Based On The Model Of Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Regulation
The eukaryotic cell cycle is a highly regulated process that ensures proper cell growth and division. It involves a series of events that culminate in the replication of DNA and the subsequent division of the cell into two daughter cells. Understanding the intricate mechanisms underlying the regulation of the cell cycle is essential for gaining insights into various biological processes and diseases such as cancer. In this post, we will explore the fascinating world of eukaryotic cell cycle regulation based on a model, discussing its phases, key players, and regulatory checkpoints. Let's dive in!
The Cell Cycle: An Overview

The cell cycle can be broadly divided into two major phases: interphase and mitosis. Interphase encompasses the bulk of the cell cycle, during which the cell grows and prepares for division. Mitosis, on the other hand, is the actual process of cell division. Let's take a closer look at each phase.
Interphase: A Time of Preparation

Interphase consists of three distinct stages: G1, S, and G2. During G1 phase, the cell grows and carries out its normal functions. As the cell progresses through G1, it reaches a point of commitment called the restriction point. From this point on, the cell is committed to continuing the cell cycle and division.
Following G1, the cell enters the S phase, during which DNA replication occurs. The genetic material is duplicated, ensuring that each daughter cell will receive a complete set of chromosomes.
Next comes G2 phase, where the cell continues to grow and prepares for mitosis. It synthesizes the necessary proteins and organelles required for cell division. During G2, the cell also undergoes a crucial checkpoint called the G2/M checkpoint, which ensures that DNA is properly replicated and intact before entering mitosis.
Mitosis: The Process of Cell Division
Mitosis is divided into four distinct phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During prophase, the nuclear membrane disassembles, and the chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes. The centrosomes move to opposite poles of the cell and form the mitotic spindle, which will aid in separating the chromosomes.
In metaphase, the chromosomes align at the metaphase plate, forming a single plane in the center of the cell. This alignment is crucial for accurate chromosome segregation during the subsequent steps.
Anaphase is characterized by the separation of sister chromatids. The mitotic spindle apparatus pulls the sister chromatids apart, ensuring that each daughter cell receives an equal and complete set of chromosomes.
During telophase, the nuclear membrane reforms around the separated sister chromatids, and the chromosomes decondense. The cell starts to divide, facilitated by the formation of a contractile ring along the equator of the cell.
Finally, cytokinesis occurs, resulting in the physical separation of the cell into two daughter cells. Each daughter cell then enters interphase and continues the cell cycle.
Regulatory Checkpoints: Maintaining Cell Cycle Integrity
In addition to the phases of the cell cycle, there are several critical regulatory checkpoints that ensure the proper progression and integrity of the cell cycle. Failure to pass these checkpoints can lead to abnormal cell division and the development of diseases such as cancer. Let's explore some of the key checkpoints.
1. G1/S Checkpoint: Deciding to Divide or Not
The G1/S checkpoint, also known as the initiation checkpoint, determines whether the cell is ready to progress from G1 phase to the S phase. At this checkpoint, the cell assesses environmental conditions, nutrient availability, and DNA damage. If the conditions are favorable and the DNA is intact, the cell will proceed to the S phase and initiate DNA replication. However, if conditions are unfavorable or if there is significant DNA damage, the cell may arrest in G1 or enter a resting state called G0.
2. G2/M Checkpoint: Ensuring Proper DNA Replication
The G2/M checkpoint ensures that DNA replication during the S phase is complete and accurate. At this checkpoint, the cell checks for DNA damage and monitors DNA synthesis. If all is well, the cell proceeds to enter mitosis. However, if DNA damage is detected or DNA replication is incomplete, the cell arrests at this checkpoint until the issues are resolved.
3. Spindle Assembly Checkpoint: Confirming Chromosomal Alignment
The spindle assembly checkpoint is a crucial checkpoint during metaphase. It ensures that all chromosomes are properly aligned at the metaphase plate. The checkpoint monitors the attachment of chromosomes to the spindle fibers and checks for tension across the kinetochores. If any misalignments or errors are detected, the cell halts progression into anaphase until the issues are corrected.
FAQs about Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Regulation
Q: What happens if a cell fails to pass the G1/S checkpoint?
A: If a cell fails to pass the G1/S checkpoint, it may enter a resting state called G0, where it temporarily stops dividing and carries out specialized functions. Some cells, such as neurons, enter G0 and remain in this state indefinitely, while others can re-enter the cell cycle if conditions become favorable again.
Q: How are regulatory checkpoints related to cancer?
A: Regulatory checkpoints play a crucial role in preventing the formation and progression of cancer. Mutations or dysregulation of genes involved in the cell cycle checkpoints can lead to uncontrolled cell division, genomic instability, and the development of tumors. Therapies targeting these checkpoints, such as checkpoint inhibitors, have shown promise in cancer treatment.
