Voltage Regulation Formula
Voltage Regulation Formula: Understanding and Calculating Voltage Regulation
When it comes to electrical systems, one of the most important factors to consider is voltage regulation. Voltage regulation refers to the ability of a transformer to maintain a steady output voltage even when the input voltage fluctuates. It is crucial to ensure that the voltage supplied to electrical appliances and devices remains within a certain acceptable range to prevent damage or malfunction.
Understanding voltage regulation and how to calculate it is essential for anyone working with electrical systems. In this article, we will explore the voltage regulation formula and delve into its significance. So, let's dive in!
What is Voltage Regulation?
Voltage regulation is the measure of how well a transformer or electrical system can maintain a constant output voltage despite fluctuations in the input voltage. It is expressed as a percentage and indicates the difference between the no-load voltage and the full-load voltage.
Basically, voltage regulation measures how the output voltage of a transformer changes when the load current varies. Transformers generally experience voltage drops due to internal resistance, leakage reactance, and other factors. Therefore, understanding the voltage regulation of a transformer is crucial to ensure proper functioning of electrical devices.
The Voltage Regulation Formula
The voltage regulation formula provides a straightforward way to calculate the voltage regulation of a transformer. It is given by the following equation:
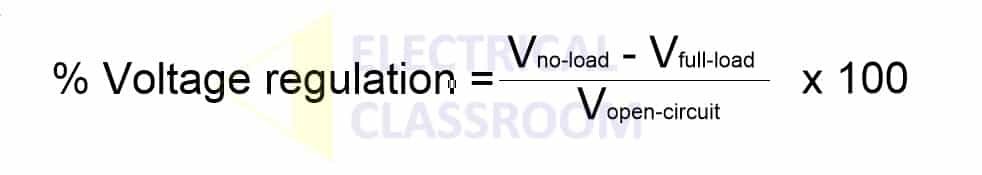
Voltage Regulation (%) = ((VNL - VFL) / VFL) x 100
Where:
- VNL is the no-load voltage
- VFL is the full-load voltage
Understanding the Components of the Formula
To have a better grasp of the voltage regulation formula, let's break down the components:
No-Load Voltage (VNL)
The no-load voltage refers to the output voltage of the transformer when there is no load connected. This is the voltage generated by the transformer when the load is disconnected or negligible. To measure the no-load voltage, the secondary winding of the transformer is left open.
Calculating the no-load voltage involves taking the voltage across the secondary winding without any load connected. This measurement allows us to understand the inherent voltage produced by the transformer without any external factors affecting it.
Full-Load Voltage (VFL)
The full-load voltage refers to the output voltage of the transformer when operating at its rated capacity or full-load. It is the voltage available at the secondary winding of the transformer when a load is connected and drawing the maximum rated current.
To measure the full-load voltage, the secondary winding of the transformer is connected to a load that consumes the maximum rated current. This measurement allows us to determine the voltage output under normal operating conditions with the load connected.
Significance of Voltage Regulation
Voltage regulation plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient and safe operation of electrical systems. Here are a few reasons why voltage regulation is essential:
1. Protects Electrical Devices
Electrical devices are designed to operate within a specific voltage range. If the voltage supplied exceeds this range, it can cause damage to the appliances, resulting in reduced lifespan and frequent breakdowns. Voltage regulation helps in maintaining the voltage within safe limits, protecting the electrical devices.
2. Prevents System Overloading
Fluctuations in voltage can lead to system overloading. When the voltage is too low, electrical devices may not receive sufficient power to operate correctly. On the other hand, high voltage can lead to increased current flow, causing overheating and potentially damaging electrical equipment.
3. Ensures Efficiency
Efficiency is a crucial factor in any electrical system. Voltage regulation ensures that the electrical system operates optimally, delivering maximum power output without any significant losses. By maintaining a stable output voltage, the voltage regulation allows the devices to function efficiently.
The Role of Voltage Regulators
Voltage regulators are electronic devices used to stabilize and control the output voltage of a transformer or electrical system. They are crucial in maintaining a steady voltage level and protecting electrical devices from damage caused by voltage fluctuations.
Voltage regulators work by continuously monitoring the output voltage and adjusting it to remain within the desired range. They ensure that the voltage supplied to electrical appliances remains constant, regardless of changes in the input voltage or load conditions.
There are various types of voltage regulators, including electromechanical regulators and solid-state regulators. Each type has its advantages and may be used in different applications based on specific requirements.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Here are some frequently asked questions related to voltage regulation:
Q1: Why is voltage regulation necessary in a transformer?
A1: Voltage regulation is necessary in a transformer to ensure a constant voltage output regardless of the variations in the input voltage. It helps protect electrical devices from damage and ensures their efficient operation.
