Brain Temperature Regulation
Brain Temperature Regulation: A Crucial Mechanism for Optimal Functioning
Our brain is a remarkable organ that constantly works behind the scenes to ensure our body functions smoothly. One of its crucial tasks is temperature regulation, which plays a vital role in maintaining optimal cognitive performance and overall well-being. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of brain temperature regulation, exploring its significance, mechanisms, and the impact it has on our daily lives.
The Significance of Brain Temperature

Brain temperature refers to the internal temperature of our brain, which needs to be carefully regulated within a narrow range for optimal functioning. The significance of maintaining the right brain temperature cannot be overstated. Let's explore some key reasons why brain temperature regulation is essential:
- Preservation of Neuronal Activity: The brain consists of billions of neurons that constantly communicate with each other. Elevated temperatures can lead to increased metabolic demands, impairing the functionality and communication between neurons. On the other hand, lower brain temperatures may slow down neural processes. Therefore, maintaining an optimal temperature is critical for preserving neuronal activity and ensuring efficient cognitive functioning.
- Protection against Damage: Extreme temperatures, whether too high or too low, can be detrimental to brain health. High temperatures increase the risk of protein denaturation and oxidative stress, potentially leading to cellular damage. Conversely, excessively low temperatures can cause hypothermia, resulting in reduced blood flow to the brain and impairing its function. Maintaining a stable brain temperature helps protect against such damages.
- Optimization of Cognitive Performance: Just as a well-tuned engine performs at its best, the brain operates optimally within a specific temperature range. Studies have shown that mild hypothermia can have positive impacts on cognitive performance, improving attention, memory, and overall mental agility. Understanding brain temperature regulation can help us identify ways to optimize our cognitive abilities and achieve peak performance.
Mechanisms of Brain Temperature Regulation
Our body has an incredible internal regulatory system that governs brain temperature. Several mechanisms work synergistically to maintain a stable temperature within the brain. Let's take a closer look at these fascinating mechanisms:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How does the body regulate brain temperature?
A: The body regulates brain temperature through several mechanisms, including:
- Local Vasodilation and Vasoconstriction: Blood vessels in the brain can dilate or constrict, controlling the amount of heat delivered to or dissipated from the brain.
- Cerebral Metabolism: The brain's metabolic activity generates heat as a byproduct, contributing to temperature regulation.
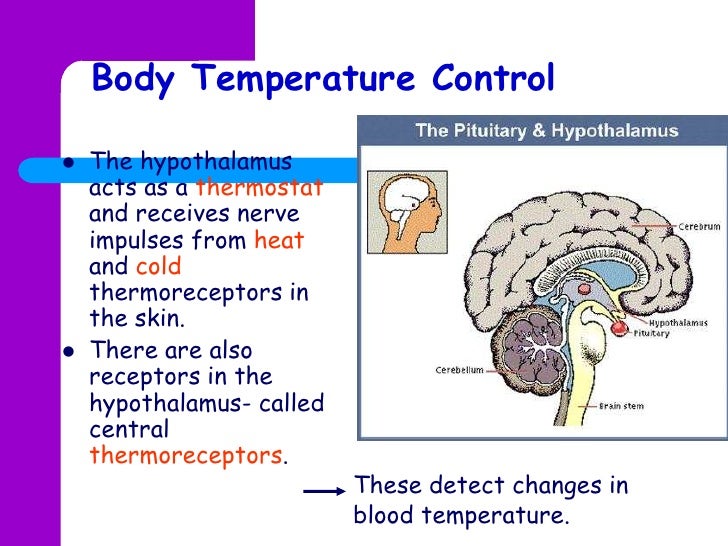
- Thermoregulatory Centers: The hypothalamus, specifically the preoptic area, acts as a central thermostat, sensing temperature changes and initiating appropriate responses to maintain the ideal brain temperature.
- Evaporative Cooling: The brain receives cooling through perspiration, where heat is dissipated through evaporation.
Q: Can external factors influence brain temperature regulation?
A: Yes, external factors can influence brain temperature regulation. Environmental conditions, such as exposure to extreme temperatures, can affect the body's ability to maintain an optimal brain temperature. Additionally, certain medical conditions and medications can alter the brain's temperature regulation mechanisms.
Q: How can individuals optimize brain temperature for improved cognitive performance?
A: While the body has its internal mechanisms to regulate brain temperature, individuals can adopt certain practices to optimize brain temperature for improved cognitive performance:
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal brain temperature. Ensure you drink enough water throughout the day.
- Exercise Regularly: Engaging in regular physical activity helps enhance blood circulation, which can contribute to better brain temperature regulation.
- Manage Stress Levels: Chronic stress can affect the body's regulatory systems, including brain temperature regulation. Adopt stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, to promote a healthy brain temperature.
- Get Sufficient Sleep: Sleep deprivation can disrupt various physiological processes, including brain temperature regulation. Prioritize quality sleep to support optimal brain functioning.
Conclusion
Brain temperature regulation is a fascinating aspect of neuroscience that influences our cognitive performance and overall well-being. Understanding the significance of brain temperature, the mechanisms involved, and how external factors can influence it empowers us to optimize our brain's functioning. By adopting healthy lifestyle practices and ensuring adequate self-care, we can pave the way for improved cognitive abilities and overall brain health.
Remember, our brain is the command center of our body, and maintaining its temperature within an optimal range is essential for unlocking our full potential.
Out Of Control
 Image Source : psu-psychology.github.io
Image Source : psu-psychology.github.io body core temperature regulation thermoregulation thermoregulatory pathophysiology control variables
Nagoya University Research Achievements
 Image Source : en.nagoya-u.ac.jp
Image Source : en.nagoya-u.ac.jp temperature sensory thermoregulation pathways brain nagoya research parabrachial nucleus lateral control thalamus feeling diagram different behavioural engaged responding external thermoreceptors
(PDF) Brain Temperature Regulation In Poor-grade Subarachnoid
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net Which Part Of Human Brain Is Concerned With The Regulation Of Body
temperature regulation hypothalamus concerned
(PDF) Thermal Characteristics Of Extracranial Vein Blood In Rabbit
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net (PDF) Comparison Of Fuzzy Control Systems For Hypothermal Brain
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net Central Mechanism Of Body Temperature Regulation And Stress Responses
temperature body regulation fever brain nagoya thermoregulation mechanism switch central nakamura med jp ac
Temperature Regulation
 Image Source : www.slideshare.net
Image Source : www.slideshare.net temperature hypothalamus thermoreceptors sweating
Temperature regulation hypothalamus concerned. Nagoya university research achievements. (pdf) brain temperature regulation in poor-grade subarachnoid. Temperature regulation. Out of control