What Is Negative Regulation
Negative regulation is a crucial aspect of biological processes, ensuring that certain cellular functions are inhibited or reduced. By understanding how negative regulation works, scientists can gain insights into various cellular mechanisms and develop treatments for a range of diseases. In this article, we will explore the concept of negative regulation, its importance, and its impact on gene regulation. So, let's dive in! Subheading 1: Understanding Negative Regulation Negative regulation refers to the process by which a biological pathway or function is inhibited or suppressed, leading to a decrease in activity. This is achieved through a variety of mechanisms that act as checks and balances within the cell, ensuring that certain functions occur within specific limits. Negative regulation plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis, controlling growth and development, and preventing excessive cellular damage. H2: Negative Regulation of the NF-κB Pathway by USP18 The NF-κB pathway is a vital signaling pathway involved in regulating immune responses, inflammation, and cell survival. Negative regulation of this pathway is essential to prevent uncontrolled immune responses, which can lead to chronic inflammation and autoimmune diseases. USP18 (ubiquitin-specific protease 18) is a protein that plays a key role in negatively regulating the NF-κB pathway.  (Image source: ResearchGate) USP18 interacts with various components of the NF-κB pathway, inhibiting its activation. It prevents the degradation of IκB (inhibitor of NF-κB) and blocks the translocation of active NF-κB to the nucleus, effectively suppressing the inflammatory response. Understanding the negative regulation of the NF-κB pathway by USP18 provides valuable insights into potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. H2: