Cell Cycle Regulation Pogil Answer Key
The Cell Cycle Regulation - A Comprehensive Answer Key
The study of cell cycle regulation is crucial to understanding various biological processes, such as growth and development, tissue repair, and reproduction. In this article, we will delve into the key concepts of cell cycle regulation using the Cell Cycle Regulation Pogil Answer Key as our guide. Whether you are a student seeking to reinforce your knowledge or a curious mind looking to expand your understanding, this comprehensive answer key will provide you with the necessary insights. So let's dive right in!
Understanding the Cell Cycle
The cell cycle refers to the sequence of events that occur in a cell's life, including its growth, replication of genetic material, and cell division. This process is highly regulated to ensure accurate transmission of genetic material and the generation of identical daughter cells. To grasp the intricacies of cell cycle regulation, it is essential to comprehend the different phases involved:
1. Interphase

Interphase represents the majority of a cell's life cycle. It is divided into three distinct stages: G1 phase, S phase, and G2 phase.
G1 Phase:
This initial phase follows cell division and serves as a period of growth where the cell undergoes metabolic activities to replenish its energy reserves and prepare for the next phase.
S Phase:
In the S phase, DNA replication occurs. The cell duplicates its chromosomes to ensure that each daughter cell receives the same genetic information during division.
G2 Phase:
During the G2 phase, the cell continues to grow while also preparing for cell division. It undergoes additional checks to ensure that DNA replication was successful and no errors occurred.
2. Mitotic Phase

The mitotic phase is the stage of cell cycle regulation where cell division occurs.
Mitosis:
Mitosis is a highly orchestrated process of cell division that ensures the accurate segregation of chromosomes into two identical daughter cells. It is divided into four key stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Cytokinesis:
Cytokinesis is the physical separation of the cell into two distinct daughter cells. This process usually occurs shortly after the completion of mitosis.
3. Cell Cycle Checkpoints
Throughout the cell cycle, various checkpoints act as control mechanisms to ensure the integrity and accuracy of cell division. These checkpoints monitor crucial events and halt the progression of the cell cycle if any abnormalities are detected. The key checkpoints are:
G1 Checkpoint:
This checkpoint, also known as the restriction point, ensures that all external growth factors and nutrients are available before the cell proceeds to DNA synthesis.
G2/M Checkpoint:
The G2/M checkpoint ensures that DNA replication occurred accurately and that there are no errors or DNA damage before the cell enters mitosis.
Spindle Checkpoint:
The spindle checkpoint, also known as the metaphase checkpoint, monitors the proper attachment of chromosomes to the spindle apparatus. If any irregularities are detected, the cell cycle is halted to prevent unequal distribution of genetic material.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Why is cell cycle regulation important?
A1: Cell cycle regulation is essential to maintain the stability and integrity of genetic material. It prevents abnormal cell growth, controls cell division, and plays a crucial role in ensuring the proper functioning of an organism.
Q2: What happens if the cell cycle is not regulated?
A2: Without proper cell cycle regulation, various issues can arise. Uncontrolled cell division can lead to the formation of tumors and cancer. Additionally, errors during DNA replication or chromosomal segregation can result in genetic abnormalities and developmental disorders.
Q3: How do cells monitor and repair DNA damage?
A3: Cells have sophisticated repair mechanisms that monitor the integrity of DNA. If any damage is detected, cells activate proteins that halt the cell cycle, allowing time for DNA repair. If repair becomes impossible, programmed cell death (apoptosis) is triggered to eliminate the damaged cell.
With this comprehensive answer key, you now have a solid understanding of the intricacies of cell cycle regulation. Remember, cell cycle regulation is crucial for maintaining the proper functioning of our bodies and preventing abnormalities. Continue exploring this fascinating topic, and you will unlock more mysteries of life's fundamental processes!
