Example Of Down Regulation
Downregulation of receptors is an important phenomenon in biology and medicine. It refers to the decrease in the number or sensitivity of receptors on the surface of cells. This regulatory mechanism plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and adapting to various physiological conditions. In this article, we will explore the concept of downregulation, its molecular mechanisms, and its significance in disease and therapy.
1. Understanding Downregulation of Receptors

Downregulation of receptors is a cellular process that involves the internalization and degradation of receptors or a decrease in their expression. This phenomenon can occur in response to various stimuli, such as prolonged exposure to ligands or other signaling molecules. The downregulation of receptors serves as a negative feedback mechanism to prevent excessive activation or signaling.
There are several molecular mechanisms through which downregulation can occur. One common mechanism is receptor-mediated endocytosis, where receptors are internalized into cells by forming clathrin-coated pits. Once internalized, the receptors can be targeted for degradation in lysosomes. Another mechanism involves the inhibition of receptor synthesis or the accelerated degradation of newly synthesized receptors.
2. Role of Downregulation in Cellular Signaling
Downregulation of receptors plays a crucial role in modulating cellular signaling pathways. By reducing the number of receptors available on the cell surface, downregulation can attenuate the strength and duration of signaling events. This fine-tuning of signaling is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and preventing aberrant activation.
Moreover, downregulation can also regulate the sensitivity of cells to specific ligands or signaling molecules. By decreasing the expression or altering the conformation of receptors, cells can become less responsive to certain stimuli. This mechanism aids in preventing overstimulation and desensitization of signaling pathways.
3. Implications in Disease and Therapy
The dysregulation of receptor downregulation processes can contribute to various diseases and disorders. For example, in certain cancer types, the downregulation of tumor suppressor receptors can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and evasion of apoptosis. Similarly, in neurodegenerative disorders, altered downregulation of neurotransmitter receptors can disrupt synaptic signaling and contribute to disease progression.
On the other hand, researchers have also explored the therapeutic potential of manipulating receptor downregulation. By targeting specific receptors involved in disease pathology, it is possible to develop drugs that can enhance or inhibit downregulation processes. This approach can optimize the therapeutic efficacy of drugs and minimize undesired side effects.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Can downregulation of receptors be reversed?
A: Yes, in certain cases, receptor downregulation can be reversible. Upon the removal of the stimulus that led to downregulation, cells can initiate mechanisms to upregulate receptor expression or enhance receptor sensitivity.
Q: Are there any factors that can accelerate the rate of receptor downregulation?
A: Yes, various factors can affect the rate of receptor downregulation. These include the concentration and duration of the ligand/receptor interaction, intracellular signaling pathways, and the presence of specific enzymes or proteins involved in receptor degradation.
Q: How is receptor downregulation studied?
A: Researchers employ various techniques to study receptor downregulation. These include mass spectrometry-based proteomics, fluorescence microscopy, gene expression analysis, and biochemical assays to assess receptor internalization, degradation, and changes in expression levels.
In conclusion, downregulation of receptors is a complex regulatory process that plays a critical role in cellular signaling and maintaining homeostasis. Understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying downregulation is essential for unraveling disease mechanisms and developing targeted therapies. By manipulating receptor downregulation, researchers and clinicians can potentially modulate cellular responses and improve treatment outcomes.
2. General Mechanisms Of The Endocrine Regulation • Functions Of Cells
upregulation downregulation receptors regulation endocrine mechanisms cell cells general
Receptors: Methods Of Studying Receptors, Number Of Receptors Per Cell
receptor regulation receptors down cell number biochemistry studying methods per pharmacology hubpages choose board
Two Top-down Elements Of Self-regulation That Include: Executive
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net regulation emotion emotions
Up-Regulation And Down-Regulation Of Receptors
regulation down receptors pricing pharmacology
Mechanisms Of Hormonal Regulation | Basicmedical Key
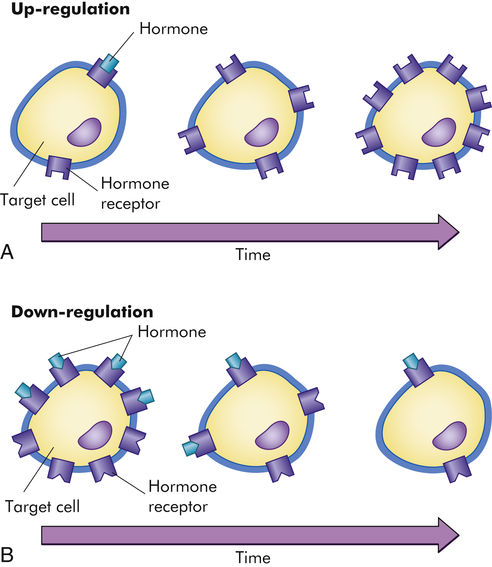 Image Source : basicmedicalkey.com
Image Source : basicmedicalkey.com regulation hormonal target hormone mechanisms cell sensitivity figure
Receptor Down Regulation
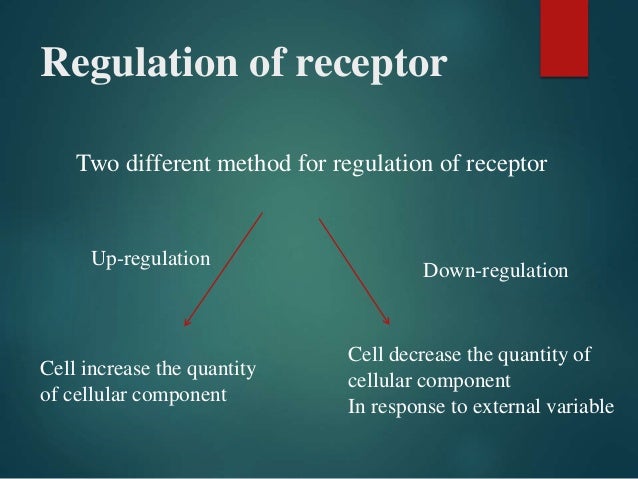 Image Source : www.slideshare.net
Image Source : www.slideshare.net regulation receptor
Down-regulation Of CWIN2 And CWIN4 Expression In Stage 12 And 13
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net Upregulation & Downregulation Of Receptors - YouTube
 Image Source : www.youtube.com
Image Source : www.youtube.com upregulation downregulation receptors receptor
Receptor regulation receptors down cell number biochemistry studying methods per pharmacology hubpages choose board. Receptors: methods of studying receptors, number of receptors per cell. Two top-down elements of self-regulation that include: executive. Regulation hormonal target hormone mechanisms cell sensitivity figure. Upregulation downregulation receptors receptor