Kidney Regulation Of Ph : What it is
Kidney Regulation Of Ph : What it is
The regulation of pH in the human body is a complex process that involves several organs and systems. One of the key players in maintaining the acid-base balance is the kidneys. The kidneys play a crucial role in filtering and excreting waste products from the blood, including excess acids and bases. In this article, we will dive deeper into the kidney's mechanism for regulating pH and explore its importance for overall health.
The Importance of pH Regulation
Before we understand how the kidneys regulate pH, let's first understand why maintaining proper pH levels in the body is essential. pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a substance, and our body fluids, including blood, have a specific pH range that they must stay within for optimal functioning. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being considered neutral, values below 7 indicating acidity, and values above 7 indicating alkalinity.
Our body relies on enzymes and other biochemical processes that are sensitive to pH levels. Even a slight deviation from the normal pH range can disrupt these processes and lead to various health issues. The kidneys, along with other buffer systems in the body, work together to maintain the pH within a narrow range, typically around 7.35 to 7.45.
Kidney's Role in pH Regulation
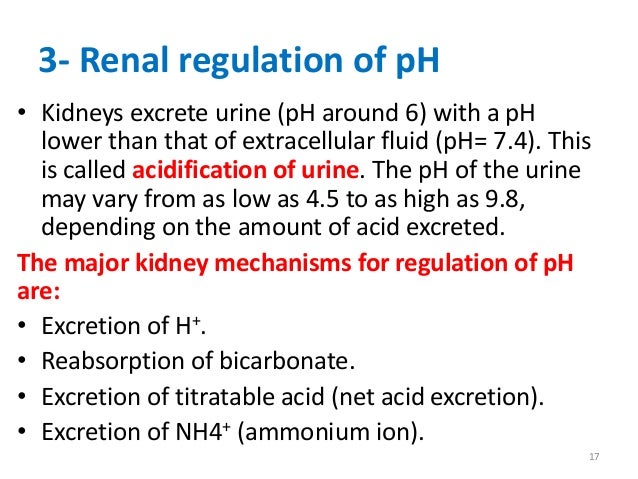
The kidneys primarily regulate pH through a process called renal bicarbonate reabsorption. Bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) act as a major buffer system in the body, helping to maintain the acid-base balance. The kidneys filter bicarbonate ions from the blood and reabsorb them back into the bloodstream when needed.
How Kidneys Reabsorb Bicarbonate
When the blood becomes too acidic, such as during conditions like metabolic acidosis, the kidneys play a crucial role in reabsorbing bicarbonate ions to restore the pH balance. This process takes place in the renal tubules, which are tiny structures in the kidneys responsible for filtering waste products from the blood.
Step 1: Filtration
During filtration, blood enters the glomerulus, which is a ball of blood vessels surrounded by a structure called Bowman's capsule. The pressure in the glomerulus forces small molecules, including bicarbonate ions, into the Bowman's capsule.
Step 2: Proximal Tubule
From the Bowman's capsule, the filtrate containing bicarbonate ions moves into the proximal tubule. In the proximal tubule, the majority of filtered bicarbonate is absorbed back into the bloodstream. This reabsorption occurs through a series of complex mechanisms involving various transporters and enzymes.
Step 3: Acid Secretion
During reabsorption, hydrogen ions (H+) are simultaneously secreted into the filtrate. These hydrogen ions combine with bicarbonate ions to form carbonic acid, which eventually breaks down into water and carbon dioxide.
The carbon dioxide generated from this process can then diffuse out of the tubule cells and enter the bloodstream. It is transported back to the lungs, where it is expelled from the body through exhalation.
Step 4: Bicarbonate Reabsorption
Once the hydrogen ions are secreted, bicarbonate ions are reabsorbed from the filtrate via a process called bicarbonate reabsorption. This reabsorption occurs in the distal tubules and the collecting ducts of the kidneys. In these tubules, bicarbonate ions combine with hydrogen ions to form carbonic acid, which then breaks down into water and carbon dioxide.
