The Role Of Insulin In Hunger Regulation Is To
The Role Of Insulin In Hunger Regulation Is To
Insulin is a hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating hunger and food intake. It is produced by the pancreas and helps control the amount of glucose (sugar) in the bloodstream. In this article, we will explore the importance of insulin in hunger regulation and how it affects our eating habits.
1. How Does Insulin Work?

Insulin acts as a key that unlocks the cells of our body, allowing glucose to enter and be used as a source of energy. When we consume carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose, which then enters our bloodstream. The pancreas senses the rise in blood sugar levels and releases insulin to facilitate the transport of glucose into our cells.
Once inside the cells, glucose is either used immediately for energy or stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles for later use. Insulin helps maintain stable blood sugar levels by promoting glucose uptake and preventing it from accumulating in the bloodstream.
2. Insulin and Hunger Signals

Besides its role in glucose regulation, insulin also influences hunger signals. When blood sugar levels drop, such as during fasting or after a meal, insulin levels decrease as well. This leads to an increase in hunger sensations, signaling to the brain that it's time to eat.
Insulin affects the hypothalamus, a region of the brain responsible for regulating appetite. It interacts with specific receptors in the hypothalamus, influencing the release of neuropeptides that control hunger and satiety.
Furthermore, insulin helps regulate the levels of other hormones involved in hunger and fullness, such as leptin and ghrelin. Leptin is released by fat cells and signals the brain when we have enough stored energy, while ghrelin, produced by the stomach, stimulates appetite. Insulin works in collaboration with these hormones to maintain a delicate balance between hunger and satiety.
3. The Impact of Insulin Resistance on Hunger
Insulin resistance occurs when our cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin. This condition is often associated with obesity and can lead to an imbalance in hunger regulation.
When cells are resistant to insulin, glucose uptake becomes impaired, and blood sugar levels remain elevated. In response, the pancreas produces even more insulin to compensate for the reduced effectiveness. However, the excessive insulin levels can disrupt the delicate mechanisms that regulate hunger, leading to an increased appetite and overeating.
Additionally, insulin resistance can affect the levels of other appetite-regulating hormones. Leptin resistance often accompanies insulin resistance, diminishing its appetite-suppressing effects. This can contribute to a constant feeling of hunger, despite having adequate energy stores.
FAQs About Insulin and Hunger Regulation
Q: Can insulin levels affect weight gain?
A: Yes, high insulin levels resulting from insulin resistance can contribute to weight gain. Insulin promotes the storage of excess glucose as fat, making it harder for the body to break down stored fat for energy.
Q: How does insulin affect cravings?
A: Insulin helps regulate cravings by stabilizing blood sugar levels. When insulin levels drop too low, it can trigger intense cravings for sugary or high-carbohydrate foods as the body seeks a quick source of energy.
Q: Can insulin resistance be reversed?
A: In many cases, insulin resistance can be reversed or significantly improved through lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight loss. Working with a healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance for managing insulin resistance.
Insulin plays a critical role in hunger regulation by controlling blood sugar levels, influencing hunger signals, and interacting with other hormones involved in appetite control. It is crucial to maintain insulin sensitivity and promote a healthy balance to support optimal hunger regulation and overall well-being.
