber.images\/biology\/2017\/02\/21110032\/Gene-Regulation.png
- Definition Of Active Cell - DEFINITIONXA. Retrieved from: https:\/\/i.pinimg.com\/736x\/8b\/08\/a3\/8b08a3a1a665a12fd83a0f313a873429--allosteric-regulation-biochemistry.jpg
What Is The Allosteric Site? Definition, Characteristics, Examples, And
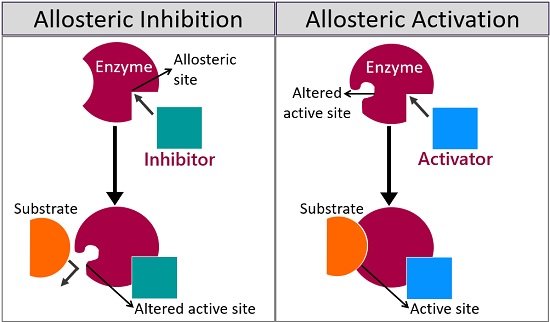 Image Source : rainis.pics
Image Source : rainis.pics Regulation Examples Biology
Regulation Of Gene - Gene Expression And Transcription Of Cell
gene regulation biology expression genes cell
7: Principles And Examples Of Metabolic Regulation-Biology LibreTexts
 Image Source : sachdevaelectroniccentre.com
Image Source : sachdevaelectroniccentre.com Positive And Negative Regulation
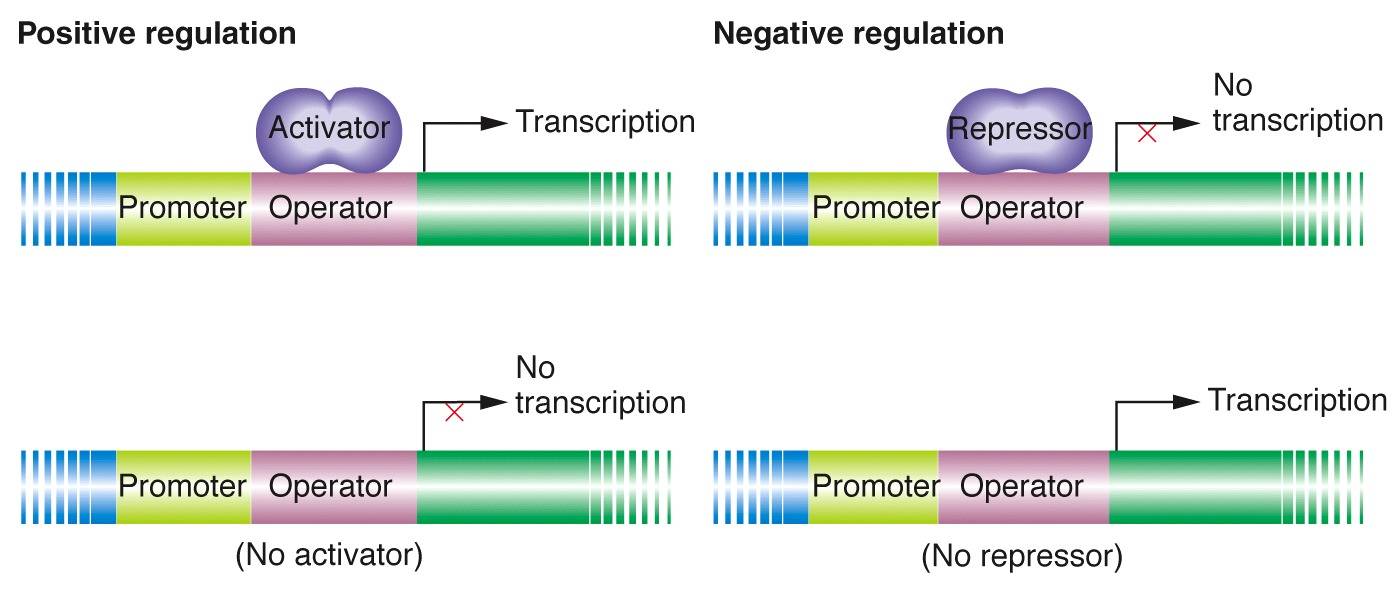 Image Source : www.mun.ca
Image Source : www.mun.ca biology regulation regulatory
Cell Cycle - Definition, Phases, Examples, Regulation | Biology Dictionary
 Image Source : biologydictionary.net
Image Source : biologydictionary.net cycle cell phases mitosis diagram division definition cells biology biologydictionary interphase circle science stages visualize infographic data part examples steps
Ectotermia E Endotermia – Made In: Science
 Image Source : madeinscience.com
Image Source : madeinscience.com Definition Of Active Cell - DEFINITIONXA
 Image Source : definitionxat.blogspot.com
Image Source : definitionxat.blogspot.com Biology regulation regulatory. Positive and negative regulation. Gene regulation biology expression genes cell. Cell cycle. Definition of active cell