Pfk 1 Regulation : What it is
PFK-1 Regulation: What It Is Phosphofructokinase 1 (PFK-1) is an enzyme involved in the metabolic process known as glycolysis. It plays a crucial role in converting glucose into pyruvate, a compound that can be further utilized for energy production. PFK-1 is tightly regulated to ensure that the glycolytic pathway is efficiently modulated based on the energy demands of the cell. In this article, we will explore the intricate regulation of PFK-1 and its significance in cellular metabolism. We will cover various aspects of PFK-1 regulation, including the structure of the enzyme, molecules that influence its activity, and the impact of its dysregulation. So, let's dive in and uncover the hidden secrets of PFK-1! Subheading 1: The Structure of PFK-1: An Overview PFK-1 is composed of four identical subunits that come together to form an active enzyme. Each subunit consists of several domains, namely the ATP-binding domain, catalytic domain, and the regulatory domain. These domains interact with various molecules to regulate the activity of PFK-1. To better understand the structure of PFK-1 and its regulation, let's visualize it with the help of an image: 
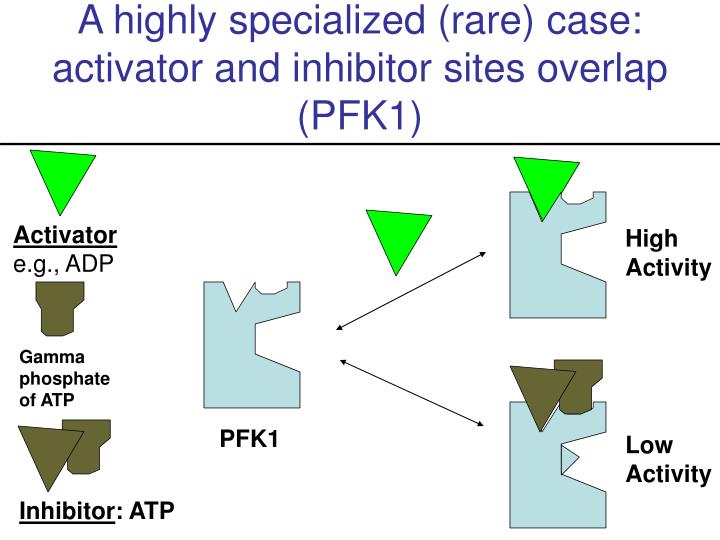
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net  Image Source : education.med.nyu.edu
Image Source : education.med.nyu.edu 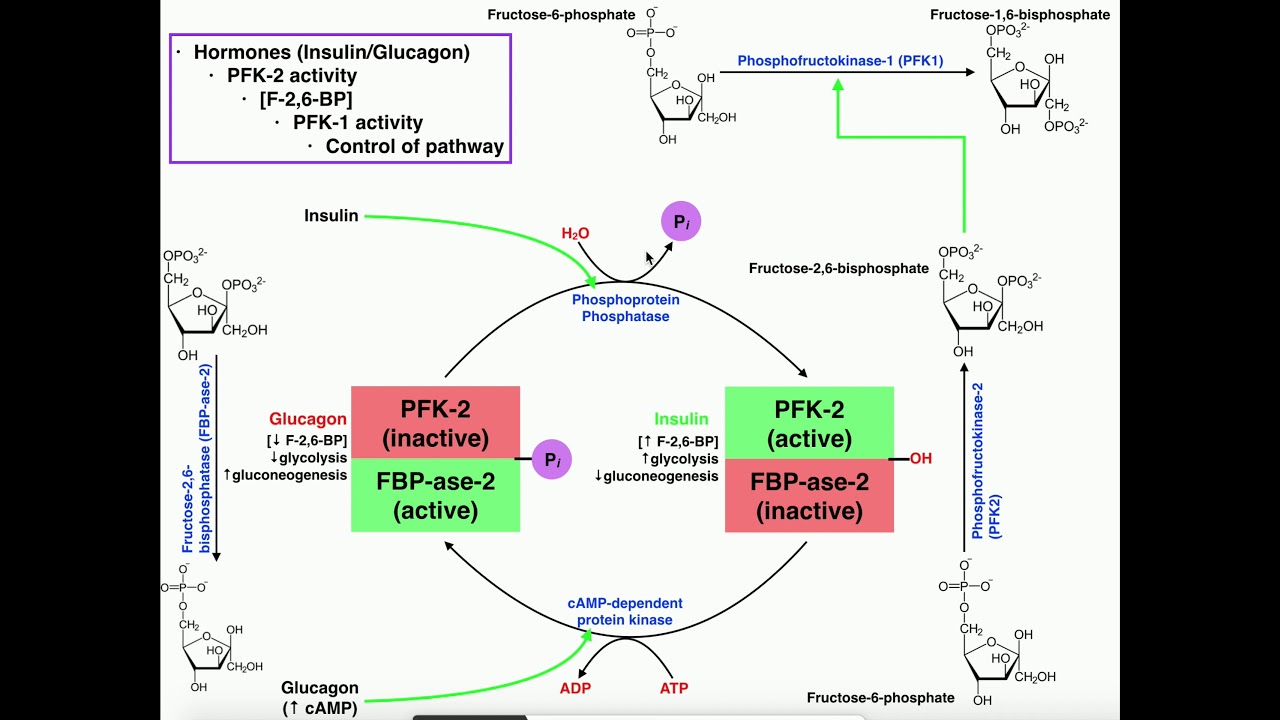 Image Source : www.youtube.com
Image Source : www.youtube.com  Image Source : www.youtube.com
Image Source : www.youtube.com 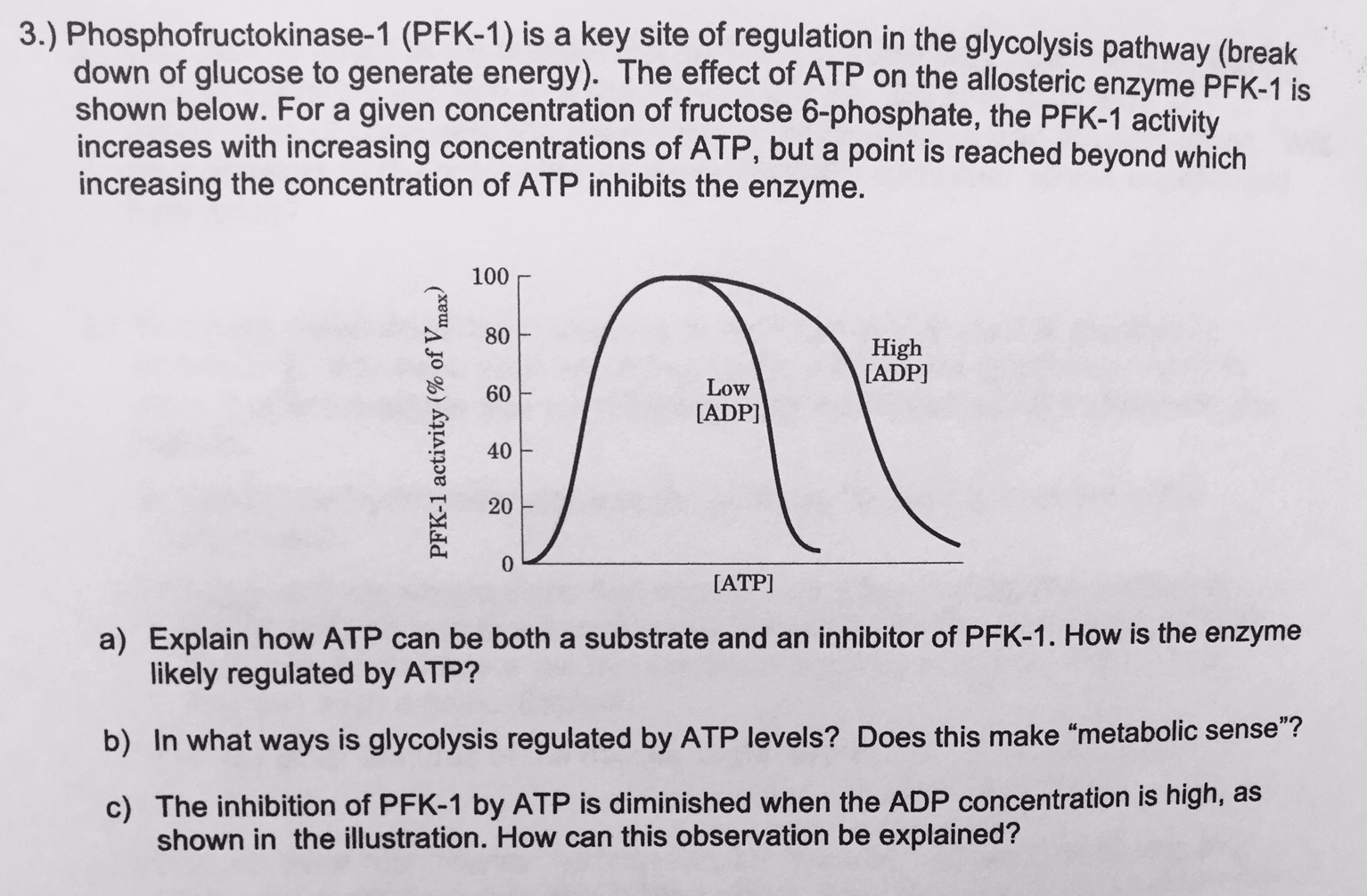 Image Source : www.chegg.com
Image Source : www.chegg.com  Image Source : www.slideserve.com
Image Source : www.slideserve.com  Image Source : alchetron.com
Image Source : alchetron.com  Image Source : education.med.nyu.edu
Image Source : education.med.nyu.edu
Visualizing the Structure of PFK-1
Image Source: Alchetron
