Regulation Biology Example
Have you ever wondered how genes are regulated in biology? Gene regulation plays a crucial role in determining gene expression and the transcription of cells. In this post, we will explore the fascinating world of gene regulation and how it impacts the functioning of living organisms.
Regulation of Gene Expression and Transcription of Cell
Gene expression refers to the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product, such as a protein. In order for gene expression to occur, the gene must first be transcribed into a molecule called mRNA. This process, known as transcription, is tightly regulated to ensure that genes are only transcribed when needed.
Regulation of gene expression occurs at various levels, including:
- Transcriptional Regulation: Transcription factors, proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences, play a key role in regulating gene expression. They can either activate or repress transcription, controlling the rate at which mRNA is produced from a gene.
- Post-Transcriptional Regulation: Once mRNA is transcribed, it can undergo various modifications that influence its stability and translation into protein. These modifications include alternative splicing, mRNA editing, and the addition of a poly(A) tail.
- Translational Regulation: Gene expression can also be regulated at the level of translation, where the mRNA is used as a template to synthesize proteins. Regulatory molecules, such as microRNAs, can bind to mRNA molecules and prevent their translation into protein.
- Post-Translational Regulation: Finally, after a protein is synthesized, it can undergo modifications that affect its activity, stability, and localization within the cell. These modifications may include phosphorylation, methylation, acetylation, and ubiquitination.
Example of Regulation in Biology

Let's take a closer look at an example of regulation in biology. One well-known example is the regulation of the lac operon in bacteria. The lac operon is a group of genes involved in the metabolism of lactose. When lactose is present in the environment, it needs to be broken down and utilized by the bacteria. However, when lactose is not available, it would be wasteful for the bacteria to produce enzymes for its breakdown.
In this case, the lac operon is regulated by a regulatory protein called the lac repressor. When lactose is absent, the lac repressor binds to a specific DNA sequence near the lac operon, blocking the transcription of the genes involved in lactose metabolism. However, when lactose is present, it binds to the lac repressor, causing a conformational change that prevents it from binding to the DNA. This allows for the transcription of the lac operon genes and enables lactose metabolism.
Significance of Gene Regulation
Gene regulation is crucial for the proper functioning of living organisms. It allows cells to respond to changing environments, developmental cues, and physiological needs. Without regulation, genes would be constantly transcribed and translated, leading to inefficient energy usage and potential harm to the organism.
Additionally, gene regulation plays a key role in cell differentiation, where different cell types arise from the same genetic material. By selectively activating and repressing specific genes, cells can acquire specialized functions and contribute to the overall complexity of an organism.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How do transcription factors regulate gene expression?
A: Transcription factors are proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences and control the rate at which genes are transcribed. They can either activate or repress transcription, depending on the specific regulatory elements they bind to and the presence of co-factors.
Q: What are microRNAs and how do they affect gene expression?
A: MicroRNAs are small non-coding RNA molecules that can bind to mRNA molecules. By binding to specific mRNA sequences, microRNAs can prevent their translation into protein, effectively downregulating gene expression. MicroRNAs play important roles in various biological processes, including development, cell differentiation, and disease.
Q: Can gene regulation be altered in diseases?
A: Yes, alterations in gene regulation are associated with many diseases, including cancer, developmental disorders, and metabolic disorders. Dysregulation of specific genes or regulatory elements can lead to abnormal cell growth, impaired development, and dysfunction of metabolic pathways. Studying gene regulation in diseases is an active area of research with important implications for future therapies.
In conclusion, gene regulation is a complex and intricate process that ensures the precise control of gene expression and transcription. Understanding the mechanisms of gene regulation allows us to comprehend how living organisms respond and adapt to their environments. Moreover, studying gene regulation in diseases opens up new avenues for therapeutic interventions.
