Fructose 2 6 Bisphosphate Regulation
Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate (F26BP) is a key regulatory molecule that plays a crucial role in controlling the metabolism of glucose in living organisms. Its levels are tightly regulated to ensure that glucose is utilized efficiently for various cellular processes. In this post, we will explore the fascinating world of F26BP regulation and its impact on cellular metabolism. 1. The Basics of F26BP Regulation Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate acts as a potent activator of phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) and inhibitor of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase-1). These two enzymes are key regulators of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, respectively. The levels of F26BP are controlled by the bifunctional enzyme 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase (PFKFB). The PFKFB enzyme can exist in different isoforms, each with distinct kinetic properties and tissue-specific expression patterns. The isoform PFKFB3 is known to be highly expressed in cancer cells and has been linked to tumor progression, making it an attractive target for cancer therapy. 2. The Role of F26BP in Glycolysis Glycolysis is the central pathway that breaks down glucose to produce energy. F26BP stimulates PFK-1, which catalyzes the phosphorylation of fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate. This allosteric activation by F26BP ensures that glycolysis is upregulated when glucose is abundant, promoting energy production. 3. F26BP and Gluconeogenesis On the other hand, F26BP inhibits FBPase-1, which catalyzes the reverse reaction in gluconeogenesis. Gluconeogenesis is the process by which glucose is synthesized from non-carbohydrate sources like amino acids and lactate. By inhibiting FBPase-1, F26BP prevents the breakdown of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, thus favoring glycolysis over gluconeogenesis. 4. Regulation of F26BP by Insulin and Glucagon Insulin and glucagon, two important hormones involved in maintaining blood glucose levels, play a crucial role in regulating F26BP levels. Insulin stimulates the expression of PFKFB and increases F26BP levels, promoting glycolysis and inhibiting gluconeogenesis. On the other hand, glucagon inhibits PFKFB and decreases F26BP levels, favoring gluconeogenesis. FAQs: Q1. What happens when F26BP levels are dysregulated? When F26BP levels are dysregulated, it can lead to metabolic disorders. For example, low F26BP levels can result in increased gluconeogenesis, leading to high blood glucose levels commonly observed in diabetes. On the other hand, high F26BP levels can favor glycolysis, promoting rapid cell proliferation and potentially contributing to cancer progression. Q2. Can F26BP be targeted for therapeutic purposes? Yes, F26BP regulation has emerged as a potential target for the development of anti-cancer drugs. Inhibition