Regulation Of B Oxidation : What it is
The regulation of beta oxidation is an intriguing and essential process in the metabolism of fatty acids. This metabolic pathway is responsible for breaking down fatty acids into acetyl-CoA molecules, which can then enter the citric acid cycle to generate energy for the body. In this article, we will delve deeper into the regulation of beta oxidation, its significance, and the factors that influence its activity.
1. Understanding Beta Oxidation
Beta oxidation is a multi-step process that occurs within the mitochondria of cells. It is primarily responsible for breaking down long-chain fatty acids into two-carbon acetyl-CoA units. The acetyl-CoA molecules can further go on to participate in the production of ATP, the body's main energy currency.

Image: Beta oxidation of fatty acid
The process of beta oxidation involves four main steps: oxidation, hydration, oxidation, and thiolysis. These steps work in a cyclic manner, progressively shortening the long-chain fatty acid and generating acetyl-CoA with each cycle.
2. Regulation of Beta Oxidation
The regulation of beta oxidation is crucial to maintain metabolic balance and homeostasis. The activity of this pathway is regulated through a variety of mechanisms, which ensure that fatty acid breakdown is optimized according to the metabolic demands of the body.
Image: Products are broken down using Beta Oxidation
The key regulatory factors of beta oxidation include:
- Enzyme Activity: The activity of enzymes involved in beta oxidation, such as carnitine palmitoyltransferase I (CPT1) and carnitine palmitoyltransferase II (CPT2), determine the rate of fatty acid oxidation. These enzymes are regulated by factors like hormones, allosteric regulators, and post-translational modifications.
- Substrate Availability: The availability of fatty acid substrates also plays a role in regulating beta oxidation. The concentration of circulating fatty acids, which can be influenced by factors like diet and adipose tissue metabolism, affects the rate of fatty acid breakdown.
- Hormonal Control: Hormones such as insulin, glucagon, and adrenaline have an impact on beta oxidation. Insulin promotes the storage of fatty acids, while glucagon and adrenaline stimulate their release and subsequent oxidation.
- Nutritional Status: The metabolic state of an individual, especially the levels of glucose and glycogen, can impact the regulation of beta oxidation. During fasting or low carbohydrate intake, beta oxidation is upregulated to utilize fatty acids as an alternative fuel source.
3. Significance of Beta Oxidation Regulation
The regulation of beta oxidation is essential for maintaining energy homeostasis in the body. It allows for the efficient breakdown of fatty acids while preventing excessive fat accumulation and oxidative stress. Additionally, the regulation of beta oxidation ensures that the metabolic needs of different tissues, such as the liver, muscles, and heart, are met.
FAQs
-
Q: Can beta oxidation be inhibited?
A: Yes, beta oxidation can be inhibited by certain factors such as malonyl-CoA, which is an intermediate in fatty acid synthesis. Malonyl-CoA inhibits CPT1, the enzyme responsible for transferring fatty acids into the mitochondria for beta oxidation.
-
Q: Does exercise affect beta oxidation?
A: Yes, exercise stimulates beta oxidation to meet the increased energy demands of the body. This is especially true during prolonged aerobic activities, where fatty acids serve as an important fuel source.
-
Q: Are there any clinical implications of beta oxidation dysregulation?
A: Yes, dysregulation of beta oxidation can lead to metabolic disorders such as fatty acid oxidation disorders (FAODs). These disorders result from genetic defects in enzymes involved in beta oxidation and can present with symptoms like hypoglycemia, muscle weakness, and liver dysfunction.
In conclusion, the regulation of beta oxidation is a complex process that ensures the efficient breakdown of fatty acids while maintaining metabolic balance. Understanding the factors that influence beta oxidation and its significance in energy metabolism is crucial for grasping the intricate workings of our body's metabolic pathways.
