Regulation Of Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis is a crucial metabolic pathway in living organisms, allowing for the synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors. This process ensures the body maintains optimal blood sugar levels, especially during fasting periods or intense physical activity. The regulation of gluconeogenesis is a complex and tightly controlled process that involves several key enzymes and regulatory factors. In this post, we will delve into the intricacies of gluconeogenesis, exploring its steps, regulation, and significance in maintaining metabolic homeostasis.
The Process of Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis is the process by which glucose is synthesized from non-carbohydrate precursors, such as amino acids, lactate, and glycerol. This pathway primarily occurs in the liver and to a lesser extent in the kidneys. Gluconeogenesis involves several enzymatic reactions that convert these precursor molecules into glucose.

Figure 1: Gluconeogenesis pathway
The key steps of gluconeogenesis include:
- Conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate: The enzyme pyruvate carboxylase catalyzes the carboxylation of pyruvate, resulting in the formation of oxaloacetate. This reaction occurs in the mitochondria.
- Conversion of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP): Oxaloacetate is transported from the mitochondria to the cytoplasm, where it is converted to PEP by the enzyme phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK).
- Conversion of PEP to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate: Several enzymatic reactions, including the reverse steps of glycolysis, are involved in converting PEP to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate.
- Conversion of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to glucose: The enzyme fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase catalyzes the hydrolysis of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, resulting in the formation of glucose.
- Production of glucose: Glucose-6-phosphatase catalyzes the final reaction, converting glucose-6-phosphate to free glucose, which can be released into the bloodstream.
Regulation of Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis is tightly regulated to prevent futile cycling between gluconeogenesis and glycolysis, as both pathways share several intermediate metabolites. The regulation of gluconeogenesis involves hormonal and allosteric control.
Key regulatory factors in gluconeogenesis include:
- Hormonal regulation by insulin and glucagon: Insulin, released in response to high blood glucose levels, inhibits gluconeogenesis. Conversely, glucagon, released in response to low blood glucose levels, stimulates gluconeogenesis.
- Allosteric regulation by metabolites: Several metabolites can either inhibit or stimulate enzymes involved in gluconeogenesis. For example, citrate and acetyl-CoA inhibit phosphofructokinase-1, a key enzyme in glycolysis, thereby indirectly promoting gluconeogenesis.
- Transcriptional regulation: Transcription factors, such as FOXO1 and CREB, play essential roles in regulating the expression of key gluconeogenic enzymes. These factors are influenced by hormonal signaling and nutrient availability.
Significance of Gluconeogenesis in Metabolic Homeostasis
Gluconeogenesis is a vital pathway that plays a crucial role in maintaining metabolic homeostasis. Its significance is evident in various physiological contexts:
- Energy balance: Gluconeogenesis allows for the production of glucose during periods of low carbohydrate intake or prolonged fasting, ensuring the body has a constant supply of glucose for energy production. This process helps prevent hypoglycemia and provides an alternative energy source.
- Muscle preservation: Gluconeogenesis helps spare muscle tissue from degradation by providing an alternative source of glucose production. This is particularly important during long-term fasting or intense exercise when glycogen stores become depleted.
- Ketogenesis regulation: Gluconeogenesis plays a role in regulating the production of ketone bodies, which are alternative energy substrates during prolonged fasting or conditions like untreated diabetes. Gluconeogenesis prevents excessive ketone body formation and maintains metabolic balance.
FAQs
Q: Can gluconeogenesis occur in all cells of the body?
A: No, gluconeogenesis primarily occurs in the liver and to a lesser extent in the kidneys. Other cells have limited or no capacity for gluconeogenesis.
Q: What are the main precursors for gluconeogenesis?
A: Gluconeogenesis utilizes non-carbohydrate precursors such as amino acids, lactate, and glycerol. These molecules undergo various enzymatic reactions to be converted into glucose.
Q: How is the regulation of gluconeogenesis different from glycolysis?
A: Although gluconeogenesis shares many intermediate metabolites with glycolysis, its regulation ensures that the two pathways do not occur simultaneously to avoid wasteful cycling. Gluconeogenesis is primarily regulated by hormonal signaling and allosteric control, whereas glycolysis is regulated by the availability of substrates and enzyme activity.
Q: What happens when gluconeogenesis is impaired?
A: Impairments in gluconeogenesis can lead to disorders such as hypoglycemia, where blood glucose levels become dangerously low. Additionally, disruptions in the regulation of gluconeogenesis can contribute to metabolic diseases such as diabetes.
