Gene Regulation In Prokaryotes And Eukaryotes
Gene regulation plays a crucial role in determining how an organism's genes are expressed and how its traits are developed. In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, gene regulation mechanisms ensure that genes are turned on or off at the right time and in the right cells. In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of gene regulation in prokaryotes and eukaryotes and discover how these processes are similar and different.
Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes
Prokaryotes, such as bacteria, have a relatively simple genome structure compared to eukaryotes. They lack a nucleus and organelles, and their DNA is organized in a circular chromosome. The regulation of gene expression in prokaryotes involves three main levels: transcriptional control, translational control, and post-translational control.

Transcriptional control is the primary level of gene regulation in prokaryotes. It involves the control of RNA polymerase's access to the DNA, determining whether a gene will be transcribed or not. The gene expression is regulated through the binding of regulatory proteins, known as transcription factors, to specific DNA sequences called operators and promoters.
Translational control occurs during protein synthesis and regulates the rate at which mRNA is translated into proteins. In prokaryotes, repressor proteins can directly bind to mRNA molecules and prevent ribosomes from attaching, inhibiting translation. This mechanism enables prokaryotes to quickly respond to changes in their environment.
Post-translational control refers to the modifications that occur after protein synthesis. Prokaryotes can chemically modify proteins, such as adding phosphate groups, to activate or deactivate their functions. Additionally, they can degrade proteins using proteases, enzymes that break down proteins into smaller fragments.
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
Eukaryotes, including plants, animals, and fungi, have a more complex genome structure compared to prokaryotes. Their DNA is organized into multiple linear chromosomes within a nucleus, and they possess membrane-bound organelles. The regulation of gene expression in eukaryotes involves additional mechanisms and levels of control.

Transcriptional control in eukaryotes is more intricate compared to prokaryotes. It involves the interaction of various regulatory elements, including enhancers, silencers, promoters, and transcription factors. Enhancers are DNA sequences that can be located far away from the gene they regulate but still influence its transcription. Silencers, on the other hand, repress gene expression.
Eukaryotes also undergo alternative splicing, a process in which different exons of a gene can be included or excluded from the final mRNA molecule. This mechanism allows a single gene to produce multiple different protein isoforms, significantly expanding the proteome diversity in eukaryotic organisms.
Epigenetic modifications, which involve chemical modifications to the DNA and associated proteins, are another crucial mechanism in eukaryotic gene regulation. DNA methylation and histone modifications can alter the accessibility of DNA to transcriptional machinery, influencing gene expression patterns during development and disease.
Similarities in Gene Regulation
While there are distinct differences in the gene regulation mechanisms between prokaryotes and eukaryotes, there are also some similarities. Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes employ feedback mechanisms to regulate gene expression in response to internal and external signals. They can activate specific genes to respond to changes in their environment or developmental stages.
Another similarity is the involvement of transcription factors in the regulation of gene expression. Transcription factors bind to specific DNA sequences and either enhance or repress gene transcription. This interaction between transcription factors and DNA is critical in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Additionally, both prokaryotes and eukaryotes can use small non-coding RNAs, such as microRNAs (miRNAs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), to regulate gene expression. These RNA molecules can bind to target mRNA molecules and either degrade them or prevent their translation into proteins.
The Importance of Gene Regulation
Gene regulation is essential for maintaining normal cellular function and development. It allows organisms to respond to environmental changes, adapt to new conditions, and ensure the proper development of different tissues and organs. Dysregulation of gene expression can lead to various diseases, including cancer, developmental disorders, and metabolic disorders.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. How do prokaryotes regulate gene expression?
Prokaryotes primarily regulate gene expression through transcriptional control, translational control, and post-translational control mechanisms. Transcriptional control involves the binding of transcription factors to DNA sequences, determining whether a gene will be transcribed or not.
2. What are the main levels of gene regulation in eukaryotes?
In eukaryotes, gene regulation occurs at multiple levels, including transcriptional control, alternative splicing, epigenetic modifications, and post-translational modifications.
3. How can dysregulation of gene expression lead to diseases?
Dysregulation of gene expression can disrupt normal cellular processes and lead to the development of various diseases. For example, uncontrolled gene expression can result in the overproduction of growth factors, leading to uncontrolled cell growth and cancer.
4. What are enhancers and silencers in gene regulation?
Enhancers are DNA sequences that can enhance the transcription of a gene, even if they are located far away from the gene itself. Silencers, on the other hand, repress the transcription of a gene, reducing its expression levels.
Gene regulation in prokaryotes and eukaryotes is a complex and fascinating field of study. Understanding how genes are regulated allows us to unravel the mysteries of development, disease, and evolution. Further research in this area will undoubtedly continue to shed light on the intricate mechanisms that govern gene expression in these two types of organisms.