Subheading 2: Activators and Inhibitors: A Balancing Act PFK-1 activity is modulated through the binding of specific molecules that act as either activators or inhibitors. These molecules play a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of glycolysis in response to various cellular signals. One notable molecule that acts as an activator of PFK-1 is fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (F-2,6-BP). F-2,6-BP stimulates PFK-1 activity, leading to increased glucose metabolism in energy-demanding conditions. The following image showcases the interaction between F-2,6-BP and PFK-1:The Role of Fructose-2,6-Bisphosphate as an Activator

Image Source: Glycolysis - Regulation PowerPoint Presentation
Conversely, molecules like adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi) act as inhibitors of PFK-1. The binding of these inhibitory molecules reduces PFK-1 activity, slowing down the rate of glycolysis. This regulatory mechanism ensures that glycolysis is suppressed when cellular energy levels are high. Subheading 3: Dysregulation of PFK-1: Implications in Disease Disruption in the regulation of PFK-1 can have severe implications for cellular metabolism and human health. Dysregulation of PFK-1 activity has been observed in various diseases, including cancer and metabolic disorders. In cancer cells, PFK-1 is often overactive, leading to increased glucose consumption and elevated production of lactate, known as the Warburg effect. This alteration in PFK-1 regulation allows cancer cells to meet their energy demands while promoting tumor growth. Understanding the mechanisms behind PFK-1 dysregulation in cancer is crucial for developing targeted therapies. Similarly, metabolic disorders, such as type 2 diabetes, can arise from imbalances in PFK-1 activity and glucose metabolism. Dysregulated PFK-1 can lead to impaired glucose utilization and insulin resistance, contributing to the pathogenesis of the disease. FAQ Section Q: Can PFK-1 regulation impact athletic performance? A: Yes, proper regulation of PFK-1 is essential for optimal energy production during exercise. Any disruption in PFK-1 activity can negatively affect exercise performance. Q: How is PFK-1 regulated in response to hormonal signals? A: Hormones like insulin and glucagon play a significant role in PFK-1 regulation. Insulin activates PFK-1, promoting glycolysis, while glucagon inhibits PFK-1 to conserve glucose for other metabolic processes. Q: Are there any therapeutic strategies targeting