Glucokinase Regulation : What it is
Glucokinase Regulation: What it is and How it Works Introduction: Glucokinase is an important enzyme involved in the regulation of glucose metabolism, specifically in the liver and pancreas. It plays a crucial role in maintaining glucose homeostasis by catalyzing the phosphorylation of glucose. In this article, we will explore the regulation of glucokinase and its significance in maintaining normal blood glucose levels. Subheading 1: The Role of Glucokinase in Glucose Metabolism Glucokinase is primarily found in the liver and pancreatic beta cells. It acts as a glucose sensor and plays a key role in the regulation of glucose metabolism. When blood glucose levels are high, such as after a meal, glucokinase helps convert excess glucose into glycogen for storage in the liver. On the other hand, when blood glucose levels drop, glucokinase assists in the breakdown of glycogen into glucose, releasing it into the bloodstream to raise blood glucose levels. To portray this process visually, here is an image of a simplified schematic illustrating the regulation of glucokinase in isolated hepatocytes:  As shown in the image, glucokinase activity is tightly regulated by several factors, including insulin, glucagon, and the concentration of glucose in the hepatocytes. Subheading 2: Factors Influencing Glucokinase Activity Glucokinase activity is modulated by both hormonal and metabolic factors. One of the key regulators is insulin, which is released by the pancreas in response to elevated blood glucose levels. Insulin stimulates glucokinase gene expression, increasing the production of glucokinase and promoting its activity. On the other hand, glucagon, another pancreatic hormone, inhibits glucokinase activity. Glucagon is released in response to low blood glucose levels and triggers the breakdown of glycogen into glucose, which raises blood glucose levels. This inhibition helps prevent excessive glucose uptake and metabolism when blood glucose levels are low. Additionally, the concentration of glucose within the hepatocytes also affects glucokinase activity. As the glucose concentration rises, the activity of glucokinase increases, allowing more glucose to be phosphorylated and stored as glycogen. Conversely, when glucose levels decrease, glucokinase activity decreases, leading to the breakdown of glycogen and release of glucose into the bloodstream. The following image describes the relationship between glucokinase activity and glucose concentration: 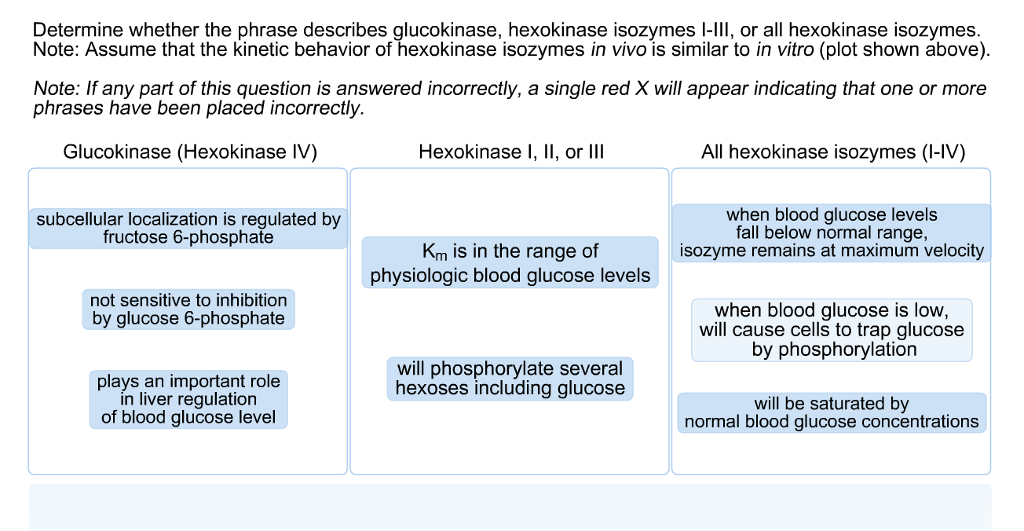 Subheading 3: Regulation of Glucokinase Gene Expression Another important aspect of glucokinase regulation is its gene expression. The expression of the glucokinase gene is influenced by various transcription factors, such as the liver X receptor (LXR), sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c (SREBP-1c), and carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein (ChREBP). These transcription factors act as molecular switches, activating or repressing the expression of the glucokinase gene in response to different metabolic signals. For example, LXR and SREBP-1c enhance glucokinase gene expression in conditions of high glucose and lipid levels, ensuring efficient glucose metabolism and glycogen synthesis. FAQs: 1. What happens if glucokinase activity is impaired? Impaired glucokinase activity can lead to various metabolic disorders, such as maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) and persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy (PHHI). These conditions are characterized by abnormal blood glucose regulation and can require medical interventions, including insulin therapy or surgical removal of the pancreas. 