Bicarbonate ions and the generated carbon dioxide are then transported back into the bloodstream, helping to restore the pH balance.
Importance of Kidney Regulation of pH
Proper regulation of pH by the kidneys is vital for overall health and well-being. Here are a few reasons why kidney regulation of pH is so crucial:
1. Maintenance of Enzyme Activity
Many enzymes in our body are sensitive to changes in pH. A deviation from the normal pH range can affect the activity of these enzymes, leading to impaired metabolism and overall cellular function. The kidneys play a significant role in maintaining the pH balance necessary for optimal enzyme activity throughout the body.
2. Acid-Base Balance
By regulating the excretion of acids and bases, the kidneys help maintain the overall acid-base balance in the body. This balance is important for numerous physiological processes, including nerve function, muscle contraction, and oxygen transport.
3. Calcium Homeostasis
The kidneys also play a crucial role in maintaining calcium homeostasis. Calcium is a vital mineral involved in bone health, muscle function, nerve signaling, and blood clotting. The kidneys help regulate the blood levels of calcium by influencing its reabsorption and excretion.
FAQs
Q: What happens if the kidneys fail to regulate pH properly?
A: If the kidneys fail to regulate pH properly, it can lead to a condition called acidosis or alkalosis, depending on the imbalance. Acidosis occurs when the blood becomes too acidic, while alkalosis occurs when the blood becomes too alkaline. Severe acidosis or alkalosis can have serious health consequences and may require medical intervention.
