Long Term Regulation Of Blood Pressure
The Long Term Regulation of Blood Pressure
Introduction
Blood pressure, the force exerted by the blood against the walls of the blood vessels, is a crucial aspect of maintaining overall health. Long-term regulation of blood pressure is essential for the proper functioning of the body, as elevated or low blood pressure levels can lead to various health complications. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of long-term blood pressure regulation, exploring the key mechanisms and factors that contribute to maintaining a healthy blood pressure level.
Factors Influencing Long-Term Blood Pressure Regulation
There are several factors that play a role in the long-term regulation of blood pressure. These factors work together to ensure that blood pressure remains within a normal range. Let's explore each of these factors in detail.
1. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS)

The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS) is a key player in the long-term regulation of blood pressure. It involves a series of processes that ultimately aim to increase or decrease blood pressure, depending on the body's needs. The system is initiated when the kidneys release an enzyme called renin in response to low blood pressure or low blood volume.
Renin acts on a protein known as angiotensinogen, which is produced in the liver, converting it into angiotensin I. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) then converts angiotensin I into angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor.
Angiotensin II causes blood vessels to constrict, narrowing their diameter and increasing blood pressure. Additionally, it stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adrenal glands, which promotes water and sodium reabsorption in the kidneys. This leads to an increase in blood volume and, consequently, an elevation in blood pressure.
2. Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
Proper fluid and electrolyte balance is crucial for maintaining long-term blood pressure regulation. The body's fluid volume and composition directly influence blood pressure levels. The kidneys play a vital role in maintaining this balance. They regulate the excretion and reabsorption of water and electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium.
When blood pressure drops, the kidneys respond by retaining sodium and excreting less water, leading to increased blood volume and elevated blood pressure. Conversely, when blood pressure is high, the kidneys excrete excess water and sodium, reducing blood volume and blood pressure.
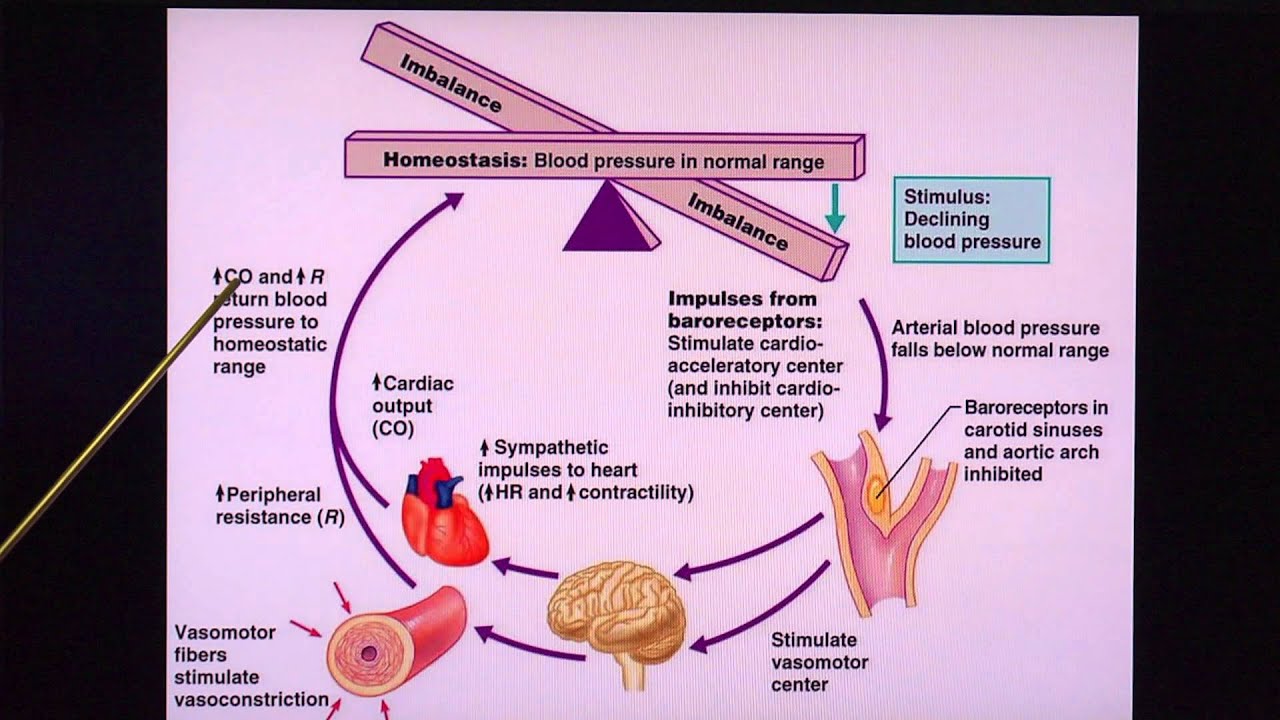
3. Hormonal Regulation
Various hormones contribute to the long-term regulation of blood pressure. One important hormone in this process is atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP), which is released by cells in the heart's atria when they are stretched due to increased blood volume.
