What Does Epigenetic Gene Regulation Rely On
What Does Epigenetic Gene Regulation Rely On?
Epigenetic gene regulation plays a crucial role in determining how genes are expressed and can have a significant impact on an organism's development, health, and disease susceptibility. Unlike genetic changes that alter the underlying DNA sequence, epigenetic modifications do not involve a change in the DNA code itself but regulate how genes are activated or silenced. These modifications create a dynamic layer of gene control that can be influenced by various factors. In this article, we will explore the key elements that epigenetic gene regulation relies on.
1. DNA Methylation: The Epigenetic Mark on DNA

DNA methylation is one of the major epigenetic modifications that affect gene regulation. In this process, a methyl group (-CH3) is added to the DNA molecule, typically in the context of a cytosine nucleotide. DNA methylation patterns can vary across different regions of the genome and are involved in regulating gene expression.
Research has shown that DNA methylation can lead to the silencing of genes by preventing the transcription machinery from accessing the gene promoter region. It acts as a molecular switch that can turn genes "off" or "on" depending on the methylation status of the DNA.
2. Chromatin Remodeling: Shaping Gene Accessibility
Chromatin is the complex of DNA, histone proteins, and other proteins that make up the structure of chromosomes. Epigenetic modifications can alter chromatin structure, making genes more or less accessible to the transcriptional machinery.

Specific modifications, such as histone acetylation, phosphorylation, or methylation, can dictate whether the chromatin is in a more open, accessible state (euchromatin), or a more condensed, less accessible state (heterochromatin).
3. Non-coding RNA: The Silent Players
Non-coding RNA molecules, which do not code for proteins, have emerged as essential regulators of gene expression through epigenetic mechanisms. These molecules can interact with DNA, chromatin, and other proteins to influence gene silencing or activation.
One well-known class of non-coding RNA is microRNAs (miRNAs), which can bind to messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and prevent their translation into proteins. By targeting specific mRNA sequences, miRNAs can downregulate gene expression and contribute to epigenetic gene regulation.
FAQs
Q: How do environmental factors influence epigenetic gene regulation?
A: Environmental factors, such as diet, stress, and exposure to toxins, can impact epigenetic gene regulation. These factors can induce changes in DNA methylation, histone modifications, and the expression of non-coding RNAs, which ultimately affect gene expression patterns and may contribute to the development of diseases.
Q: Can epigenetic changes be inherited?
A: Yes, some epigenetic modifications can be inherited from one generation to the next. This phenomenon is known as "epigenetic inheritance" and has been observed in various organisms. However, the exact mechanisms and extent of epigenetic inheritance are still subjects of ongoing research.
Q: Are epigenetic modifications reversible?
A: Yes, many epigenetic modifications are reversible, which means that they can be dynamically altered in response to internal and external cues. This plasticity allows cells and organisms to adapt to changing environments and signals. Researchers are also exploring various approaches to modulate epigenetic modifications for potential therapeutic interventions.
Epigenetic gene regulation relies on a complex network of interactions between DNA methylation, chromatin remodeling, and non-coding RNA molecules. Understanding these mechanisms and their influence on gene expression is vital for unraveling the mysteries of development, evolution, and disease.
Sources:
- "Biology 2e, Genetics, Gene Expression, Eukaryotic Epigenetic Gene."
