Regulation In Biology Example
Regulation in Biology: A Fascinating Journey into Metabolic Control
Have you ever wondered how living organisms maintain a state of equilibrium amidst changing environmental conditions? How do they modulate the expression of genes or adjust their metabolic activities to adapt to ever-changing circumstances? The answer lies in the intricate world of biological regulation.
Join us as we embark on an exciting exploration of regulatory mechanisms in biology, shining a light on the remarkable ways organisms remain dynamic and responsive. From positive and negative regulation to metabolic regulatory pathways, we'll unravel the mysteries behind these essential processes.
A Glimpse into Positive and Negative Regulation

Underneath the surface of intricate biological systems lies a delicate balance maintained by positive and negative regulation. These regulatory mechanisms ensure that biological processes occur at appropriate times and rates, enabling organisms to function optimally.
In positive regulation, specific regulatory factors, often proteins, activate gene expression or metabolic pathways when certain conditions are met. Think of it as an "on" switch – the presence of the activating factor ignites the process, allowing it to proceed. This mechanism plays a crucial role in numerous physiological processes, from embryonic development to immune responses.
On the other hand, negative regulation serves as the "off" switch. Regulatory factors can repress gene expression or inhibit metabolic pathways when required. This mechanism prevents unnecessary energy expenditure or halts processes that may be harmful in certain contexts.
Positive and negative regulation often work hand in hand to maintain the delicate balance of life. By carefully orchestrating these dual processes, organisms can adapt to changing conditions in their environment while preserving internal stability.
The Intricacies of Metabolic Regulation

If positive and negative regulation lay the groundwork for broader control, metabolic regulation represents the engine driving the intricate machinery of living organisms. This fascinating mechanism enables organisms to efficiently allocate resources, respond to varying energy demands, and maintain metabolic homeostasis.
Metabolic regulation involves the control of metabolic pathways – complex sets of chemical reactions responsible for various cellular processes. From the synthesis and breakdown of molecules to energy production, these pathways determine the overall metabolism of an organism.
One prominent example is the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle or citric acid cycle. The TCA cycle serves as a central hub for energy production and serves as a connecting point between several other metabolic pathways. Regulation of the TCA cycle ensures the appropriate generation of energy-rich molecules, such as ATP, to meet the energy demands of the organism.
Additionally, metabolic regulation involves feedback mechanisms and allosteric control. Feedback mechanisms allow metabolites produced in a pathway to either inhibit or activate enzymes involved in that very pathway, ensuring that the cellular environment remains balanced.
Allosteric control, on the other hand, involves the binding of specific molecules to regulatory sites on enzymes, influencing their activity. This mechanism allows for fine-tuning of metabolic processes in response to molecular signals or changing environmental conditions.
Unveiling the Wonders of Regulatory Networks
Regulatory mechanisms in biology extend beyond isolated pathways or individual reactions. Organisms often employ elaborate networks of interconnections, allowing for intricate coordination and integration. By studying these networks, scientists gain a deeper understanding of how living systems maintain homeostasis and adapt to their surroundings.
One of the most fascinating regulatory networks is the interconnected web of transcription factors. Transcription factors are proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences, controlling the rate of gene transcription – the process by which DNA is converted into RNA. These networks of transcription factors enable precise control and fine-tuning of gene expression in response to various stimuli.
Moreover, post-translational modifications play a vital role in regulatory networks. Processes such as phosphorylation, methylation, and acetylation can alter the functional properties of proteins, including enzymes and transcription factors, influencing their activities and interactions with other molecules.
Overall, the study of regulatory networks uncovers remarkable insights into the dynamic nature of biological control, highlighting the interconnectedness of various regulatory mechanisms and their role in shaping the characteristics and behaviors of living organisms.
FAQs
1. What is the significance of biological regulation?
Biological regulation ensures that organisms maintain a state of equilibrium by modulating gene expression, metabolic activities, and physiological processes. It allows organisms to respond to varying environmental conditions, adapt to internal and external challenges, and uphold overall homeostasis.
2. How do positive and negative regulation work together?
Positive and negative regulation work in harmony to regulate biological processes. Positive regulation activates processes when specific conditions are met, while negative regulation represses or inhibits processes when required. This delicate interplay ensures that processes occur at the right time and in the right amounts, optimizing the functioning of living organisms.