ANP acts on the kidneys, promoting the excretion of sodium and water, thereby reducing blood volume and blood pressure. Another hormone involved in blood pressure regulation is antidiuretic hormone (ADH), also known as vasopressin. ADH acts on the kidneys, decreasing water excretion and increasing blood volume and pressure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How does exercise impact long-term blood pressure regulation?
A: Regular exercise has a positive impact on long-term blood pressure regulation. It strengthens the heart and promotes the dilation of blood vessels, leading to improved blood flow and lower blood pressure levels.
Q: What dietary factors influence blood pressure regulation?
A: A healthy diet plays a significant role in long-term blood pressure regulation. Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting sodium, saturated fats, and refined sugars can help maintain healthy blood pressure levels.
Q: Can stress affect long-term blood pressure regulation?
A: Yes, chronic stress can have a negative impact on blood pressure regulation. The body's stress response involves the release of stress hormones, such as adrenaline and cortisol, which can elevate blood pressure. It is important to manage stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and a healthy lifestyle.
In conclusion, the long-term regulation of blood pressure involves various intricate mechanisms, including the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System, fluid and electrolyte balance, and hormonal regulation. By understanding these factors, we can work towards maintaining optimal blood pressure levels and promoting overall cardiovascular health.
44 Blood Pressure Homeostasis Diagram - Wiring Diagram Source
 Image Source : iambeholder.blogspot.com
Image Source : iambeholder.blogspot.com Blood Vessels Pathology. (Subject 14) - презентация онлайн
term long regulation blood vessels ppt
Pin On Physiology
 Image Source : www.pinterest.com
Image Source : www.pinterest.com regulation physiology
PPT - Use The Video Clip: CH 19 - Anatomy Of The Blood Vessels For A
blood pressure term regulation long maintaining short flow mechanism control vessels vessel anatomy ch structure clip use review video
PPT - Peripheral Circulation And Regulation PowerPoint Presentation
regulation term pressure blood long peripheral circulation mechanism ppt powerpoint presentation
Pin On Medical
 Image Source : www.pinterest.cl
Image Source : www.pinterest.cl Blood Pressure Homeostasis
 Image Source : anatomycollection.z21.web.core.windows.net
Image Source : anatomycollection.z21.web.core.windows.net PPT - REGULATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE PowerPoint Presentation, Free
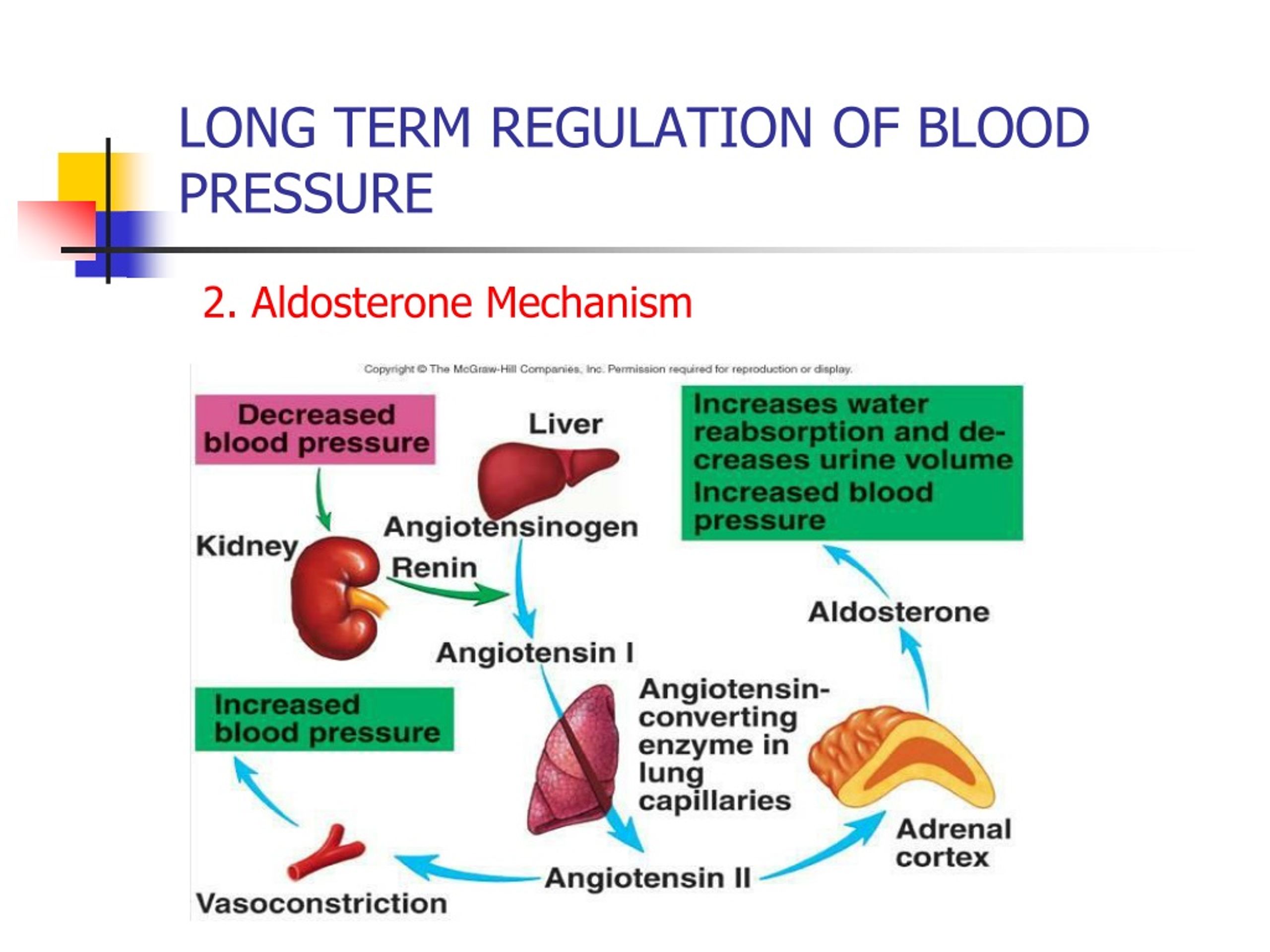 Image Source : www.slideserve.com
Image Source : www.slideserve.com blood pressure regulation term long mechanism ppt renal control body powerpoint presentation fluid
Regulation physiology. Regulation term pressure blood long peripheral circulation mechanism ppt powerpoint presentation. 44 blood pressure homeostasis diagram. Blood pressure term regulation long maintaining short flow mechanism control vessels vessel anatomy ch structure clip use review video. Blood vessels pathology. (subject 14)