Cell Cycle Regulation Pogil Answer Key - Perfect Docs
 Image Source : perfectdocpdf.blogspot.com
Image Source : perfectdocpdf.blogspot.com regulation pogil organelles grows proteins
Cell_cycle_regulation_pogil - Cell Cycle Regulation How Does A Cell
 Image Source : www.coursehero.com
Image Source : www.coursehero.com pogil cell cycle regulation
The Cell Cycle Worksheet Answer Key Pogil › Athens Mutual Student Corner
 Image Source : athensmutualaid.net
Image Source : athensmutualaid.net Pogil Answer Key The Cell Cycle › Athens Mutual Student Corner
 Image Source : athensmutualaid.net
Image Source : athensmutualaid.net The Cell Cycle Pogil Worksheet Answer Key › Athens Mutual Student Corner
 Image Source : athensmutualaid.net
Image Source : athensmutualaid.net The Cell Cycle Answers (1) - THE CELL CYCLE A POGIL Activity 1 HOW MANY
 Image Source : www.coursehero.com
Image Source : www.coursehero.com pogil
Cell Cycle Regulation Worksheet Answer Key Pogil Worksheet : Resume
 Image Source : www.thesecularparent.com
Image Source : www.thesecularparent.com cell worksheet regulation cycle pogil
Regulating The Cell Cycle Worksheet — Db-excel.com
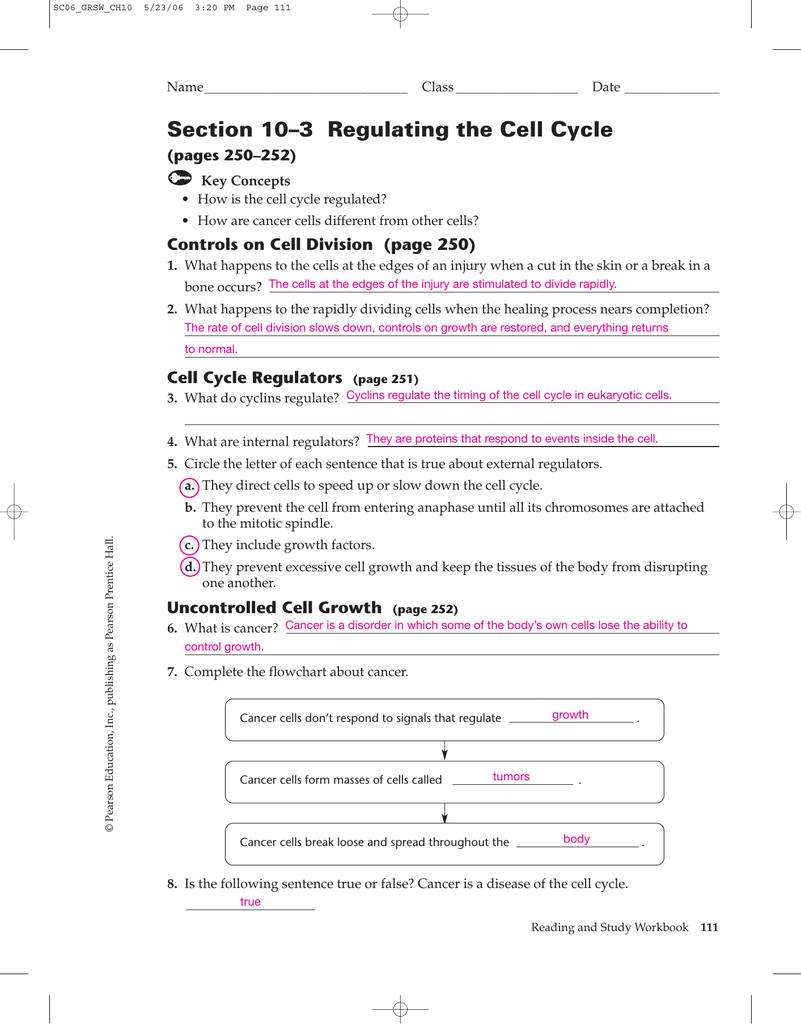 Image Source : db-excel.com
Image Source : db-excel.com cycle cell regulating worksheet excel db education nature
Cell_cycle_regulation_pogil. Regulating the cell cycle worksheet — db-excel.com. Cycle cell regulating worksheet excel db education nature. The cell cycle worksheet answer key pogil › athens mutual student corner. Cell cycle regulation worksheet answer key pogil worksheet : resume