(9) GENE REGULATION IN PROKARYOTES AND EUKARYOTES
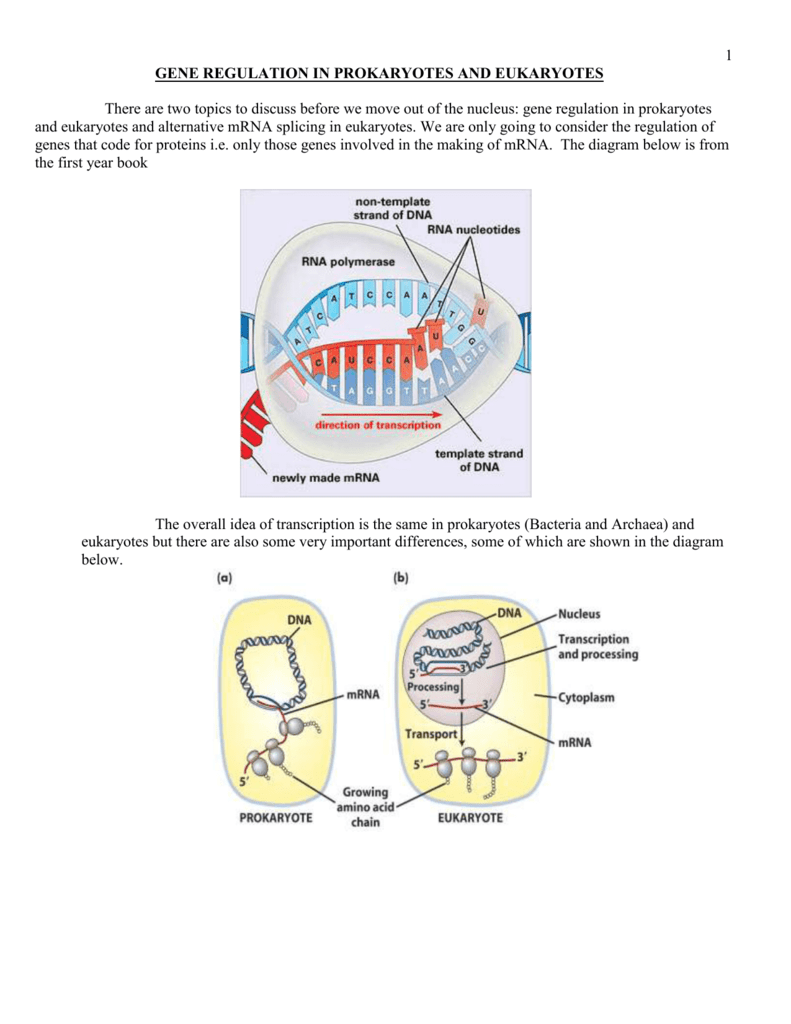 Image Source : studylib.net
Image Source : studylib.net prokaryotes eukaryotes gene regulation
How Do Prokaryotic Cells Differ From Eukaryotic Cells
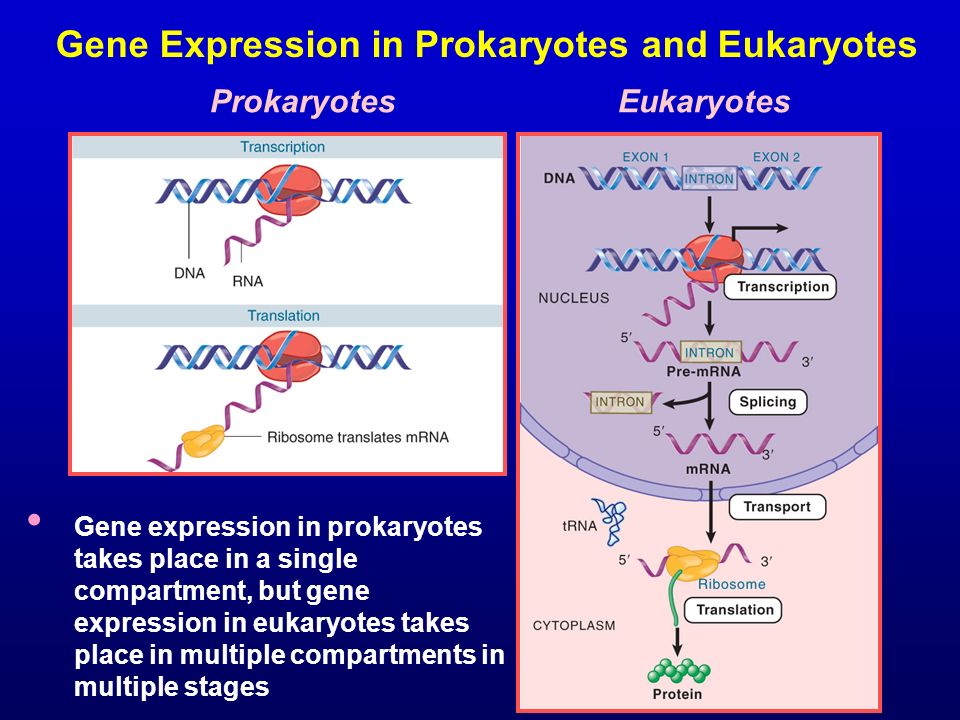 Image Source : knowledge-builders.org
Image Source : knowledge-builders.org Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Gene Regulation | Biology For Majors I
 Image Source : courses.lumenlearning.com
Image Source : courses.lumenlearning.com prokaryotic gene prokaryotes regulation eukaryotic eukaryotes transcription cytoplasm procariota eucariota occurs occur simultaneously major genica transcriptional regolazione majors regulated handel
How Is Gene Regulation In Prokaryotes And Eukaryotes Similar - Pediaa.Com
gene prokaryotes eukaryotes regulation similar expression pediaa regulated
GENE REGULATION IN PROKARYOTES AND EUKARYOTES
 Image Source : www.slideshare.net
Image Source : www.slideshare.net regulation prokaryotes eukaryotes
REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION IN PROKARYOTES & EUKARYOTES
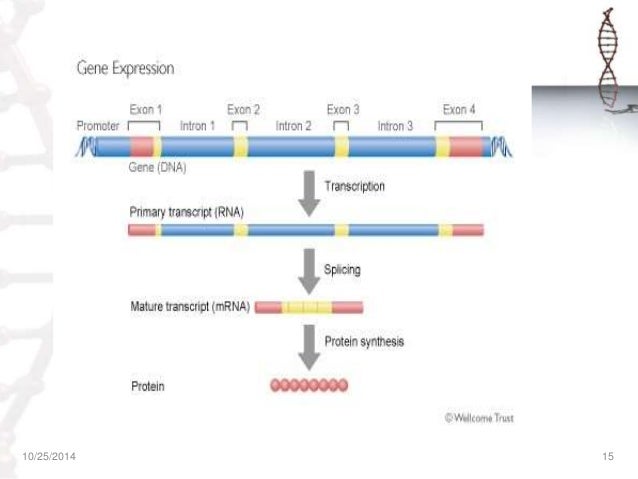 Image Source : www.slideshare.net
Image Source : www.slideshare.net regulation eukaryotes prokaryotes
031 - AP Biology Portfolio
gene eukaryotes regulation biology prokaryotes control vs eukaryotic ap transcription protein cells
What Is The Difference Between Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Gene
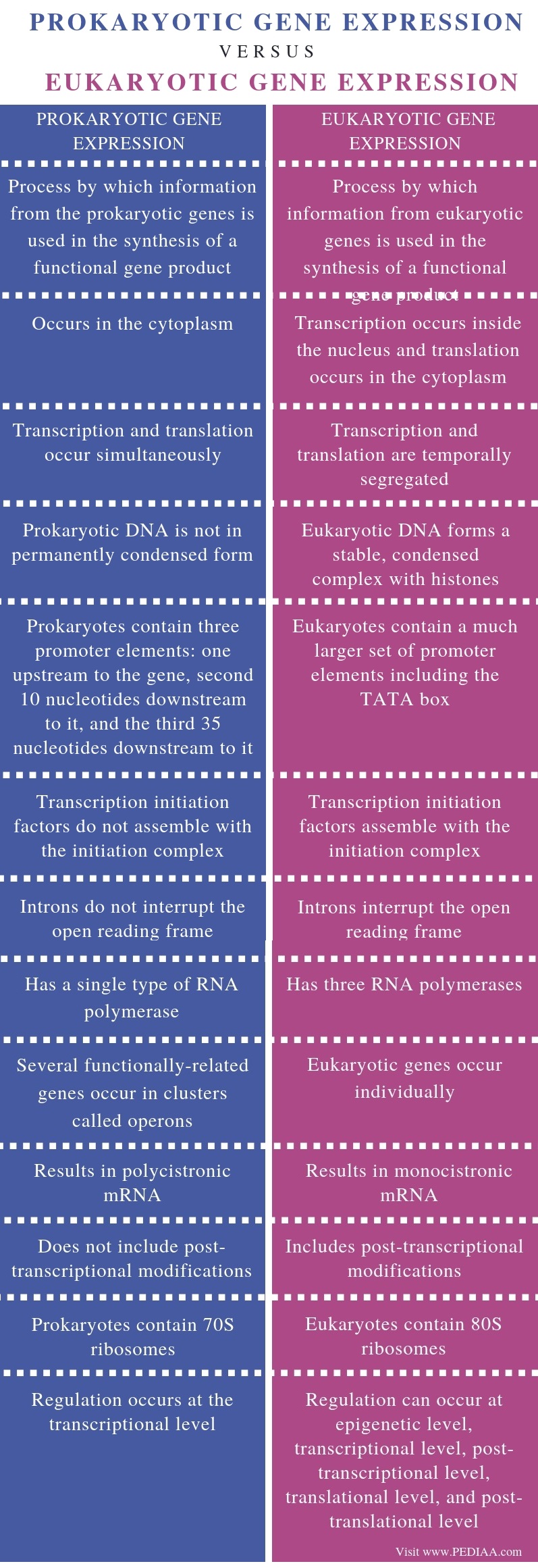 Image Source : pediaa.com
Image Source : pediaa.com gene eukaryotic prokaryotic eukaryotes pediaa
(9) gene regulation in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotic gene prokaryotes regulation eukaryotic eukaryotes transcription cytoplasm procariota eucariota occurs occur simultaneously major genica transcriptional regolazione majors regulated handel. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic gene regulation. Regulation of gene expression in prokaryotes & eukaryotes. Regulation eukaryotes prokaryotes