Negative Gene Regulation in Action Negative gene regulation refers to the processes through which gene expression is inhibited or reduced. It plays a crucial role in cellular development, differentiation, and response to external stimuli. Understanding negative gene regulation is essential for comprehending various biological mechanisms and their implications in health and disease. 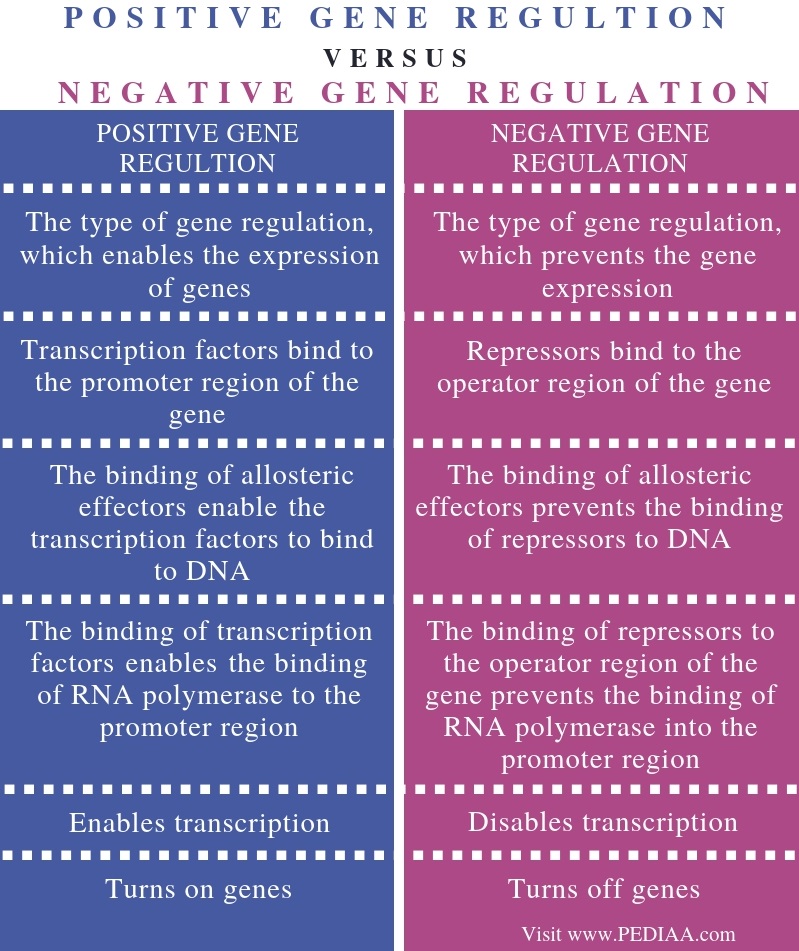 (Image source: Pediaa) Negative gene regulation can occur at various stages of gene expression, including transcription, mRNA processing, translation, and post-translational modifications. It involves the binding of repressor proteins or regulatory RNAs to specific regions of DNA or RNA, preventing the initiation or progression of gene expression. This regulation ensures that genes are only expressed when needed, preventing unnecessary protein synthesis and conserving cellular resources. H2: Negative Regulation of Cellular Growth Cell growth and proliferation are tightly regulated processes in multicellular organisms. Negative regulation mechanisms are essential for maintaining proper control over cell division, preventing uncontrolled proliferation, and the development of tumors. Failure in these regulatory mechanisms can lead to cancer and other diseases related to abnormal cell growth. One of the well-known negative regulators of cell growth is the tumor suppressor protein p53. Mutations or dysregulation of p53 can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and an increased risk of cancer. p53 acts as a transcription factor, activating genes that inhibit cell division or induce cell death (apoptosis) in response to DNA damage or other cellular stresses. Its role as a "guardian of the genome" highlights the importance of negative regulation in preventing the proliferation of damaged or