Positive Regulation Of The Lac Operon
Positive Regulation of the Lac Operon: Exploring the Role of cAMP in Genetics
The Lac operon is an essential genetic system found in the bacteria Escherichia coli (E. coli) that allows the organism to efficiently metabolize lactose. This fascinating regulatory mechanism involves the interplay between various molecules and enzymes to control the expression of genes responsible for lactose utilization. In this article, we delve into the details of the positive regulation of the Lac operon, with a particular focus on cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and its role in the genetics of E. coli.

The positive regulation of the Lac operon centers around the presence of cAMP, a small molecule that acts as a signaling molecule in many cellular processes. In the context of the Lac operon, cAMP plays a crucial role in activating gene expression and enabling the efficient breakdown of lactose.
The Lac Operon: A Brief Overview
Before we dive into the specifics of positive regulation, let's have a quick recap of the Lac operon and its significance in bacterial genetics. The Lac operon consists of three genes: lacZ, lacY, and lacA, which together are responsible for the metabolism of lactose. When lactose is present in the environment, the Lac operon allows the transcription of these genes, leading to the synthesis of enzymes required for lactose utilization.
The Lac operon is regulated by a set of control elements and molecules that ensure its proper functioning. One of the crucial factors involved in this regulation is cAMP, which we will now explore in more detail.
cAMP: A Signaling Molecule in the Lac Operon
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate, abbreviated as cAMP, is a small molecule derived from adenosine triphosphate (ATP). It acts as a secondary messenger in many biological processes, including the positive regulation of the Lac operon. The production of cAMP is tightly regulated based on the availability of glucose in the environment, playing a crucial role in the bacterial metabolism of lactose.
Positive Regulation: How cAMP Activates the Lac Operon
Positive regulation refers to the activation of gene expression by the binding of specific molecules or factors. In the case of the Lac operon, cAMP acts as the positive regulator by binding to a protein called the catabolite activator protein (CAP) or the cAMP receptor protein (CRP).
The Role of CAP/cAMP Complex in Lac Operon Regulation
The CAP/cAMP complex plays a pivotal role in the activation of the Lac operon. When glucose levels are low and lactose is available, cAMP levels increase within the bacterial cell. The increased concentration of cAMP allows it to bind to CAP, forming the CAP/cAMP complex.
The Formation of the CAP/cAMP-DNA Complex and Transcription Activation
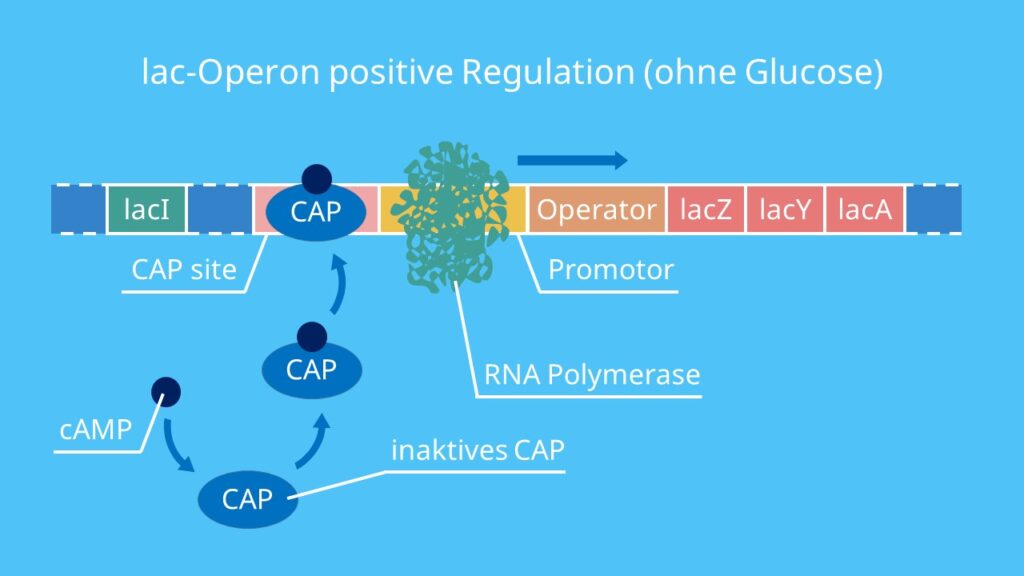
Once the CAP/cAMP complex is formed, it binds to a specific DNA region known as the CAP site, which is located adjacent to the promoter region of the Lac operon. This binding of the CAP/cAMP complex to the CAP site facilitates the recruitment of RNA polymerase to the promoter region, resulting in the initiation of transcription.
The binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter region is enhanced by the presence of the CAP/cAMP complex, leading to increased transcriptional activity of the Lac operon genes. This ultimately results in the synthesis of the necessary enzymes for lactose metabolism, allowing the bacteria to effectively utilize lactose as an energy source.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are some common questions that often arise when discussing the positive regulation of the Lac operon:
1. What happens if glucose levels are high?
If glucose levels are high, the CAP/cAMP complex formation is hindered. As a result, the Lac operon is not fully activated, leading to reduced expression of the lacZ, lacY, and lacA genes. The preference for glucose as an energy source inhibits the utilization of lactose, ensuring that the bacterium prioritizes glucose metabolism over lactose metabolism.
2. How does cAMP level affect Lac operon regulation?
The level of cAMP within the bacterial cell is inversely proportional to the availability of glucose. In the absence of glucose, cAMP levels rise, favoring the formation of the CAP/cAMP complex. However, in the presence of glucose, cAMP levels decrease, limiting the formation of the CAP/cAMP complex and reducing the activation of the Lac operon.
