Glucose Regulation Concept Map
In the field of biology, glucose regulation plays a crucial role in maintaining a stable internal environment in living organisms. This concept map aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of glucose regulation, highlighting the key components and processes involved. So, let's delve into this fascinating topic and explore the intricate details of glucose regulation!
The Glucose Regulation Concept

The concept of glucose regulation is centered around the body's ability to maintain optimal blood glucose levels. This involves a delicate balance between glucose uptake, storage, and utilization in various tissues and organs.
Hormonal Control and Homeostasis

Hormones play a crucial role in glucose regulation, ensuring that blood glucose levels remain within a narrow range. Insulin, produced by the pancreas, allows cells to take up glucose from the bloodstream, lowering blood glucose levels. On the other hand, glucagon, also produced by the pancreas, stimulates glucose release from the liver, thus increasing blood glucose levels.
In addition to insulin and glucagon, other hormones such as cortisol, epinephrine, and growth hormone also influence glucose regulation. Each hormone interacts with specific target cells and tissues, contributing to the overall homeostasis of blood glucose levels.
Glucose Uptake, Storage, and Utilization
Glucose uptake occurs primarily in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. These tissues express glucose transporters (GLUT) on their cell membranes that allow glucose to enter the cells. Insulin plays a vital role in facilitating glucose uptake by promoting the translocation of GLUT transporters to the cell surface.
Once inside the cells, glucose is either used for immediate energy production or converted into glycogen for storage. Liver and muscle cells act as major glycogen storage sites. Glycogen serves as a readily available energy reserve that can be rapidly mobilized when needed.
When glucose intake exceeds the energy requirements of the body, the excess glucose is converted into fatty acids and stored as adipose tissue. This process is vital for long-term energy storage and allows the body to draw on these reserves during periods of fasting or increased energy demand.
Maintenance of Blood Glucose Level and Actions in Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, or abnormally low blood glucose levels, triggers a series of actions to restore blood glucose to normal levels. In such situations, the body activates a counter-regulatory response to prevent glucose levels from dropping too low.
When blood glucose levels fall, the pancreas reduces insulin secretion while increasing the release of glucagon. It stimulates the liver to break down stored glycogen into glucose, releasing it into the bloodstream. This mechanism ensures a steady supply of glucose to maintain essential bodily functions.
Furthermore, the body also relies on other mechanisms, such as the release of cortisol and epinephrine, to increase blood glucose levels during hypoglycemia. These hormones activate glucose production and mobilization, providing a rapid energy source to counteract low blood sugar.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. Why is glucose regulation important?