Positive And Negative Regulation
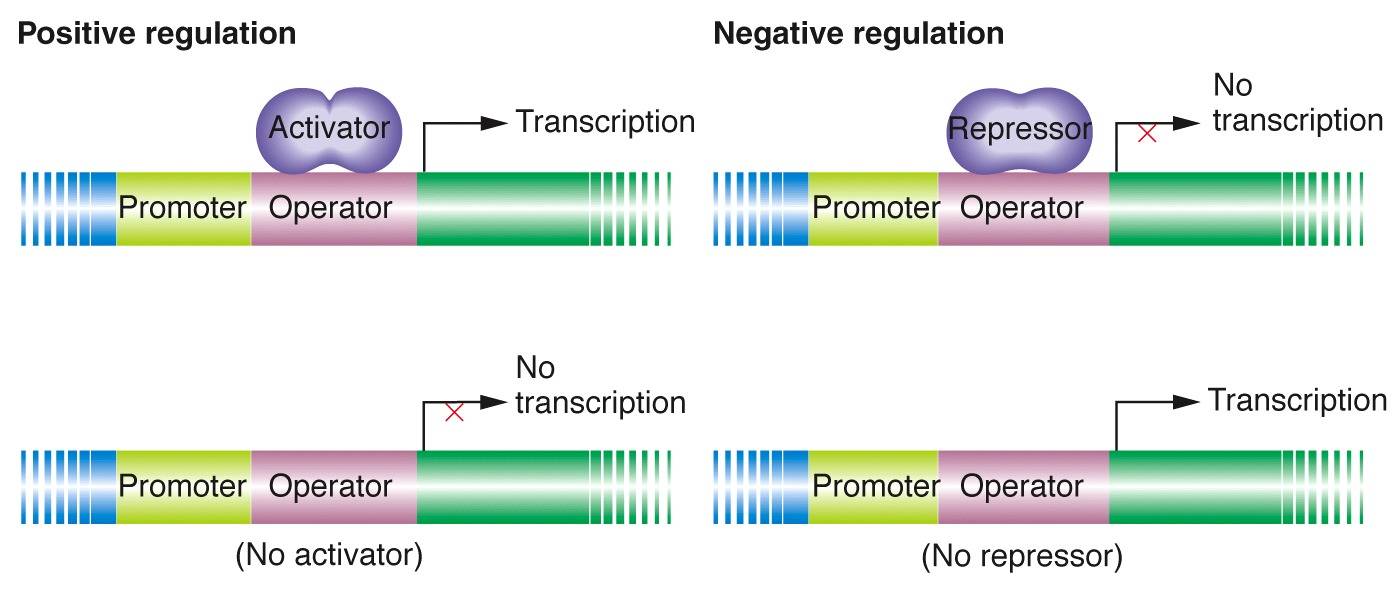 Image Source : www.mun.ca
Image Source : www.mun.ca biology regulation regulatory
Example Of Regulation In Biology
 Image Source : regulationlatest.blogspot.com
Image Source : regulationlatest.blogspot.com Latest Regulation: Regulation Definition Biology Example
 Image Source : regulationlatest.blogspot.com
Image Source : regulationlatest.blogspot.com mechanisms transcription
Your Brain's Cortisol Control Hub — The Behavior Hub
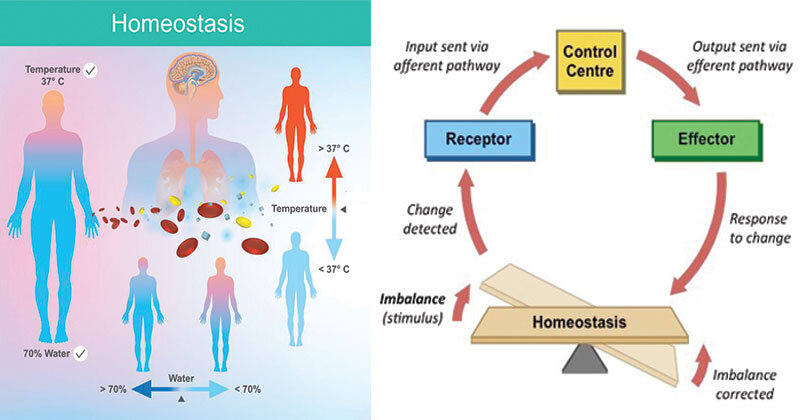 Image Source : www.thebehaviorhub.com
Image Source : www.thebehaviorhub.com homeostasis biology hypothalamus physiology anatomy microbenotes stimulus regulating cortisol nervous microbe bioninja