Pin By Bonnie Whitelock On Nutraphoria Recipes | Insulin Resistance
 Image Source : www.pinterest.com
Image Source : www.pinterest.com insulin resistance insulina nachfrage insulino insuline diabetes schema glucose glucosio insulinresistenz processo ciclo resistenza vettore identificato sangue pancreas excess bcaas
Presentation Name On Emaze
 Image Source : www.emaze.com
Image Source : www.emaze.com Insulin Levels, Hunger, And Food Intake: An Example Of Feedback Loops
 Image Source : diabetestalk.net
Image Source : diabetestalk.net ghrelin hunger hormone feedback leptin insulin weight loop intake food fat ins body obesity nervous regulation diabetes fit hormones nucleus
Whole Health Source: Testing The Insulin Model: A Response To Dr. Ludwig
 Image Source : wholehealthsource.blogspot.ca
Image Source : wholehealthsource.blogspot.ca insulin weight obesity response model energy hypothyroidism leptin intake brain food regulation body fat feedback work dr negative hypothesis expenditure
Mithaliraj इंसुलिन | परिभाषा, संरचना, और कार्य | ब्रिटानिका - Reward
 Image Source : eatdrinkmilwaukee.com
Image Source : eatdrinkmilwaukee.com Metabolism And Your Hormones | Jillian Michaels
 Image Source : www.jillianmichaels.com
Image Source : www.jillianmichaels.com hormones metabolic ghrelin weight metabolism grelina leptina selfhacked leptin inflammation decrease endocrine
Пин на доске Fitness
 Image Source : www.pinterest.ph
Image Source : www.pinterest.ph Ghrelin Hormonu Hakkında Bilmek İstediğiniz Her Şey! | Op. Dr. Murat Üstün
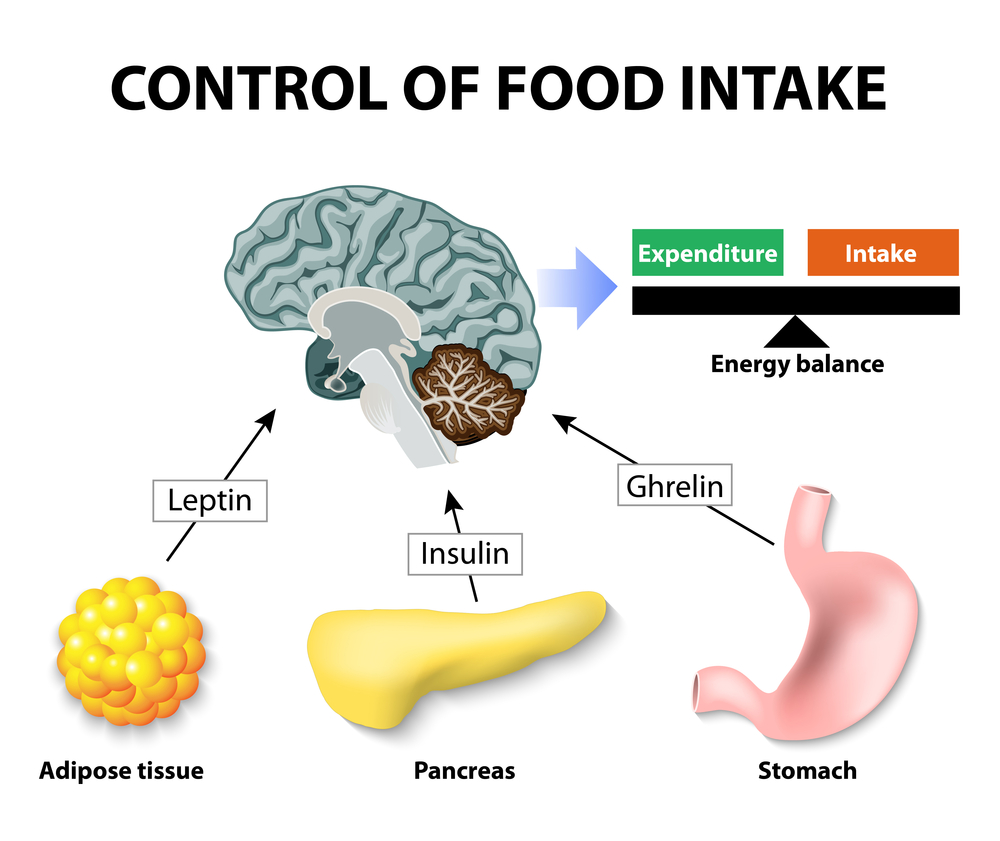 Image Source : drmuratustun.com
Image Source : drmuratustun.com Metabolism and your hormones. Insulin weight obesity response model energy hypothyroidism leptin intake brain food regulation body fat feedback work dr negative hypothesis expenditure. Whole health source: testing the insulin model: a response to dr. ludwig. Ghrelin hormonu hakkında bilmek i̇stediğiniz her şey!. Insulin levels, hunger, and food intake: an example of feedback loops