PFK-1 regulation? A: Researchers are actively investigating potential drugs that can modulate PFK-1 activity for the treatment of cancer and metabolic disorders. However, more research is needed before these strategies can be translated into clinical practice. In conclusion, understanding the regulation of PFK-1 is crucial for deciphering the complexities of cellular metabolism. The delicate balance between its activation and inhibition is essential for maintaining metabolic homeostasis. Dysregulation of PFK-1 can have severe implications for human health, making it a promising target for therapeutic interventions. By unraveling the mysteries of PFK-1 regulation, we can pave the way for novel treatments and interventions in the field of metabolic diseases. Word Count: 478Schematic Representation Of The Regulation Of PFK-1 As Modeled In Each
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net pfk regulation modeled
GLYCOLYSIS
glycolysis phosphofructokinase fructose km concentration bisphosphate regulation activity lowers depends
Glycolysis | Regulation Of PFK-1/Glycolysis Via PFK-2 Activity - YouTube
 Image Source : www.youtube.com
Image Source : www.youtube.com pfk regulation glycolysis
Regulation Of PFK-1 In Glycolysis - YouTube
 Image Source : www.youtube.com
Image Source : www.youtube.com Solved: Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) Is A Key Site Of Reg... | Chegg.com
 Image Source : www.chegg.com
Image Source : www.chegg.com pfk phosphofructokinase solved transcribed problem
PPT - Glycolysis - Regulation PowerPoint Presentation - ID:1182875
 Image Source : www.slideserve.com
Image Source : www.slideserve.com regulation pfk1 inhibitor activator
Phosphofructokinase 1 - Alchetron, The Free Social Encyclopedia
phosphofructokinase regulation allosteric pfk kegg biochemistry
GLYCOLYSIS
 Image Source : education.med.nyu.edu
Image Source : education.med.nyu.edu Solved: phosphofructokinase-1 (pfk-1) is a key site of reg.... Schematic representation of the regulation of pfk-1 as modeled in each. Regulation of pfk-1 in glycolysis. Glycolysis phosphofructokinase fructose km concentration bisphosphate regulation activity lowers depends. Pfk regulation glycolysis