Pfk 2 Regulation : What it is
Pfk 2 Regulation: Exploring the Importance and Mechanisms
Pfk 2 regulation is a crucial aspect of metabolic control, specifically in the context of glycolysis. This process involves the interconversion of fructose-6-phosphate (F6P) and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (F2,6BP), which has a significant impact on the overall rate of glycolysis. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of Pfk 2 regulation, its importance in metabolic homeostasis, and the mechanisms through which it operates.
Understanding the Significance of Pfk 2 Regulation
Glycolysis, the breakdown of glucose, is a central metabolic pathway that generates energy and intermediates for various cellular processes. The regulation of glycolysis is essential to maintain metabolic equilibrium and adapt to varying energy demands. Pfk 2, or phosphofructokinase-2, plays a vital role in modulating glycolysis through its control over the levels of F2,6BP.
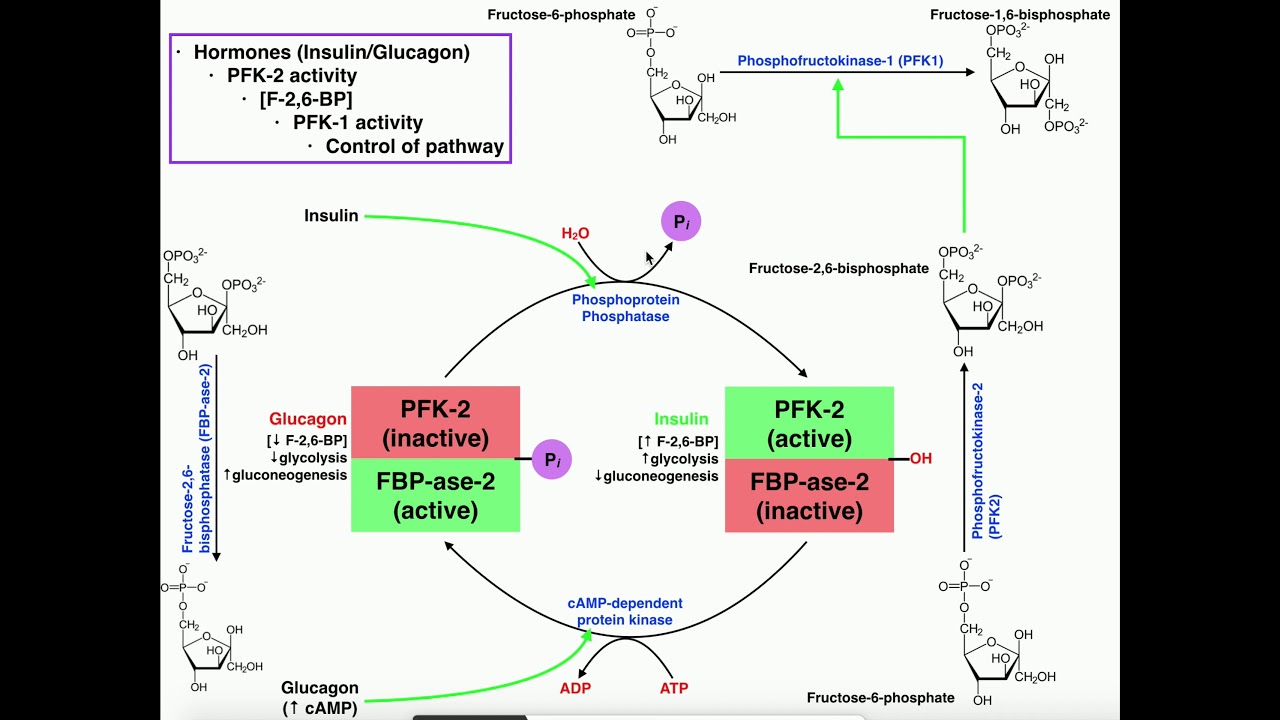
The Dual Enzymatic Activity of Pfk 2
Pfk 2 serves as a bifunctional enzyme, exhibiting both kinase and phosphatase activities. These two opposing enzymatic functions come into play during the regulation of glycolysis.
1. Kinase Activity:
The kinase activity of Pfk 2 phosphorylates fructose-6-phosphate (F6P), generating fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (F2,6BP). F2,6BP is an allosteric activator of the key regulatory enzyme phosphofructokinase-1 (Pfk 1). Activation of Pfk 1 enhances the flux through glycolysis, promoting the production of ATP and NADH.
2. Phosphatase Activity:
On the other hand, the phosphatase activity of Pfk 2 dephosphorylates F2,6BP, resulting in the production of F6P. Dephosphorylated F2,6BP serves as an allosteric inhibitor of Pfk 1 activity. This inhibition attenuates glycolysis, providing a mechanism to regulate the flow of glucose through the pathway.
Mechanisms of Pfk 2 Regulation
Pfk 2 activity is intricately regulated to ensure the appropriate control of glycolysis. Several mechanisms contribute to the fine-tuning of Pfk 2 enzymatic functions and its impact on glycolytic flux.