Q: Are there any additional checkpoints in the cell cycle?
A: Apart from the G1/S, G2/M, and spindle assembly checkpoints, there are other checkpoints that ensure the fidelity of DNA replication and repair, as well as cell growth and nutrient availability. These additional checkpoints help coordinate various cellular processes and maintain the overall integrity of the cell cycle.
In conclusion, the eukaryotic cell cycle is a precisely regulated process that ensures proper cell growth and division. Interphase prepares the cell for division, while mitosis is the actual process of cell division. Regulatory checkpoints maintain the integrity of the cell cycle, preventing abnormal cell division. Understanding the intricacies of cell cycle regulation is crucial for advancing our knowledge in various biological fields and developing targeted therapies for diseases like cancer.
The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle
 Image Source : merithub.com
Image Source : merithub.com Ciclo Celular Eucarionte Coggle Diagram - Gambaran
 Image Source : 45.153.231.124
Image Source : 45.153.231.124 This Diagram Shows A Simplified Representation Of The Eukaryotic Cell
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net eukaryotic cycle simplified
Cell Cycle Regulation - Simplebiol
 Image Source : simplebiol.com
Image Source : simplebiol.com regulation biorender
The Cell Cycle
 Image Source : www.thinglink.com
Image Source : www.thinglink.com answers division checkpoints
The Cell Cycle - Phases - Mitosis - Regulation - TeachMePhysiology
 Image Source : teachmephysiology.com
Image Source : teachmephysiology.com cycle cell phases mitosis growth regulation
(Get Answer) - Question: Based On The Model Of Eukaryotic Cell Cycle
 Image Source : www.transtutors.com
Image Source : www.transtutors.com What's The Difference Between Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells
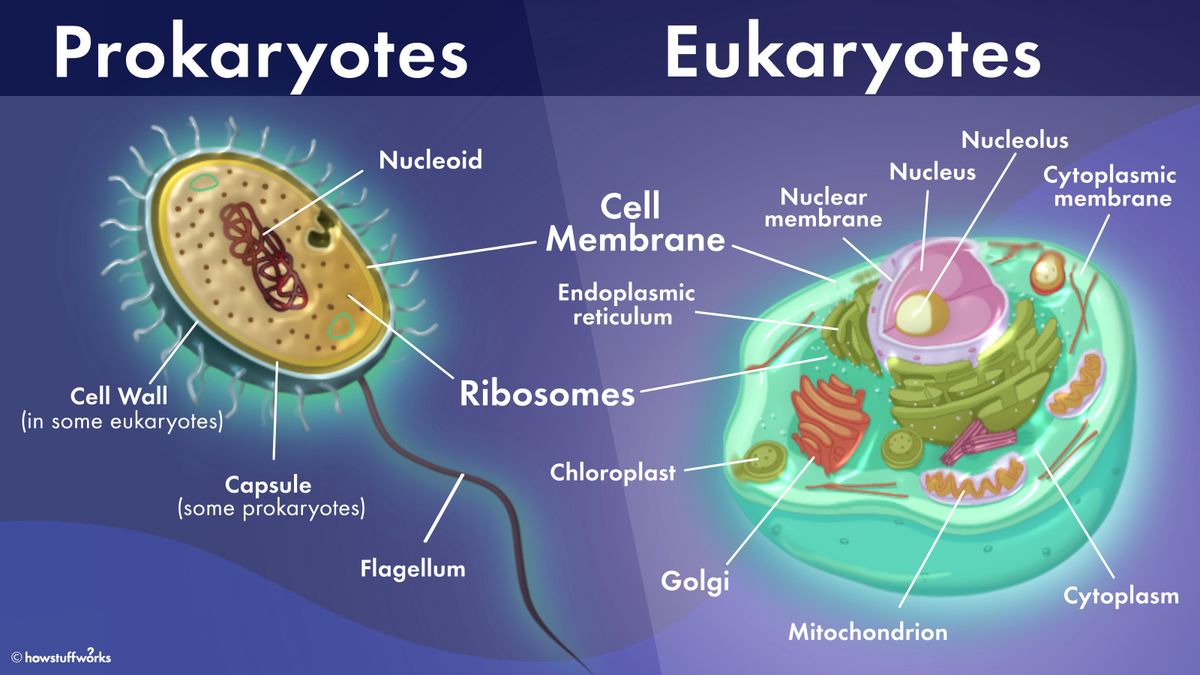 Image Source : science.howstuffworks.com
Image Source : science.howstuffworks.com eukaryotic prokaryotic cells difference eukaryotes prokaryotes membrane cellular eukaryote organelles nucleus howstuffworks microscopic reticulum endoplasmic edurev chapter contrast eucariota procariota
This diagram shows a simplified representation of the eukaryotic cell. Ciclo celular eucarionte coggle diagram. The eukaryotic cell cycle. What's the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The cell cycle