In conclusion, gluconeogenesis is a highly regulated and essential metabolic pathway that allows for the synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors. This process ensures the body maintains optimal blood sugar levels, especially during fasting or in conditions of increased energy demand. Understanding the regulation and significance of gluconeogenesis provides valuable insights into metabolic homeostasis and its dysregulation in various pathological states.
Gluconeogenesis Regulation - YouTube
 Image Source : www.youtube.com
Image Source : www.youtube.com gluconeogenesis regulation
Gluconeogenesis Porcess, Steps & Pathway
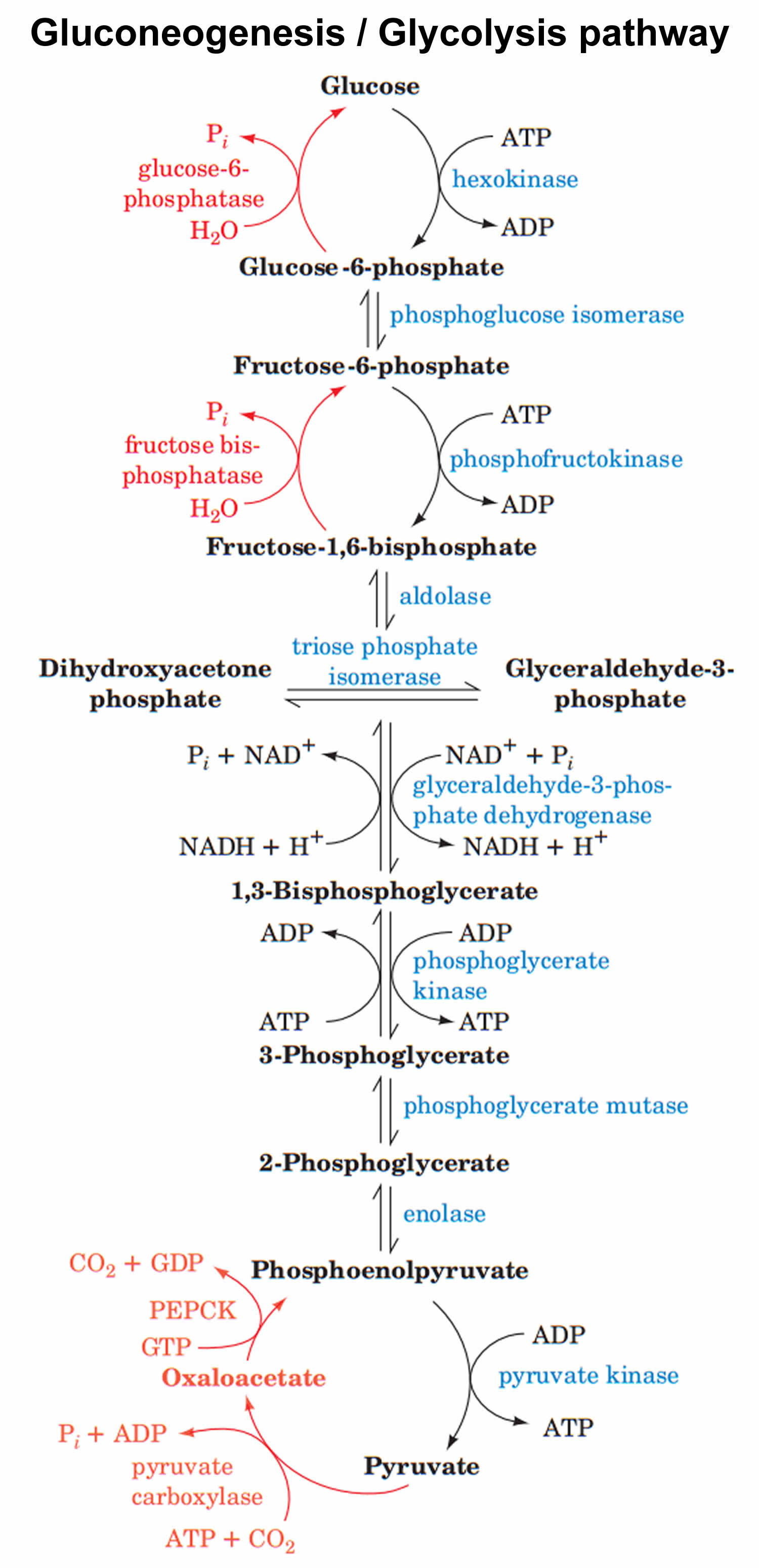 Image Source : healthjade.net
Image Source : healthjade.net gluconeogenesis pathway regulation steps