Regulation Of Fatty Acid Biosynthesis (a) And β-oxidation (b) In
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net Beta Oxidation Of Fatty Acid | Fatty Acid Catabolism And Its Regulation
 Image Source : www.youtube.com
Image Source : www.youtube.com oxidation fatty catabolism regulation
PPT - Oxidation Of Fatty Acids And K Etogenesis PowerPoint Presentation
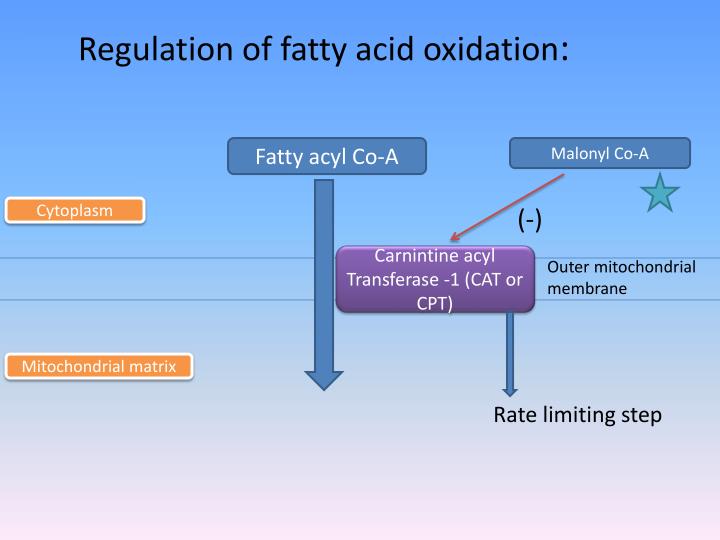 Image Source : www.slideserve.com
Image Source : www.slideserve.com fatty oxidation acids
Products Are Broken Down Using Beta Oxidation Which Occurs
Lecture 16 - Beta Oxidation Flashcards | Quizlet
 Image Source : quizlet.com
Image Source : quizlet.com Beta-oxidation Of Fatty Acid (2022)
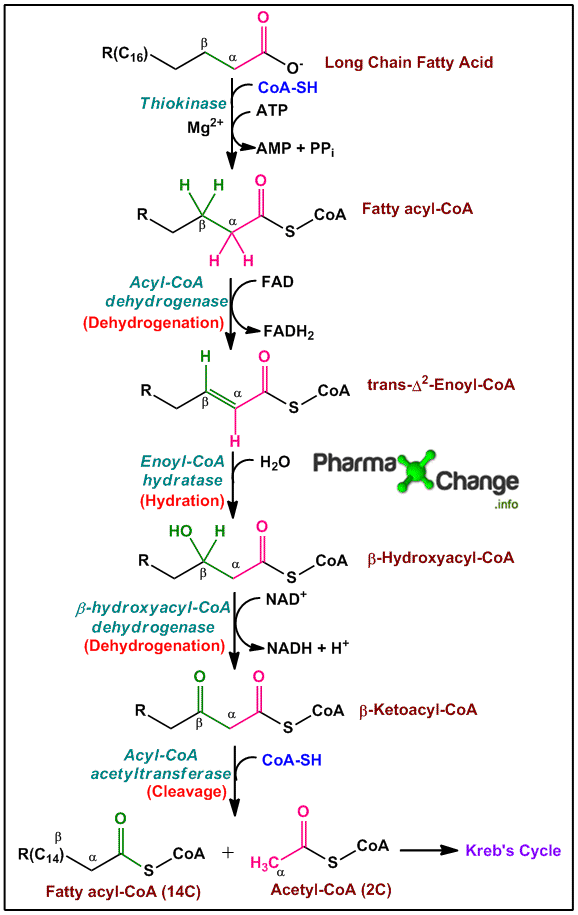 Image Source : clickytouch.com
Image Source : clickytouch.com When Is Acetyl Coa Produced Apex - LawrencekruwRussell
 Image Source : lawrencekruwrussell.blogspot.com
Image Source : lawrencekruwrussell.blogspot.com Frontiers | Defective Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Oxidation And
 Image Source : www.frontiersin.org
Image Source : www.frontiersin.org oxidation fatty mitochondrial frontiersin defective diseases lipotoxicity fmed
When is acetyl coa produced apex. Oxidation fatty mitochondrial frontiersin defective diseases lipotoxicity fmed. Beta-oxidation of fatty acid (2022). Regulation of fatty acid biosynthesis (a) and β-oxidation (b) in. Oxidation fatty catabolism regulation