Glucose regulation is vital for maintaining the overall health and well-being of an organism. Optimal blood glucose levels ensure that cells have a constant supply of energy for essential metabolic processes. Imbalances in glucose regulation can lead to various health conditions, including diabetes mellitus.
2. How does insulin affect glucose regulation?
Insulin facilitates glucose uptake by cells and promotes the storage of excess glucose in the form of glycogen or fatty acids. Its role is crucial in preventing high blood glucose levels and maintaining homeostasis.
3. What happens if blood glucose levels drop too low?
If blood glucose levels drop below the normal range, it can lead to hypoglycemia. In response, the body initiates a counter-regulatory response to restore blood glucose to optimal levels, primarily through the release of hormones such as glucagon, cortisol, and epinephrine.
This comprehensive concept map provides a detailed overview of glucose regulation, covering the essential processes and hormonal control involved. Understanding the intricacies of glucose regulation enables us to appreciate the remarkable mechanisms that our bodies employ to maintain stability and optimal functioning.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this concept map is for educational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. Please consult a healthcare professional for specific medical concerns or conditions.
Sources:
- Blood glucose regulation concept map activity answers - Brainly.com
- In Class - Alysa Chirillo, Project Lead the Way Biomed Portfolio
9.2 Metablic Regulation Concepts – Nursing Pharmacology
 Image Source : pressbooks.bccampus.ca
Image Source : pressbooks.bccampus.ca Solved 4. Complete This Concept Map On The Regulation Of | Chegg.com
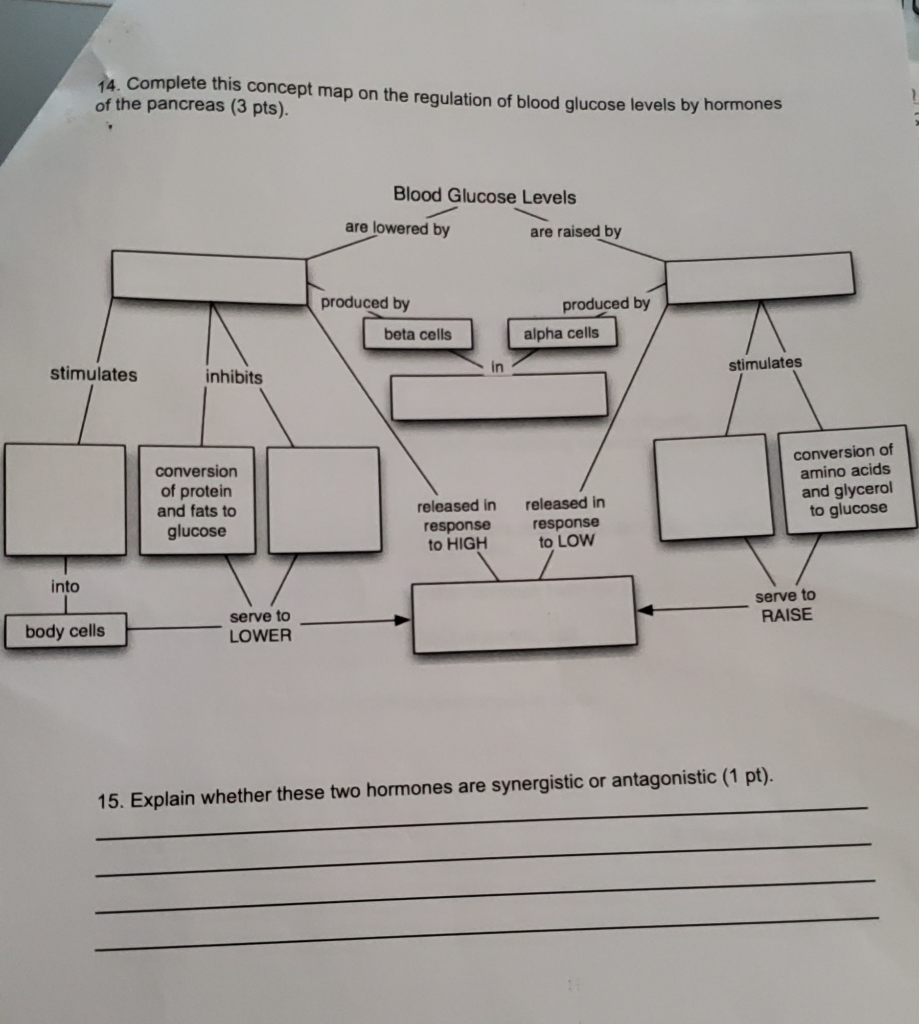 Image Source : www.chegg.com
Image Source : www.chegg.com glucose regulation transcribed
In Class - Alysa Chirillo, Project Lead The Way Biomed Portfolio
 Image Source : alysachirillopltwbiomedportfolio.weebly.com
Image Source : alysachirillopltwbiomedportfolio.weebly.com blood regulation feedback sugar loop
Pin Von Lindsay Pfankuch Auf A&P2
 Image Source : www.pinterest.de
Image Source : www.pinterest.de National 4 Biology - Maintaining Stable Body Conditions - Revision 5
 Image Source : www.pinterest.co.uk
Image Source : www.pinterest.co.uk glucose blood flowchart bbc
Blood Sugar Regulation - Biology Encyclopedia - Cells, Body, Function
regulation blood glucose sugar feedback negative homeostatic system liver concentrations endocrine body loop function pancreas cells used hormone decrease human
Solved Fight Or Flight Response When Blood Glucose Levels | Chegg.com
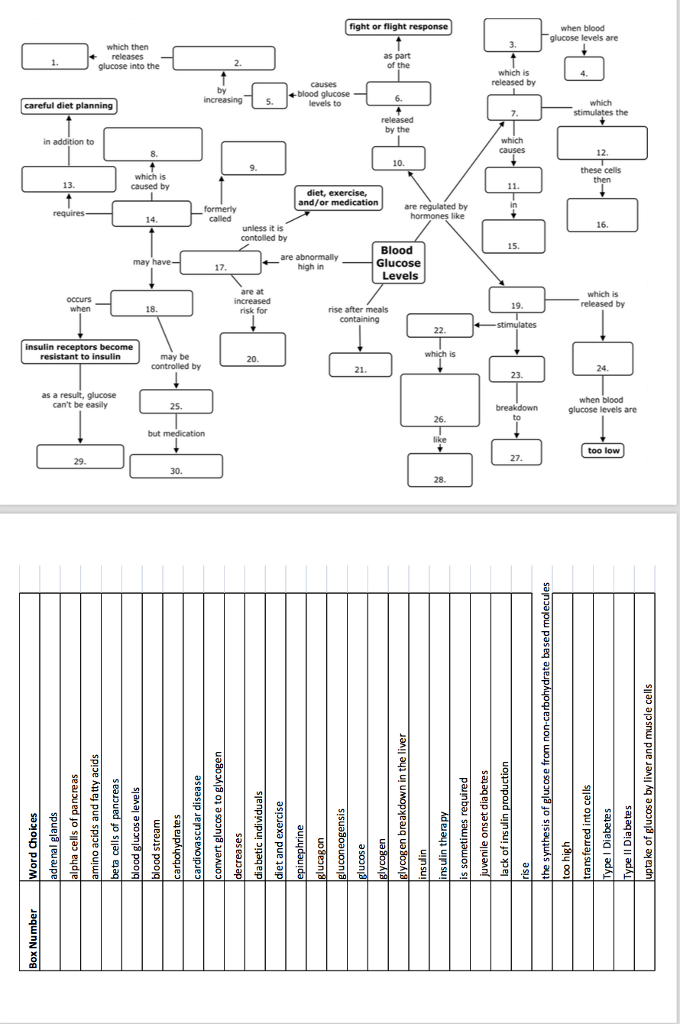 Image Source : www.chegg.com
Image Source : www.chegg.com glucose blood concept map regulation answers activity solved cells levels exercise
Blood Glucose Regulation Concept Map Activity Answers - Brainly.com
 Image Source : brainly.com
Image Source : brainly.com blood concept glucose map regulation activity answers
Glucose regulation transcribed. Blood glucose regulation concept map activity answers. National 4 biology. Solved fight or flight response when blood glucose levels. Glucose blood flowchart bbc