3. Are there any other regulatory factors involved in Lac operon control?
Yes, apart from cAMP and CAP, lac repressor protein also plays a crucial role in Lac operon regulation. The lac repressor protein binds to the operator region of the Lac operon, preventing the binding of RNA polymerase and hindering gene expression. However, the binding of lactose to the lac repressor protein causes a conformational change, rendering it incapable of binding to the operator region. This event further facilitates the activation of the Lac operon.
Overall, the positive regulation of the Lac operon, specifically through the action of cAMP, is an intricate and precisely controlled process. Understanding the various molecular players and their roles in this genetic mechanism helps us unravel the fascinating world of gene regulation in bacteria like E. coli.
Lac Operon - Concept, Diagram, Notes, Gene Regulation
 Image Source : byjus.com
Image Source : byjus.com operon regulation lactose byjus promoter genes bacteria coli
Is The Lac Operon A Negative Or Positive Control System? | Socratic
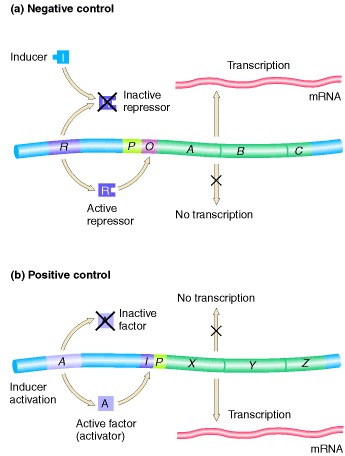 Image Source : socratic.org
Image Source : socratic.org positive operon negative lac control system socratic transcription read
Positive Regulation Of Lac Operon/ CAMP / Genetics / Lactose / E. Coli
 Image Source : www.youtube.com
Image Source : www.youtube.com operon lac regulation
Positive Regulation Of The Lac Operon By The Activator (see Online
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net lac operon activator
PPT - G E N E T I C S N E W S PowerPoint Presentation, Free Download
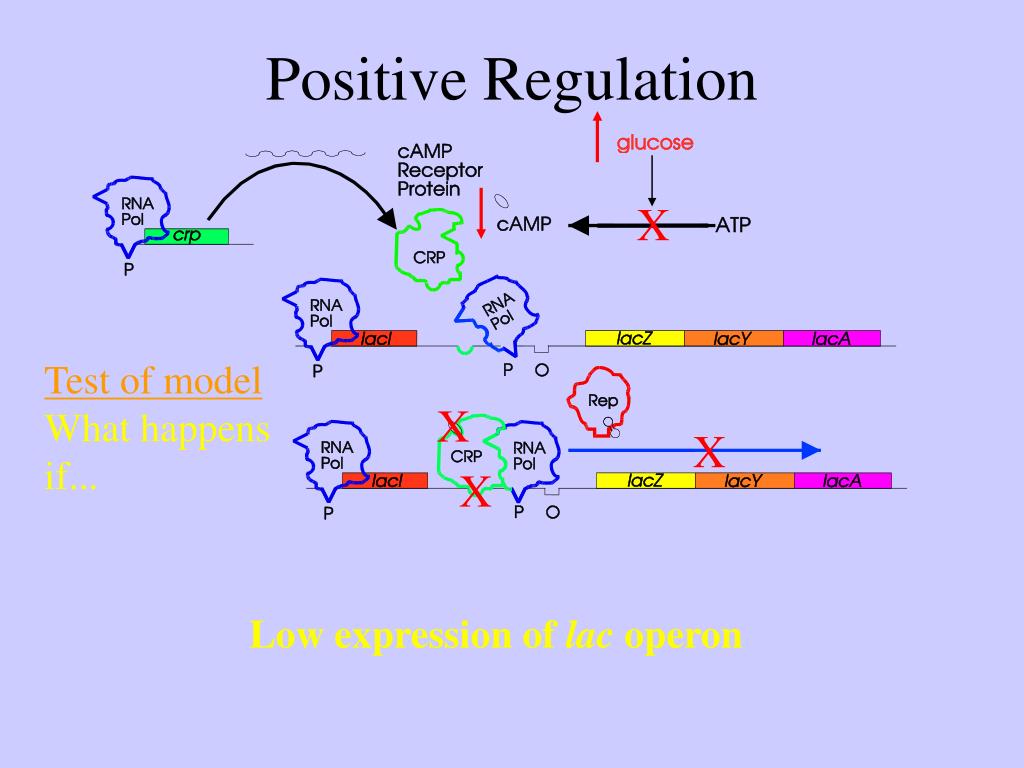 Image Source : www.slideserve.com
Image Source : www.slideserve.com regulation operon
Image Result For Lac Operon | Genetics & Genomics | Pinterest
 Image Source : www.pinterest.com
Image Source : www.pinterest.com operon lac biology regulation regulatory expression science positive gene result molecular proteins life mechanism model concentration dna bacteria genes interact
Lac Operon: Mechanism And Regulation • Microbe Online
 Image Source : microbeonline.com
Image Source : microbeonline.com Lac-Operon • Operon-Modell, Genregulation Prokaryoten · [mit Video]
![Lac-Operon • Operon-Modell, Genregulation Prokaryoten · [mit Video]](https://d1g9li960vagp7.cloudfront.net/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/lac-Operon_positive_Regulation-_ohne_Glucose_WP-1024x576.jpg) Image Source : studyflix.de
Image Source : studyflix.de Operon lac biology regulation regulatory expression science positive gene result molecular proteins life mechanism model concentration dna bacteria genes interact. Regulation operon. Lac operon. Positive regulation of the lac operon by the activator (see online. Lac-operon • operon-modell, genregulation prokaryoten · [mit video]