3. How does metabolic regulation impact overall metabolism?
Metabolic regulation plays a fundamental role in allocating resources, regulating energy production, and maintaining metabolic homeostasis. It ensures energy availability to support vital cellular processes, prevents unnecessary energy expenditure, and enables organisms to respond to varying energy demands.
Embark on this captivating journey into the world of regulation in biology and marvel at the awe-inspiring mechanisms that govern life. Discover how organisms dance to the rhythm of positive and negative regulation, witness the power of metabolic control, and explore the intricate networks that shape living systems.
Latest Regulation: Regulation Definition Biology Example
 Image Source : regulationlatest.blogspot.com
Image Source : regulationlatest.blogspot.com mechanisms transcription
PPT - Biology 10.2 Gene Regulation And Structure PowerPoint
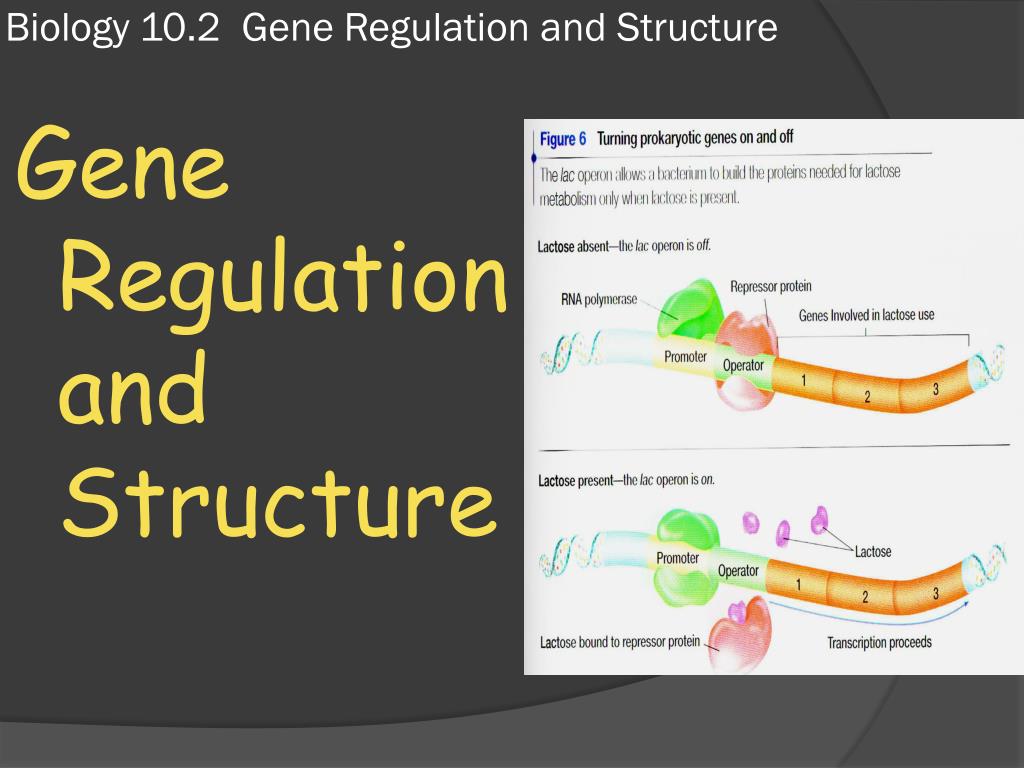 Image Source : www.slideserve.com
Image Source : www.slideserve.com regulation gene biology structure ppt powerpoint presentation