Definition Of Active Cell - DEFINITIONXA
 Image Source : definitionxat.blogspot.com
Image Source : definitionxat.blogspot.com Regulation Of Gene - Gene Expression And Transcription Of Cell
gene regulation biology expression genes cell
PPT - Biology 10.2 Gene Regulation And Structure PowerPoint
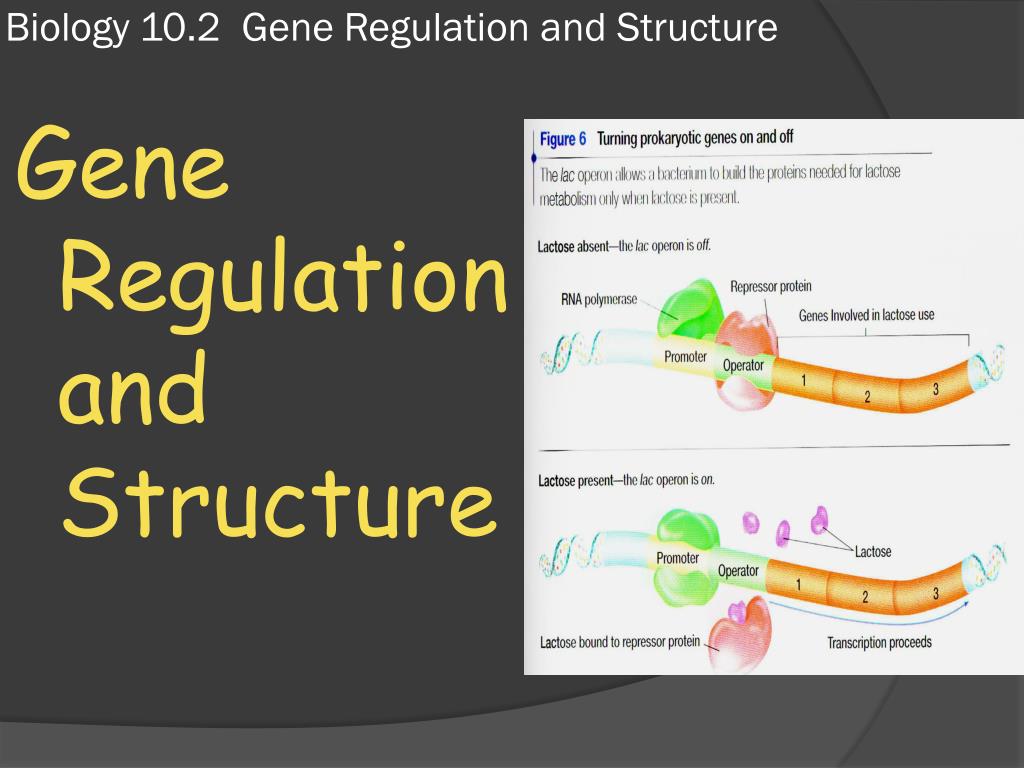 Image Source : www.slideserve.com
Image Source : www.slideserve.com regulation gene biology structure ppt powerpoint presentation
Biological Evolution Animals Scheme Cartoon Vector | CartoonDealer.com
Your brain's cortisol control hub — the behavior hub. Regulation of gene. Example of regulation in biology. Biology regulation regulatory. Latest regulation: regulation definition biology example