- "Epigenetic regulation of chromatin structure. The majority of DNA is"
Epigenetic Mechanisms | Gu Laboratory
 Image Source : gulaboratory.com
Image Source : gulaboratory.com Frontiers | Role Of Epigenetic Regulation In Plasticity Of Tumor Immune
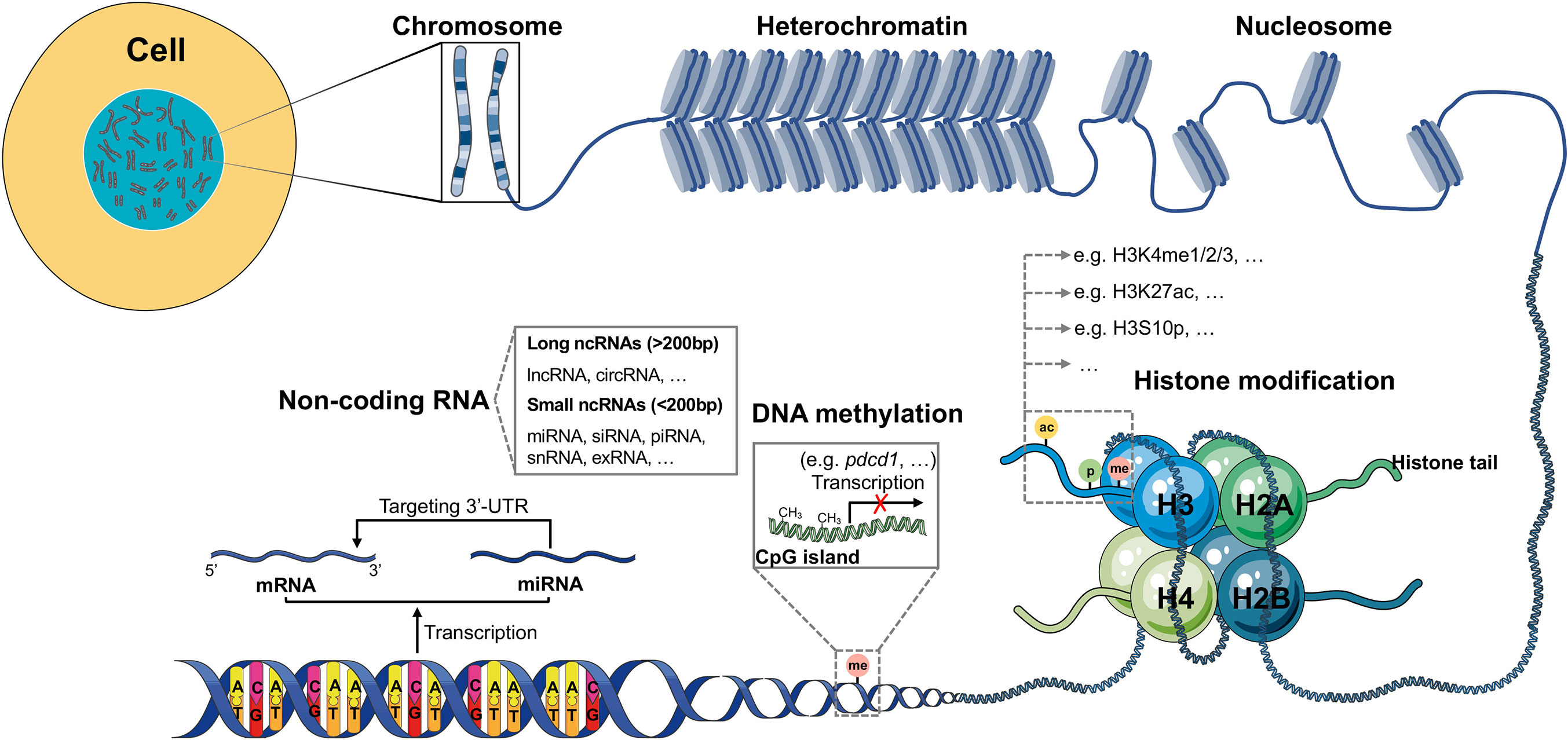 Image Source : www.frontiersin.org
Image Source : www.frontiersin.org epigenetic regulation epigenetics tumor plasticity microenvironment modifications genes frontiersin immune fimmu
What Is Epigenetics ? – Goldenhands Epigenetic Solutions
epigenetics epigenetic definition genes sins fathers chart krantz david off healing does health study
[PDF] Epigenetic Gene Expression And Regulation
![[PDF] Epigenetic Gene Expression and Regulation](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/51hdYwhdPWL.jpg) Image Source : ebookpart.info
Image Source : ebookpart.info Biology 2e, Genetics, Gene Expression, Eukaryotic Epigenetic Gene
 Image Source : opened.cuny.edu
Image Source : opened.cuny.edu gene expression regulation epigenetic biology dna histone histones eukaryotic proteins modification modifications affect nucleotides nucleosome spacing figure chromosome nucleosomes compaction
Biology 2e, Genetics, Gene Expression, Eukaryotic Epigenetic Gene
 Image Source : opened.cuny.edu
Image Source : opened.cuny.edu transcription dna gene nucleosomes histone cuny epigenetic eukaryotic regulation histones tails
Epigenetic Regulation Of Chromatin Structure. The Majority Of DNA Is
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net chromatin regulation epigenetic histone heterochromatin gene transcription majority packaged activation methylated enhancer
Epigenetic Regulation As A Basis For Long-Term Changes In The Nervous
 Image Source : new.ihna.ru
Image Source : new.ihna.ru Gene expression regulation epigenetic biology dna histone histones eukaryotic proteins modification modifications affect nucleotides nucleosome spacing figure chromosome nucleosomes compaction. Biology 2e, genetics, gene expression, eukaryotic epigenetic gene. Epigenetic mechanisms. Chromatin regulation epigenetic histone heterochromatin gene transcription majority packaged activation methylated enhancer. Transcription dna gene nucleosomes histone cuny epigenetic eukaryotic regulation histones tails