Regulation Of Gene - Gene Expression And Transcription Of Cell
gene regulation biology expression genes cell
Example Of Regulation In Biology
 Image Source : regulationlatest.blogspot.com
Image Source : regulationlatest.blogspot.com What Is Gene Regulation? | Socratic
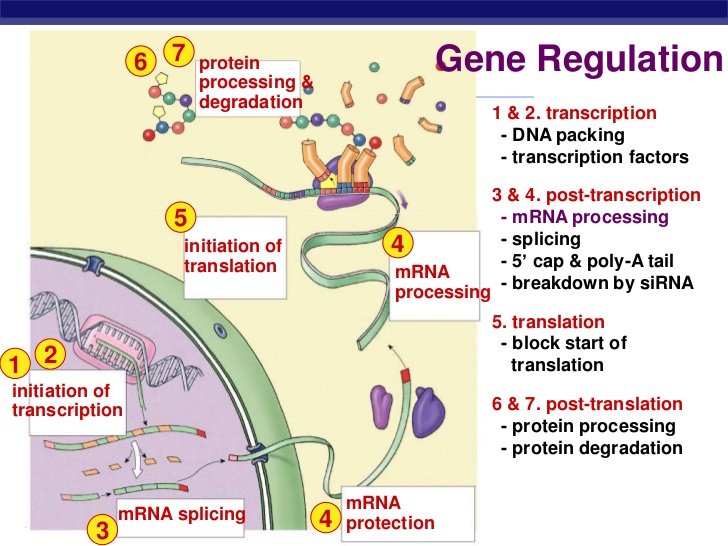 Image Source : socratic.org
Image Source : socratic.org regulation transcription socratic eukaryotic mrna during
Definition Of Active Cell - DEFINITIONXA
 Image Source : definitionxat.blogspot.com
Image Source : definitionxat.blogspot.com Positive And Negative Regulation
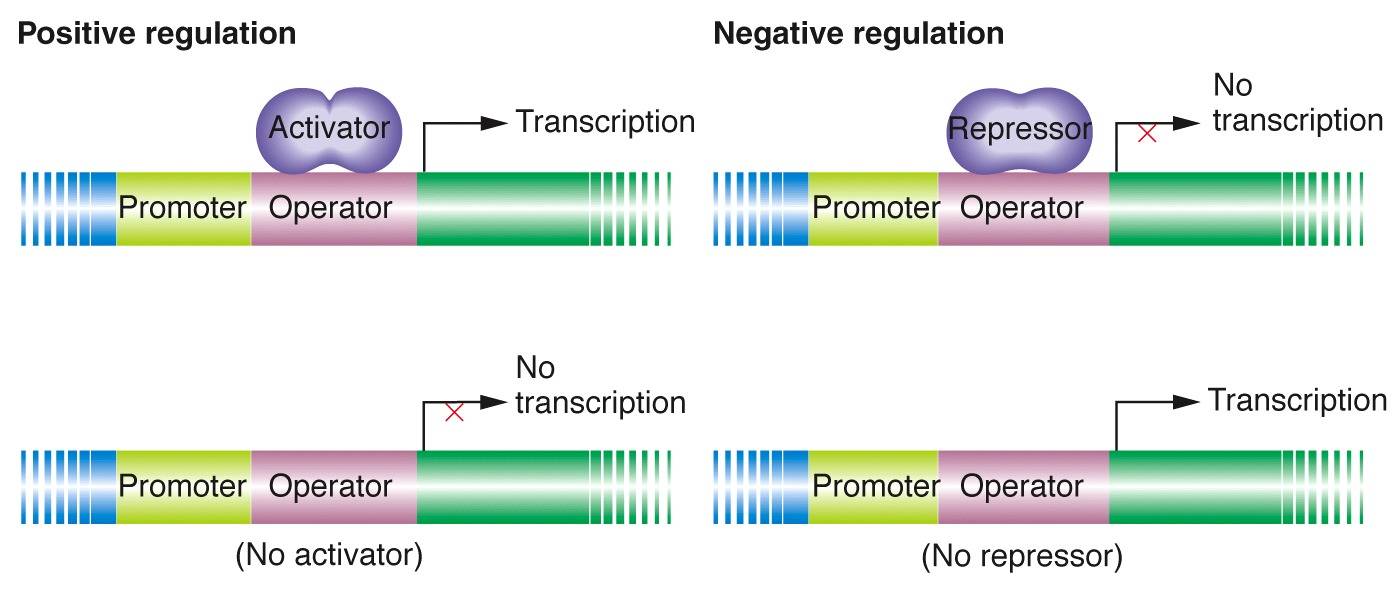 Image Source : www.mun.ca
Image Source : www.mun.ca biology regulation regulatory
7: Principles And Examples Of Metabolic Regulation - Biology LibreTexts
 Image Source : bio.libretexts.org
Image Source : bio.libretexts.org regulation metabolic examples principles biology libretexts
Example of regulation in biology. Latest regulation: regulation definition biology example. Mechanisms transcription. Biology regulation regulatory. Regulation metabolic examples principles biology libretexts