mutated cells. H2: Negative Regulation FAQs FAQ 1: What is the difference between negative and positive regulation? Negative regulation involves the inhibition or suppression of a biological function, pathway, or gene expression. On the other hand, positive regulation refers to the activation or enhancement of a function, pathway, or gene expression. FAQ 2: How do cells ensure the right balance between positive and negative regulation? Cells maintain the balance between positive and negative regulation through various feedback mechanisms. These mechanisms sense the cellular environment and adjust the levels of positive and negative regulators accordingly to achieve homeostasis. FAQ 3: Can negative regulation be targeted for therapeutic interventions? Yes, understanding negative regulation mechanisms opens avenues for therapeutic interventions. By manipulating negative regulators, scientists can potentially develop treatments for diseases involving uncontrolled cellular processes or aberrant gene expression. In conclusion, negative regulation is a critical aspect of cellular processes, ensuring proper control over various functions. From the negative regulation of the NF-κB pathway by USP18 to the suppression of gene expression, these regulatory mechanisms play vital roles in maintaining homeostasis, preventing excessive cellular growth, and protecting against diseases. By unraveling the intricacies of negative regulation, scientists pave the way for future advancements in understanding and treating a wide range of conditions. 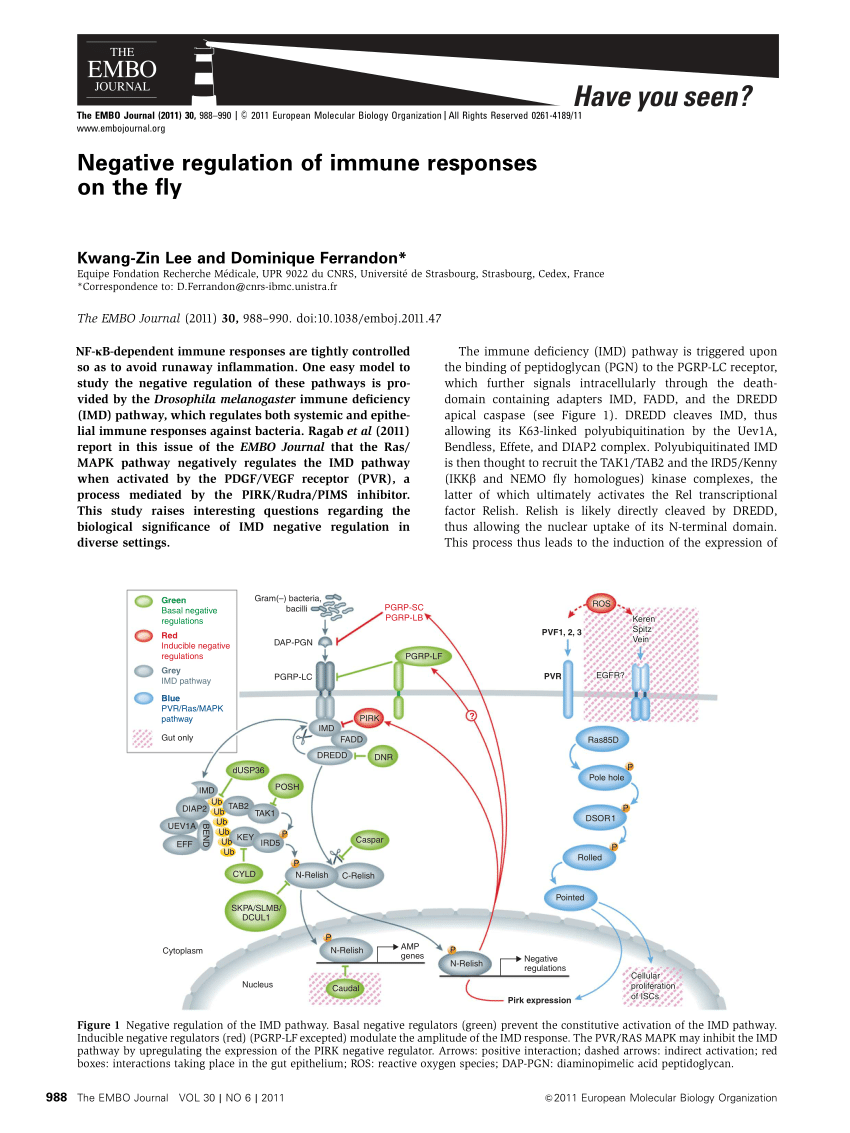 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net  Image Source : pediaa.com
Image Source : pediaa.com 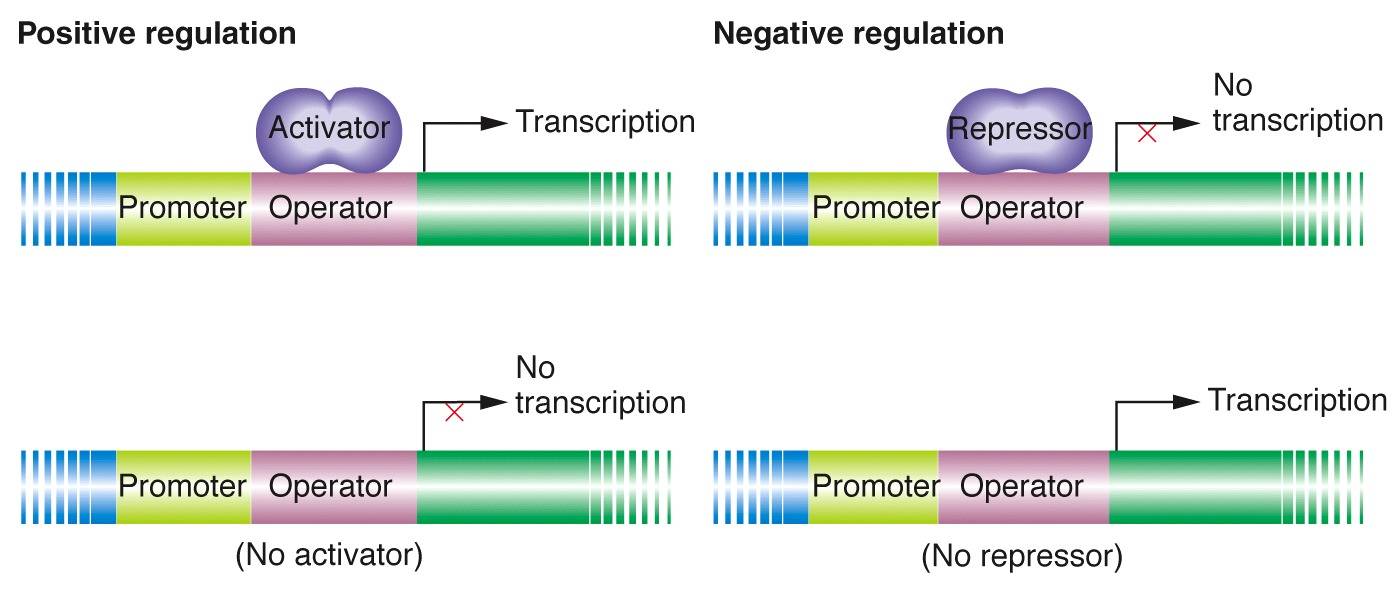 Image Source : www.mun.ca
Image Source : www.mun.ca  Image Source : www.pinterest.com
