Distress Tolerance Vs Emotional Regulation
Distress Tolerance Vs Emotional Regulation: Understanding the Key Differences
When it comes to managing our emotions, two concepts often come into play: distress tolerance and emotional regulation. While they both aim to help individuals cope with difficult emotions, they differ in their approach and purpose. In this article, we will explore the key differences between distress tolerance and emotional regulation and how they impact our emotional well-being.
1. Distress Tolerance: Accepting and Surviving the Unavoidable
Distress tolerance refers to one's ability to withstand and accept distressing emotions or situations without resorting to impulsive or unhealthy behaviors. It is about recognizing that certain circumstances cannot be changed or avoided, and instead of trying to control or eliminate the distress, focusing on developing skills to tolerate, survive, and even thrive in such situations.

Using the DIALECTICAL BEHAVIOR TRAINING approach, individuals can learn various distress tolerance skills to effectively manage their emotions. The acronym ACCEPTS, which stands for Activities, Contributing, Comparisons, Emotions, Pushing Away, Thoughts, and Sensations, provides a framework for developing healthy coping mechanisms.
1.1 Activities
Engaging in activities can be an effective way to distract yourself from distressing emotions. This can include hobbies, exercise, or other recreational pursuits that provide a sense of enjoyment and divert your attention from negative thoughts or feelings. By immersing yourself in pleasant activities, you can temporarily reduce distress and regain emotional stability.
1.2 Contributing
Contributing to others can boost your sense of self-worth and purpose, thereby helping you tolerate distress. Engaging in acts of kindness or volunteering not only helps distract you from your own distress but also gives you a sense of fulfillment and satisfaction. When you contribute to the well-being of others, you create positive connections and foster a sense of belonging in your community.
2. Emotional Regulation: Managing and Modulating Your Emotions
Emotional regulation, on the other hand, focuses on managing and modulating one's emotions in order to maintain emotional balance and stability. It involves recognizing and understanding your emotions, as well as implementing strategies to regulate and control them effectively. While distress tolerance emphasizes acceptance, emotional regulation emphasizes the ability to regulate your internal emotional state.
Emotional regulation skills can be learned and practiced to enhance our emotional well-being and improve our ability to navigate challenging situations. By developing these skills, individuals can effectively manage their emotions and avoid impulsive or destructive behaviors.
2.1 Identifying and Understanding Emotions
Before you can regulate your emotions, it is crucial to first identify and understand them. Emotional intelligence plays a key role in this process. By becoming aware of your emotions and their triggers, you can gain insight into your emotional responses and develop strategies to regulate them effectively. This self-awareness enables you to respond to emotions in a more informed and controlled manner.
2.2 Cognitive Reappraisal
Cognitive reappraisal involves reframing or reinterpreting a situation in order to change your emotional response to it. By challenging negative or irrational thoughts and replacing them with more positive or realistic ones, you can alter your emotional experience. This cognitive restructuring allows you to regulate your emotions by consciously shifting your perception of the situation.
3. The Benefits of Developing Distress Tolerance and Emotional Regulation
Both distress tolerance and emotional regulation skills are crucial for our emotional well-being and overall mental health. By developing these skills, we can experience a range of benefits, including:
- Reduced stress levels
- Improved emotional stability
- Enhanced personal relationships
- Better decision-making abilities
- Increased self-esteem and self-confidence
- Reduced risk of mental health disorders
Now that you understand the key differences between distress tolerance and emotional regulation, let's address some frequently asked questions to further clarify these concepts.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: Can distress tolerance and emotional regulation be learned?
A1: Absolutely! Distress tolerance and emotional regulation are skills that can be developed and improved through practice and dedication. With the right guidance and support, individuals can learn effective strategies to cope with distressing emotions and regulate their emotional responses.
Q2: Are distress tolerance and emotional regulation techniques interchangeable?
A2: While there may be some overlap between distress tolerance and emotional regulation techniques, they serve different purposes. Distress tolerance focuses on accepting and surviving unavoidable distress, while emotional regulation aims to manage and modulate one's internal emotional state. Both skills are valuable and complement each other in promoting emotional well-being.
Q3: How can I develop distress tolerance and emotional regulation skills?
A3: Developing distress tolerance and emotional regulation skills requires practice and consistency. Consider seeking therapy or counseling to learn specific techniques and strategies tailored to your needs. Engaging in self-help activities, such as reading books or participating in support groups, can also provide valuable insights and guidance on developing these skills.
In conclusion, distress tolerance and emotional regulation play crucial roles in our ability to cope with challenging emotions. By understanding the key differences between these concepts and actively developing these skills, we can navigate difficult situations with grace and improve our overall emotional well-being.