Q: Can diet affect kidney regulation of pH?
A: Yes, diet can have an impact on kidney regulation of pH. Certain foods can increase the acidity or alkalinity of the blood, placing additional stress on the kidneys' pH-regulating mechanisms. It is important to maintain a balanced and healthy diet to support optimal kidney function.
Q: Can medications influence kidney regulation of pH?
A: Yes, certain medications can affect the kidney's ability to regulate pH. For example, diuretics can increase the excretion of bicarbonate ions, leading to acidosis. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional regarding any medications and their potential impact on kidney function.
Conclusion
The kidneys are vital organs in the body responsible for many functions, including the regulation of pH. By reabsorbing bicarbonate ions and excreting excess acids or bases, the kidneys help maintain the delicate acid-base balance necessary for optimal physiological function. Understanding the kidney's role in pH regulation is key to appreciating the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle and supporting kidney health.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only. It should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Please consult with a qualified healthcare provider for specific questions regarding your health.
Respiratory Mechanism For The Regulation Of PH || Acid Base Balance
 Image Source : www.youtube.com
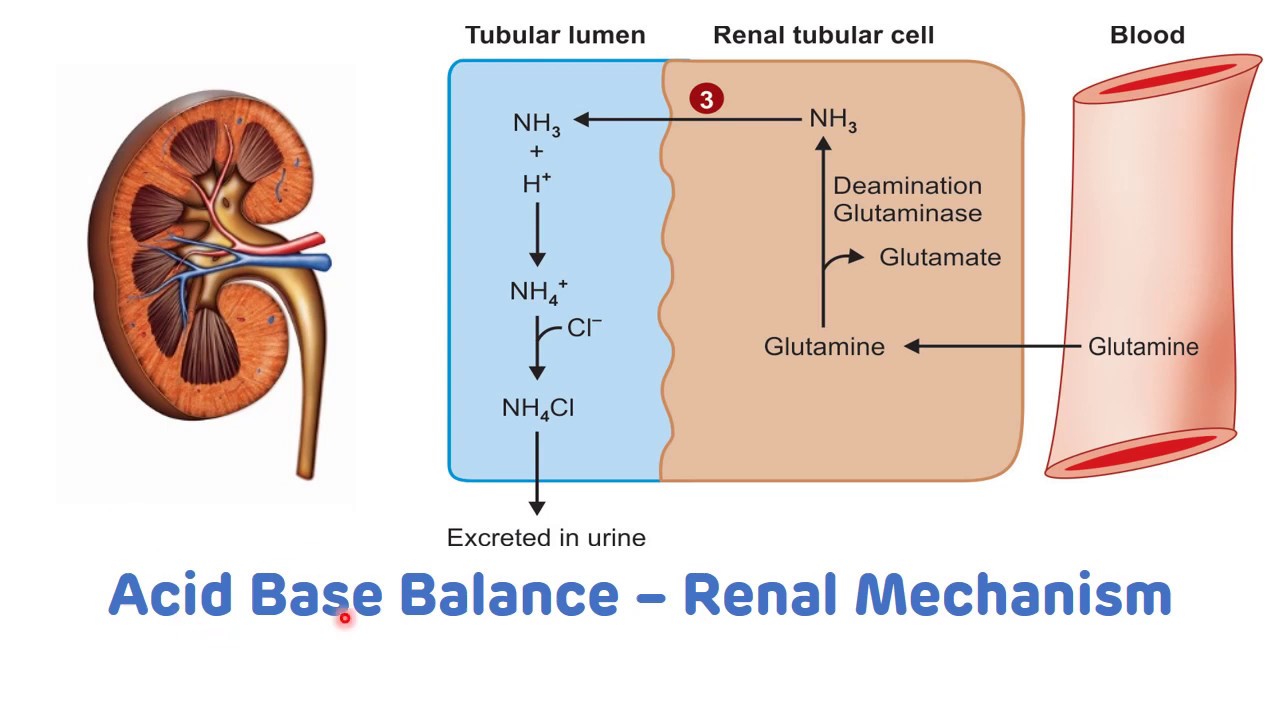
Image Source : www.youtube.com The Role Of The Kidney In Acid-base Balance | Osmosis
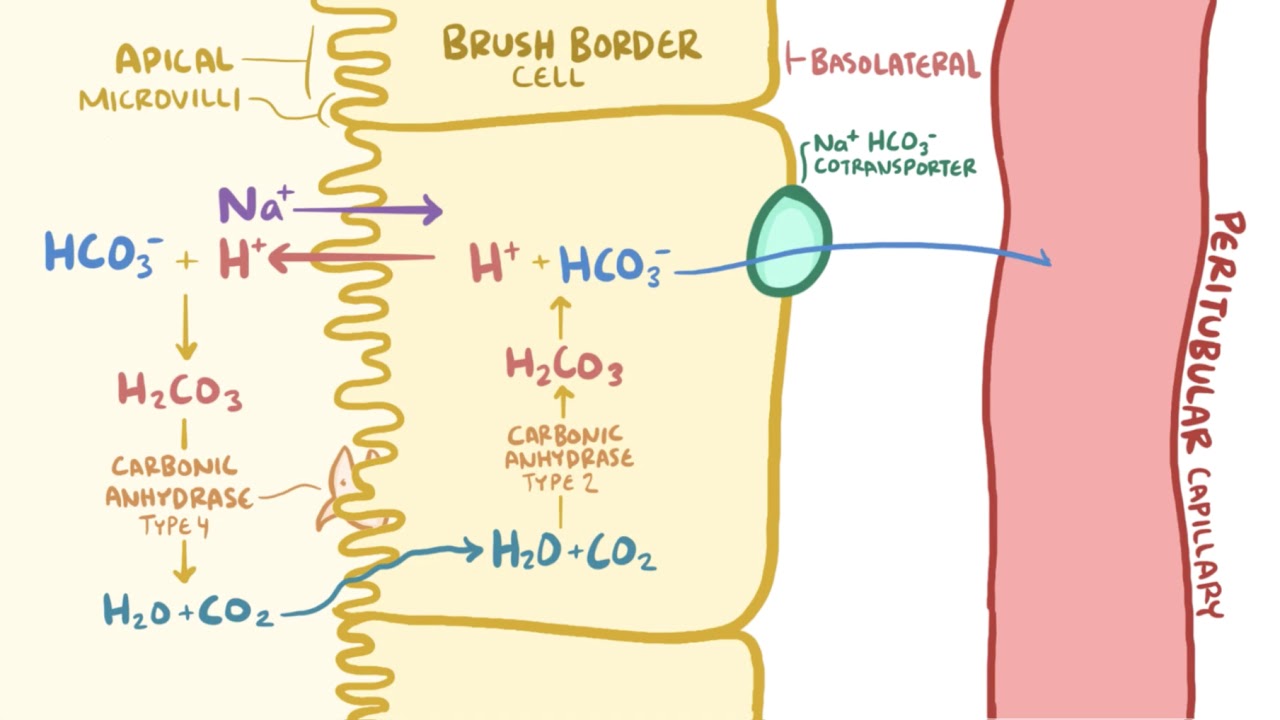 Image Source : www.osmosis.org
Image Source : www.osmosis.org acid base kidney balance role renal physiology osmosis
Acid-base Balance:- Part 1 - Introduction To The Acid-Base Balance
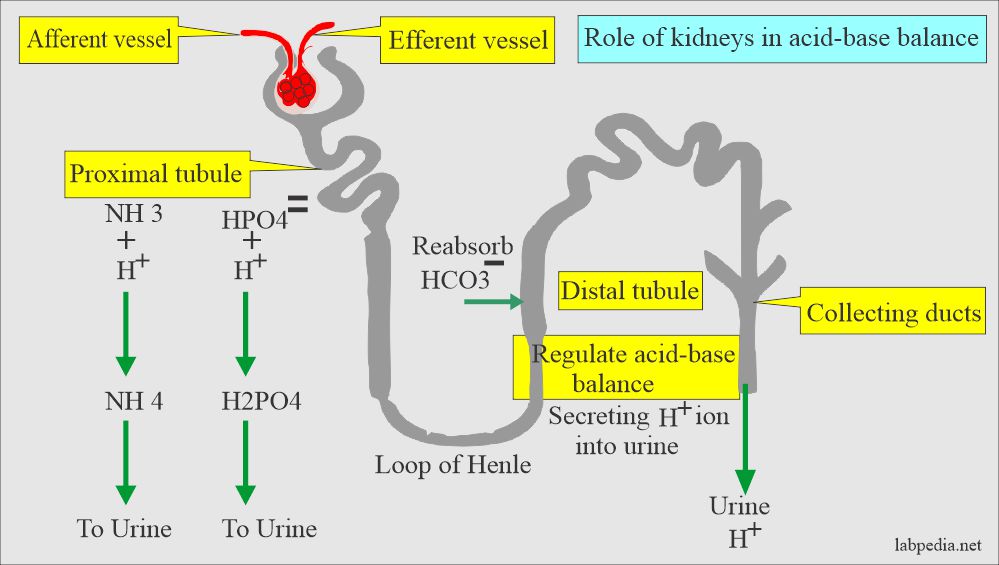 Image Source : labpedia.net
Image Source : labpedia.net kidneys acidosis kidney metabolic nh4 labpedia alkalosis hco3 nh3
The Regulation Of Ph By Cells Is Accomplished Primarily Through
 Image Source : micheal-has-pope.blogspot.com
Image Source : micheal-has-pope.blogspot.com Renal Mechanism For The Regulation Of PH || Acid Base Balance - YouTube
 Image Source : www.youtube.com
Image Source : www.youtube.com renal regulation
Renal Regulation Of PH - YouTube
 Image Source : www.youtube.com
Image Source : www.youtube.com ph regulation renal
Lec 9 Level 4-de (biological Buffer)
 Image Source : www.slideshare.net
Image Source : www.slideshare.net ph renal biological lec urine
PPT - Kidney Functions And Regulation PowerPoint Presentation, Free
 Image Source : www.slideserve.com
Image Source : www.slideserve.com kidney regulation functions ppt presentation kidneys blood balance water powerpoint slideserve slide1 maintain normal
Ph regulation renal. The role of the kidney in acid-base balance. The regulation of ph by cells is accomplished primarily through. Kidneys acidosis kidney metabolic nh4 labpedia alkalosis hco3 nh3. Acid-base balance:- part 1