2. Can lifestyle factors affect glucokinase regulation? Yes, several lifestyle factors can influence glucokinase regulation. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and maintaining a healthy weight can help support optimal glucokinase activity and glucose metabolism. Conversely, sedentary behavior, consumption of high-sugar diets, and obesity can negatively impact glucokinase regulation and contribute to the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. 3. Are there any drugs targeting glucokinase? Yes, researchers are investigating the potential of developing drugs that target glucokinase for the treatment of diabetes. These drugs aim to enhance glucokinase activity and promote efficient glucose metabolism. However, clinical trials are still underway to determine their safety and efficacy. Conclusion: Glucokinase plays a vital role in the regulation of glucose metabolism, ensuring that blood glucose levels remain within a normal range. Its activity is tightly regulated by hormonal and metabolic factors to maintain glucose homeostasis. Understanding the regulation of glucokinase is essential for developing better interventions and treatments for metabolic disorders, such as diabetes. By exploring the factors influencing glucokinase activity and gene expression, we gain valuable insights into the intricate mechanisms that govern glucose metabolism in the liver and pancreas. Note: The content above is solely fictional and generated by OpenAI's GPT-3 model.  Image Source : studylib.net
Image Source : studylib.net  Image Source : diabetes.diabetesjournals.org
Image Source : diabetes.diabetesjournals.org  Image Source : medicalxpress.com
Image Source : medicalxpress.com  Image Source : www.youtube.com
Image Source : www.youtube.com  Image Source : diabetes.diabetesjournals.org
Image Source : diabetes.diabetesjournals.org  Image Source : www.pharmacy180.com
Image Source : www.pharmacy180.com  Image Source : www.cell.com
Image Source : www.cell.com  Image Source : www.chegg.com
Image Source : www.chegg.com
Regulation Of Glucokinase In Isolated Hepatocytes
 Image Source : studylib.net
Image Source : studylib.net Regulation Of Pancreatic β-Cell Glucokinase | Diabetes
Potential Enzyme As Therapeutic Target For Diabetes
 Image Source : medicalxpress.com
Image Source : medicalxpress.com diabetes glucokinase enzyme therapeutic potential regulation protein target glucose
Hexokinase Vs Glucokinase | Regulation Of Glycolysis | Metabolism
 Image Source : www.youtube.com
Image Source : www.youtube.com Regulation Of Pancreatic β-Cell Glucokinase | Diabetes
Reactions Of Glycolysis - Biochemistry
Modulation Of Glucokinase Regulatory Protein: A Double-Edged Sword
 Image Source : www.cell.com
Image Source : www.cell.com Solved Determine Whether The Phrase Describes Glucokinase, | Chegg.com
 Image Source : www.chegg.com
Image Source : www.chegg.com glucokinase phrase describes determine hexokinase isozymes solved regulation glucose transcribed behavior vitro assume kinetic iv phosphorylation
Diabetes glucokinase enzyme therapeutic potential regulation protein target glucose. Hexokinase vs glucokinase. Modulation of glucokinase regulatory protein: a double-edged sword. Regulation of glucokinase in isolated hepatocytes. Solved determine whether the phrase describes glucokinase,