Regulation Of Glycolysis And Gluconeogenesis
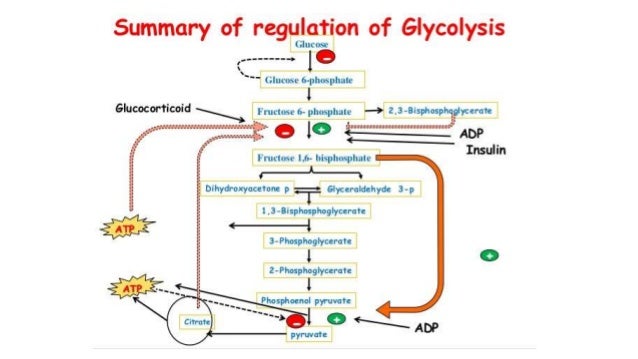 Image Source : www.slideshare.net
Image Source : www.slideshare.net gluconeogenesis regulation glycolysis
Glycolysis & Gluconeogenesis [ Pyruvate Carboxylase & Fructoss 1,6
 Image Source : www.pinterest.co.uk
Image Source : www.pinterest.co.uk glycolysis gluconeogenesis pathways diagram pathway steps enzymes biology gluconeogenic glycolytic simple notes pyruvate reverse step biochemistry respiration cellular important enzyme
GLUCONEOGENESIS & ITS REGULATION
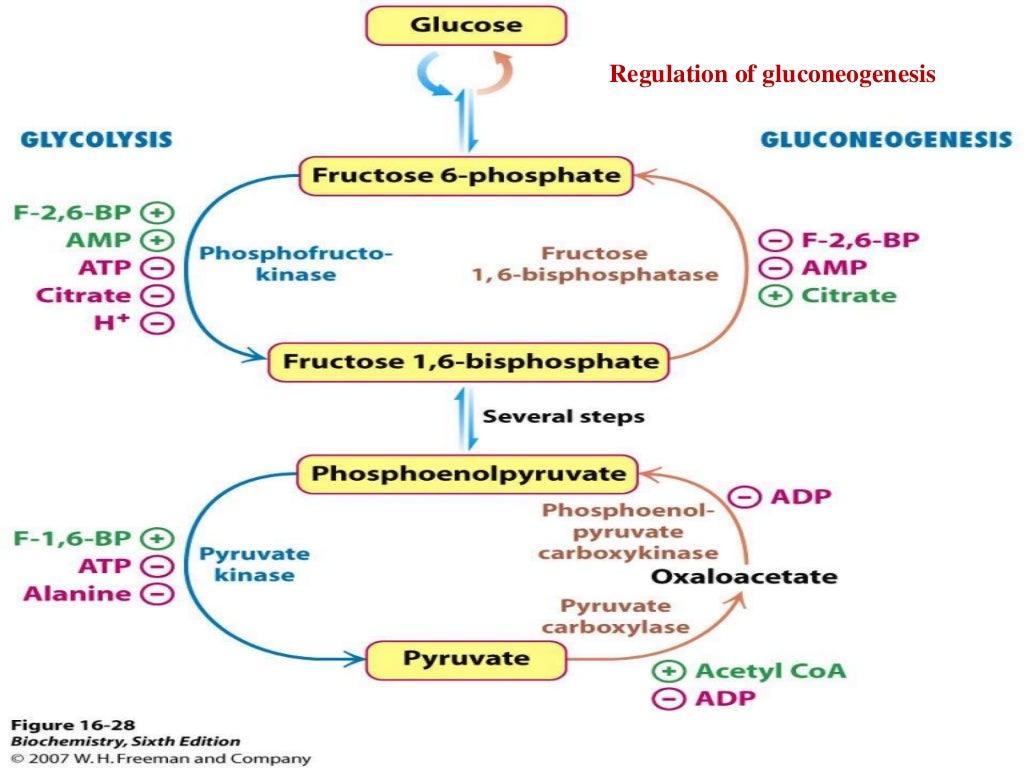 Image Source : www.slideshare.net
Image Source : www.slideshare.net gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis - The Pathway And | Biochemistry Notes, Medical
 Image Source : www.pinterest.com