Image Source : www.pinterest.com  Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net  Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net  Image Source : www.differencebetween.com
Image Source : www.differencebetween.com 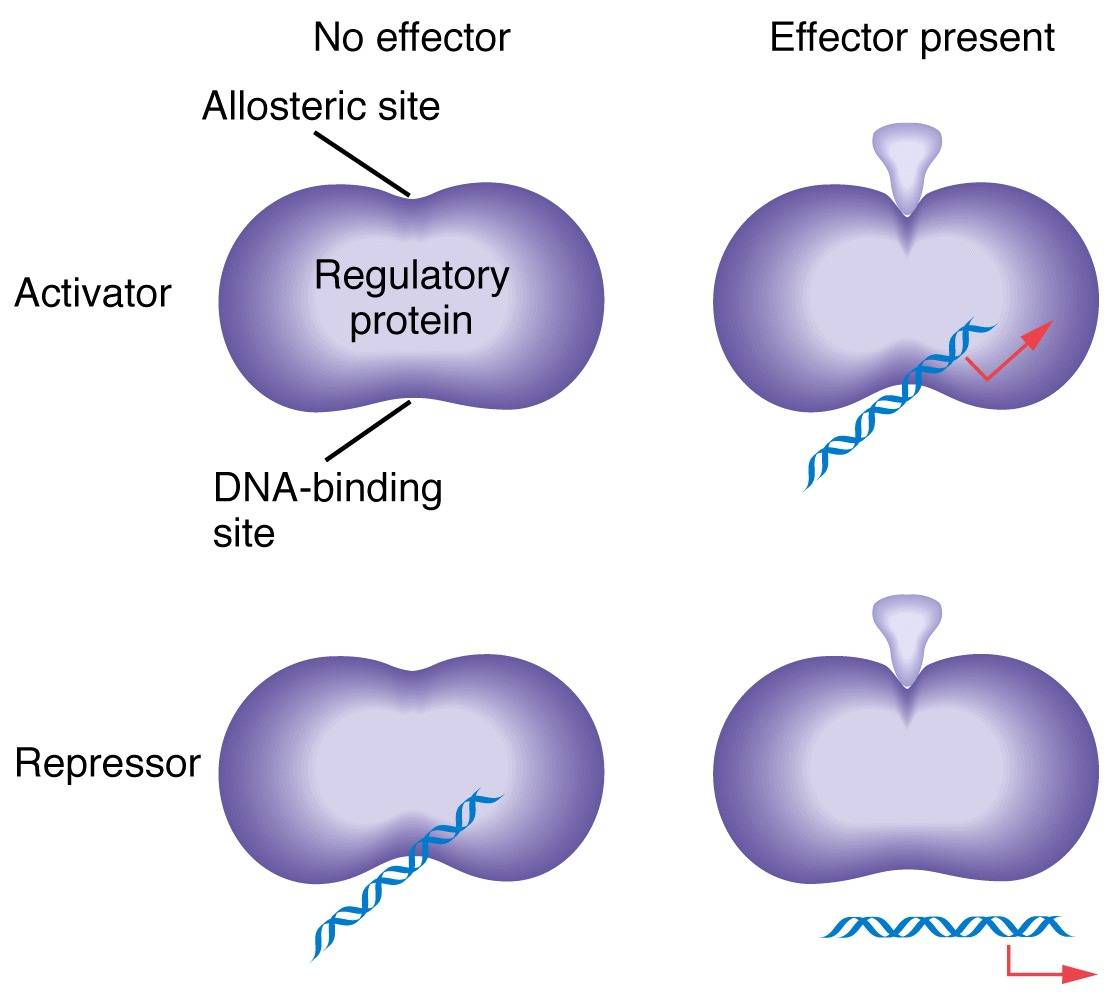 Image Source : www.mun.ca
Image Source : www.mun.ca
(PDF) Negative Regulation Of Immune Responses On The Fly
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net negative regulation responses immune fly
What Is The Difference Between Positive And Negative Gene Regulation
 Image Source : pediaa.com
Image Source : pediaa.com positive regulation gene negative difference between pediaa
Positive And Negative Regulation
 Image Source : www.mun.ca
Image Source : www.mun.ca biology regulation regulatory
Negative & Positive Gene Regulation | Relatable, Transcription, Map
 Image Source : www.pinterest.com
Image Source : www.pinterest.com gene transcription negative positive regulation eukaryotic regulatory bind binding control prokaryotes genes rna factors figure dogma show sites examples polymerase
Working Model Of The Negative Regulation Of The NF-κB Pathway By USP18
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net Negative Regulation Of Autophagy By TCTP. In The Initiation Step Of
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net autophagy tctp initiation ampk
Difference Between Positive And Negative Gene Regulation | Compare The
 Image Source : www.differencebetween.com
Image Source : www.differencebetween.com regulation gene between positif regulasi negatif peraturan
Positive And Negative Regulation
 Image Source : www.mun.ca
Image Source : www.mun.ca allosteric negative molecules
Negative regulation responses immune fly. (pdf) negative regulation of immune responses on the fly. Autophagy tctp initiation ampk. Biology regulation regulatory. Allosteric negative molecules