Distress Tolerance Skills Accepts Worksheet Distress - Image Result For
 Image Source : aninlopez.blogspot.com
Image Source : aninlopez.blogspot.com Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) Is A Skills-based Therapy Model
 Image Source : www.pinterest.com
Image Source : www.pinterest.com dbt therapy skills dialectical group behavior behaviour emotional regulation dialectal through change model distress tolerance life behavioral acceptance improve mindfulness
The Mediating Role Of Emotional Distress Tolerance In Relationship
tolerance anxiety discrepancy distress variables
Distraction (A.C.C.E.P.T.S.) - DIALECTICAL BEHAVIORAL TRAINING
 Image Source : www.pinterest.com
Image Source : www.pinterest.com tolerance dbt distraction accepts skill handout fear dialectical emotion counseling abandonment coronavirus behavior
Emotion Regulation Vs Distress Tolerance | The Wellbeing Doctor
 Image Source : thewellbeingdoctor.uk
Image Source : thewellbeingdoctor.uk emotion regulation tolerance distress
35 Emotional Regulation And Distress Tolerance Ideas | Coping Skills
 Image Source : www.pinterest.com
Image Source : www.pinterest.com regulation collect tolerance later emotional
Distress Tolerance Module – Sharing My Song
 Image Source : sharingmysong.com
Image Source : sharingmysong.com tolerance distress coping counseling behavioral mental emdr grounding wellbeing paz emotional therapeutic rationale greenwood
Emotion Regulation - DBT Self Help
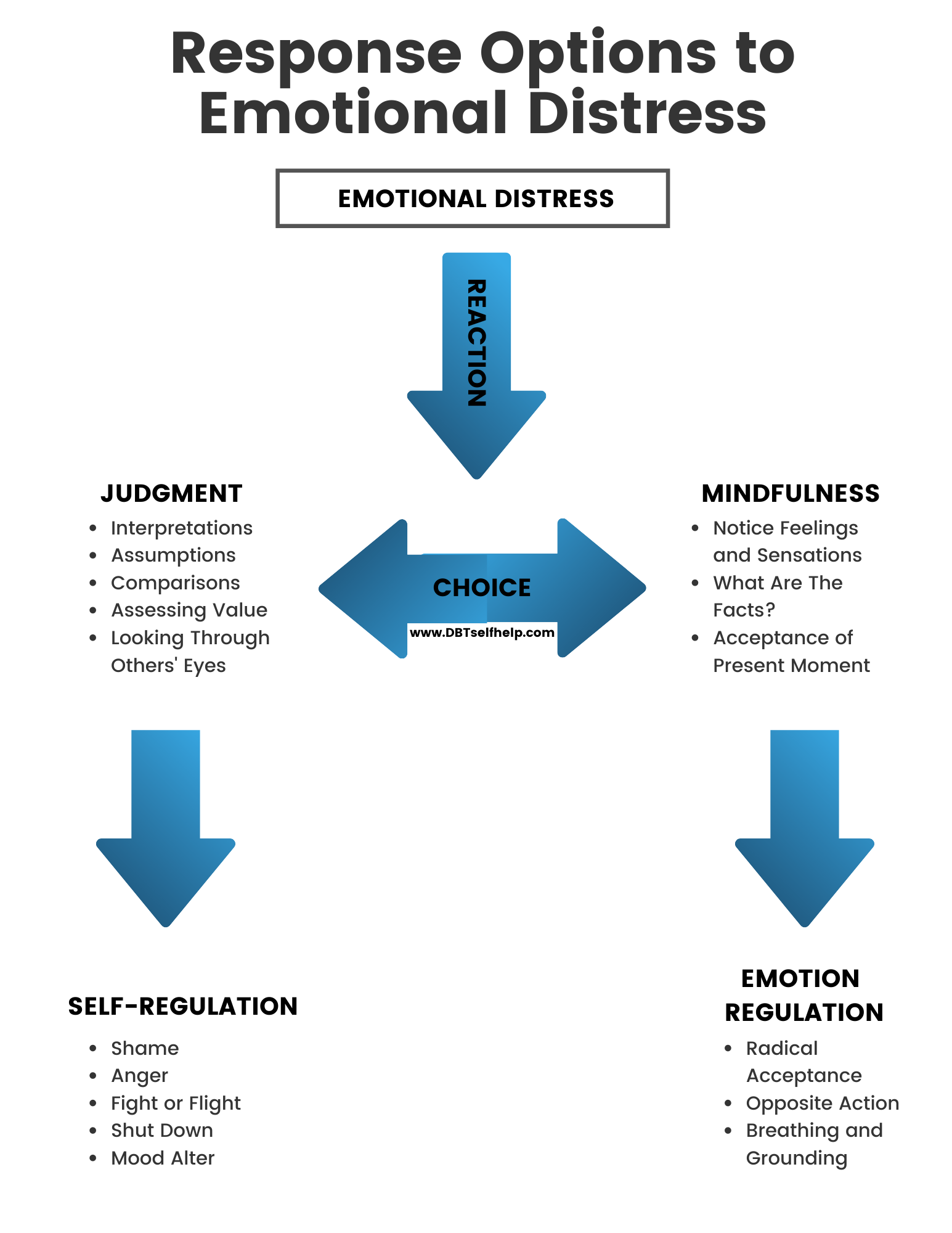 Image Source : dbtselfhelp.com
Image Source : dbtselfhelp.com Distress tolerance skills accepts worksheet distress. The mediating role of emotional distress tolerance in relationship. Tolerance anxiety discrepancy distress variables. Distress tolerance module – sharing my song. Dialectical behavior therapy (dbt) is a skills-based therapy model