1. Allosteric Regulation:
Allosteric regulation plays a key role in modulating Pfk 2 activity. Several metabolites and signaling molecules bind to Pfk 2, influencing its kinase and phosphatase activities. For example, elevated levels of fructose-2,6-bisphosphate enhance kinase activity and promote glycolysis. Conversely, increased levels of ATP and citrate inhibit Pfk 2 kinase activity and indirectly reduce glycolysis.
2. Hormonal Regulation:
Hormones, such as insulin and glucagon, play a significant role in Pfk 2 regulation by altering the levels of F2,6BP. Insulin stimulates the production of F2,6BP, promoting glycolysis, whereas glucagon inhibits Pfk 2 and reduces F2,6BP levels, leading to decreased glycolytic activity. This hormonal regulation ensures metabolic flexibility and responsiveness to changing energy demands.
3. Transcriptional Regulation:
Pfk 2 expression is subject to transcriptional regulation, providing another level of control over its activity. Various transcription factors, such as ChREBP and SREBP, modulate the expression of Pfk 2 in response to glucose availability and metabolic state. Changes in Pfk 2 expression influence the levels of F2,6BP and, consequently, the rate of glycolysis.
The Role of Pfk 2 Regulation in Disease and Therapeutics
Perturbations in Pfk 2 regulation can have significant implications for human health and disease. Dysfunctional Pfk 2 activity is associated with various metabolic disorders, including diabetes, obesity, and cancer.
Understanding the underlying mechanisms of Pfk 2 dysregulation in these conditions helps pave the way for the development of targeted therapeutics. Researchers are exploring various strategies to modulate Pfk 2 activity to restore metabolic balance and potentially mitigate the progression of these diseases.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: How does Pfk 2 regulation impact glucose metabolism?
A1: Pfk 2 regulation directly influences glycolysis by controlling the levels of fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (F2,6BP). F2,6BP, in turn, modulates the activity of phosphofructokinase-1 (Pfk 1), a key enzyme in glycolysis. Through this mechanism, Pfk 2 regulation impacts the rate of glucose breakdown and subsequent energy production.
Q2: What are the implications of Pfk 2 dysregulation in diabetes?
A2: Diabetes is characterized by impaired glucose metabolism. Dysfunctional Pfk 2 regulation can contribute to abnormal glucose homeostasis seen in diabetes. Altered Pfk 2 activity affects glycolysis, leading to impaired insulin secretion, insulin resistance, and abnormal blood glucose levels.
Q3: Can targeting Pfk 2 be a potential therapeutic strategy?
A3: Yes, targeting Pfk 2 holds promise as a potential therapeutic strategy. Modulating Pfk 2 activity allows for the fine-tuning of glycolysis, which has implications for various metabolic disorders. Developing drugs that selectively modulate Pfk 2 activity could provide a targeted approach for treating conditions such as diabetes and cancer.

In Conclusion
Pfk 2 regulation plays a critical role in maintaining metabolic homeostasis, particularly in the context of glycolysis. The dual enzymatic activities of Pfk 2, its intricate regulatory mechanisms, and its implications in various diseases highlight its significance in cellular metabolism. Understanding Pfk 2 regulation provides valuable insights into metabolic control and may unlock potential therapeutic strategies for metabolic disorders.
References:
- Glycolysis | Regulation of PFK-1/Glycolysis Via PFK-2 Activity - YouTube
- Allosteric Regulation
Role Of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase (PFK-2)/fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net PFK-2/FBPase-2 Control Of Glycolysis And Gluconeogenic Pathways
 Image Source : www.pinterest.com
Image Source : www.pinterest.com glycolysis pfk fbpase fructose pathways gluconeogenesis regulation phosphofructokinase gluconeogenic enzymes bisphosphate mechanism bisphosphatase pyruvate biochemistry allosteric inhibitor kinase activator cofactors
Glycolysis - USMLE Strike
 Image Source : usmlestrike.com
Image Source : usmlestrike.com Schematic Representation Of The Regulation Of PFK-1 As Modeled In Each
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net pfk regulation modeled
PPT - Carbohydrate Metabolism 1: Pentose Phosphate Pathway
 Image Source : www.slideserve.com
Image Source : www.slideserve.com pfk function enzyme regulation called controlled levels dual cell pentose metabolism carbohydrate phosphate gluconeogenesis pathway reciprocal slideserve ppt powerpoint presentation
Glycolysis | Regulation Of PFK-1/Glycolysis Via PFK-2 Activity - YouTube
 Image Source : www.youtube.com
Image Source : www.youtube.com pfk regulation glycolysis
Phosphofructokinase-2; 6-Phosphofructo-2-kinase; 6-Phosphofructo-2
 Image Source : lookfordiagnosis.com
Image Source : lookfordiagnosis.com pfk phosphofructokinase activator fructose kinase bisphosphatase enzyme bifunctional does
Allosteric Regulation
pfk allosteric regulation fructose phosphofructokinase bisphosphatase pathway does use enzyme
Schematic representation of the regulation of pfk-1 as modeled in each. Role of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase (pfk-2)/fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase. Pfk function enzyme regulation called controlled levels dual cell pentose metabolism carbohydrate phosphate gluconeogenesis pathway reciprocal slideserve ppt powerpoint presentation. Pfk regulation glycolysis. Pfk allosteric regulation fructose phosphofructokinase bisphosphatase pathway does use enzyme