of PFKFB3, the isoform highly expressed in cancer cells, has been shown to impair cancer cell growth and sensitize tumors to chemotherapy. Several inhibitors of PFKFB3 are currently being investigated in preclinical and clinical studies. Q3. Are there any physiological conditions that can influence F26BP levels? Yes, various physiological conditions can influence F26BP levels. For example, high-intensity exercise can lead to increased F26BP levels, promoting glycolysis and energy production. Additionally, fasting or prolonged periods of low glucose availability can decrease F26BP levels, favoring gluconeogenesis and maintaining blood glucose levels. In conclusion, the regulation of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate is a fascinating area of study that has significant implications for cellular metabolism. Understanding the intricate mechanisms underlying F26BP regulation can provide valuable insights into various metabolic disorders and potentially lead to the development of novel therapeutic strategies.  Image Source : clfs690.alivetek.org
Image Source : clfs690.alivetek.org  Image Source : alchetron.com
Image Source : alchetron.com  Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net  Image Source : solofaq.com
Image Source : solofaq.com 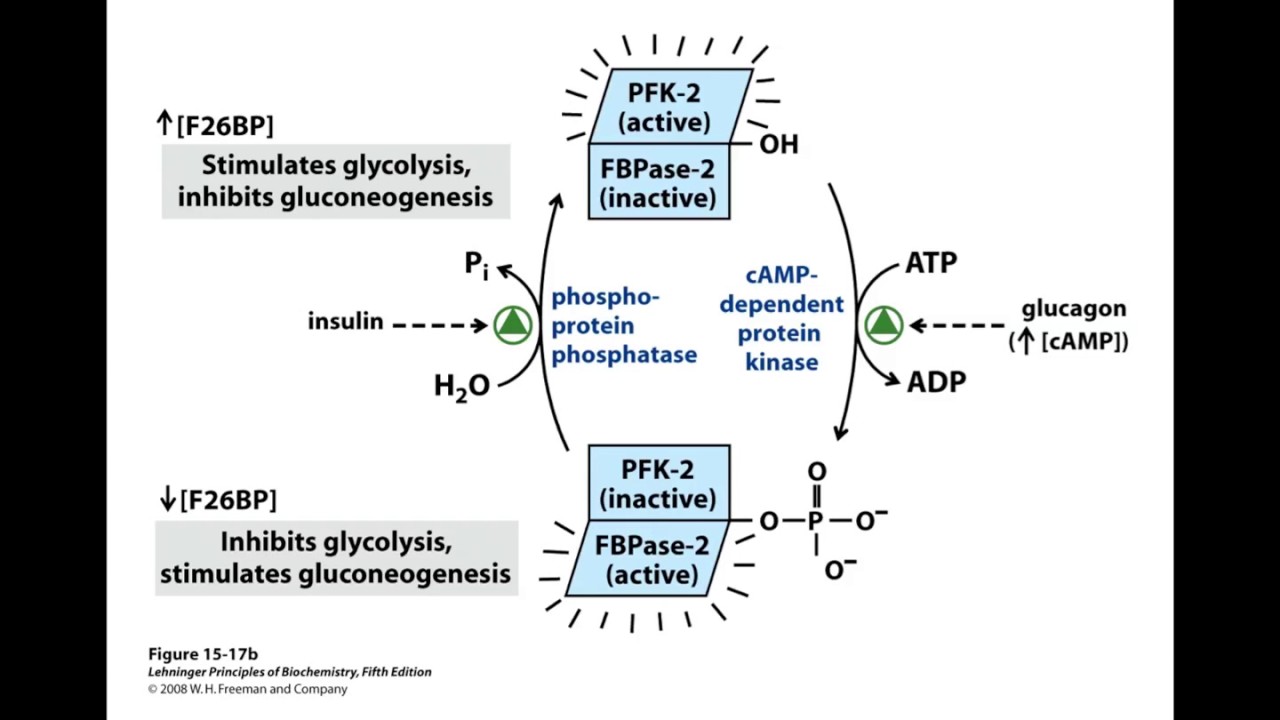 Image Source : www.youtube.com
Image Source : www.youtube.com  Image Source : www.robertbarrington.net
Image Source : www.robertbarrington.net  Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net  Image Source : alchetron.com
Image Source : alchetron.com
Phosphofructokinase-2
phosphofructokinase fructose bisphosphate regulation
Fructose 2,6 Bisphosphate - Alchetron, The Free Social Encyclopedia
 Image Source : alchetron.com
Image Source : alchetron.com fructose bisphosphate alchetron
TIGAR Functions As A Fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. Schematic Of
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net ¿La Insulina Activa La Fosfofructoquinasa? – Solo Preguntas Frecuentes!!
 Image Source : solofaq.com
Image Source : solofaq.com F26BP - YouTube
 Image Source : www.youtube.com
Image Source : www.youtube.com Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate
 Image Source : www.robertbarrington.net
Image Source : www.robertbarrington.net gluconeogenesis fructose bisphosphate glycolysis insulin allosteric showing biochemistry
7 Synthesis And Degradation Of Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate, The Most
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net Fructose 2,6 Bisphosphate - Alchetron, The Free Social Encyclopedia
 Image Source : alchetron.com
Image Source : alchetron.com fructose bisphosphate metabolism glucose alchetron effects
Fructose bisphosphate metabolism glucose alchetron effects. 7 synthesis and degradation of fructose-2,6-bisphosphate, the most. ¿la insulina activa la fosfofructoquinasa? – solo preguntas frecuentes!!. Fructose bisphosphate alchetron. F26bp