Q2: How can I calculate the percentage voltage regulation of a transformer?
A2: To calculate the percentage voltage regulation of a transformer, you can use the voltage regulation formula mentioned earlier in this article. Measure the no-load voltage and the full-load voltage and substitute the values in the formula to obtain the percentage voltage regulation.
Q3: What are the factors affecting voltage regulation?
A3: Several factors can affect voltage regulation in a transformer, including the resistance of the windings, magnetic leakage, core losses, and load variation. Understanding these factors is crucial for designing and maintaining electrical systems.
Q4: Can voltage regulation be negative?
A4: Yes, voltage regulation can be negative. A negative voltage regulation indicates that the output voltage increases with increasing load current. This can occur in some systems when the internal resistance of the transformer is relatively low.
Conclusion
Voltage regulation is a vital aspect of electrical systems, ensuring that devices and appliances receive a consistent and safe power supply. By understanding the voltage regulation formula and its significance, electrical professionals can design efficient systems and protect equipment from potential damage caused by fluctuations in voltage.
Remember, voltage regulation plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall stability and reliability of electrical systems. So, the next time you encounter a transformer or electrical system, make sure to consider the importance of voltage regulation and its impact on the devices powered by it.
Image Source:
1. Electrical Classroom
2. Circuit Globe
Voltage-regulation-formula | Electrical Classroom
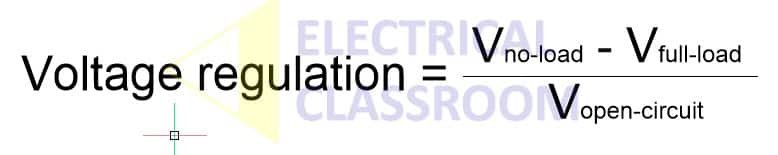 Image Source : www.electricalclassroom.com
Image Source : www.electricalclassroom.com regulation formula maximum
Percentage Voltage Drop - SuckvinderAlex
 Image Source : suckvinderalex.blogspot.com
Image Source : suckvinderalex.blogspot.com Voltage Regulation Of Transformer - Your Electrical Guide
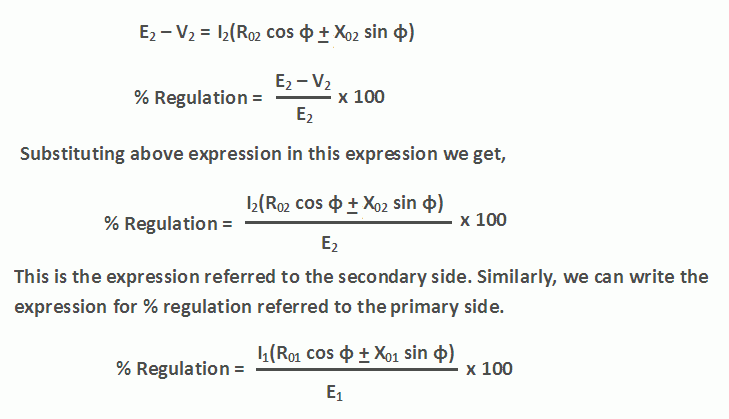 Image Source : www.yourelectricalguide.com
Image Source : www.yourelectricalguide.com regulation formula
Percentage-Voltage-regulation-formula | Electrical Classroom
 Image Source : www.electricalclassroom.com
Image Source : www.electricalclassroom.com regulation percentage
Solved Show Work!!!!use This Voltage Regulation Formula To | Chegg.com
 Image Source : www.chegg.com
Image Source : www.chegg.com regulation voltage
What Is Voltage Regulation Of A Transformer? - Definition And
voltage regulation transformer load circuit definition mathematically secondary terminal
9.6 Voltage Regulation
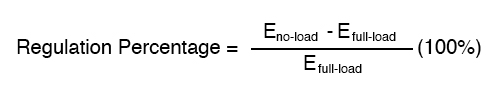 Image Source : www.technocrazed.com
Image Source : www.technocrazed.com regulation voltage formula load
Latest Regulation: Regulation Formula For Transformer
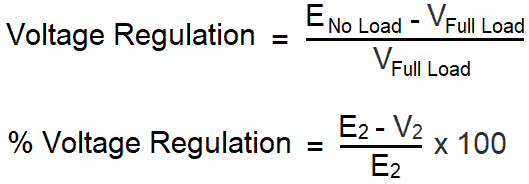 Image Source : regulationlatest.blogspot.com
Image Source : regulationlatest.blogspot.com regulation transformer transformers
Regulation percentage. Voltage regulation transformer load circuit definition mathematically secondary terminal. Percentage voltage drop. Regulation transformer transformers. Regulation voltage