Image Source : www.pinterest.com ABLEPIHA: February 2011
 Image Source : ablepiha.blogspot.com
Image Source : ablepiha.blogspot.com gluconeogenesis biochemistry biology chemistry why brain atp acids amino so difficult medical use dietitian metabolism importance essay glycolysis imageshack process
Gluconeogenesis Porcess, Steps & Pathway
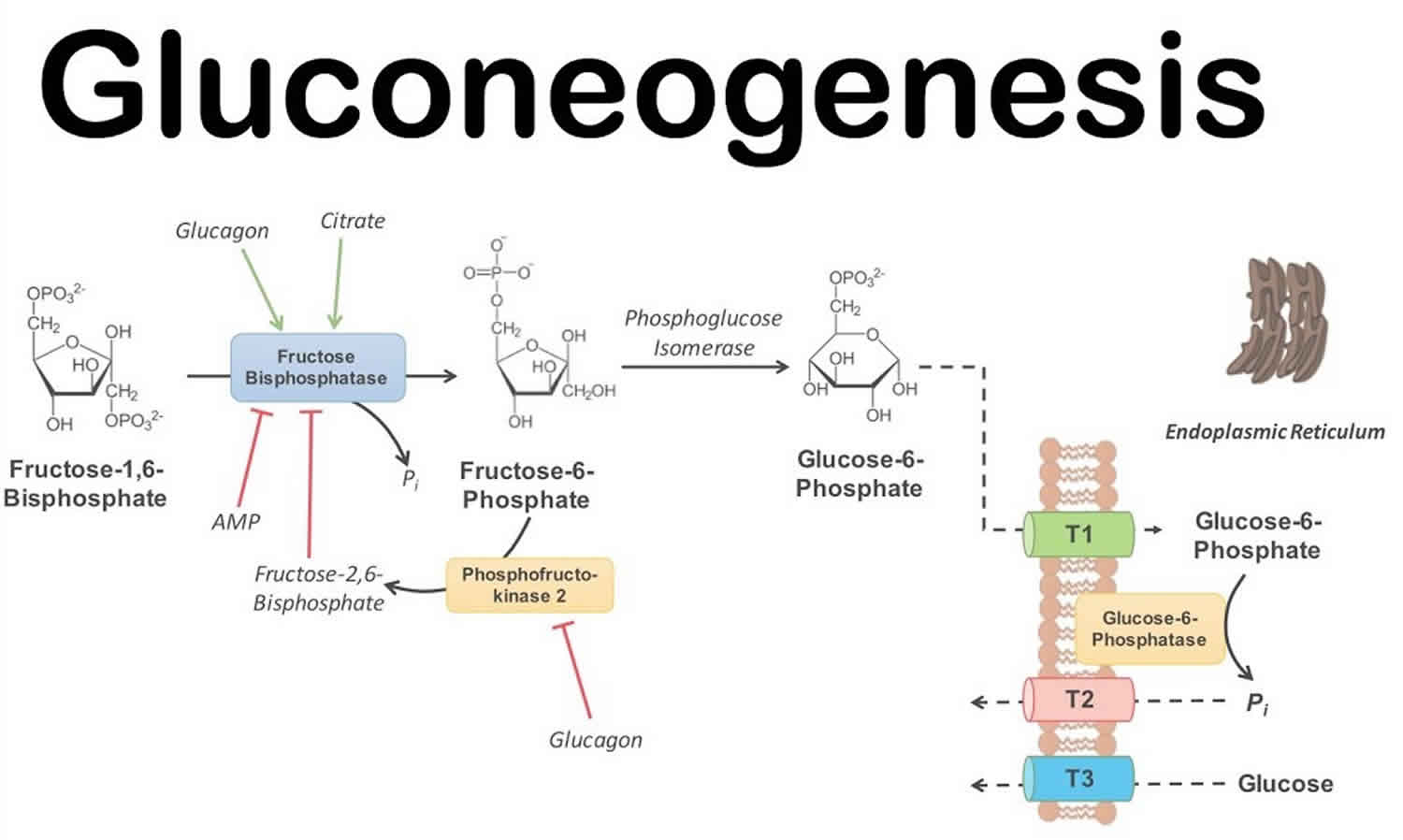 Image Source : healthjade.net
Image Source : healthjade.net gluconeogenesis regulation steps glucose pathway blood kidney glycerol function contents which
Regulation of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. Gluconeogenesis regulation steps glucose pathway blood kidney glycerol function contents which. Gluconeogenesis porcess, steps & pathway. Ablepiha: february 2011. Glycolysis & gluconeogenesis [ pyruvate carboxylase & fructoss 1,6