Extrinsic Regulation: What It Is and How It Affects Our Body Introduction: In the fascinating field of exercise physiology, our body constantly adapts to various stimuli to maintain homeostasis. One crucial aspect of this adaptation is the extrinsic regulation of blood flow and blood pressure. This intricate mechanism allows our body to respond to different demands, such as during exercise or changes in the external environment. In this article, we will dive deeper into the concept of extrinsic regulation, exploring its significance, mechanisms, and impact on our overall well-being. 1. The Basics of Extrinsic Regulation: Extrinsic regulation refers to the control of bodily functions that are initiated and regulated by external factors, primarily involving the autonomic nervous system and endocrine system. These systems work together to ensure our body responds appropriately to changes in environmental conditions, maintaining equilibrium and supporting optimal physiological function. 1.1 The Autonomic Nervous System: At the core of extrinsic regulation lies the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which is responsible for regulating vital processes that occur involuntarily. The ANS consists of two main branches: the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS), often referred to as the "fight-or-flight" and "rest-and-digest" systems, respectively. 1.2 The Endocrine System: The endocrine system works in tandem with the autonomic nervous system to regulate bodily functions. It accomplishes this through the release of hormones, which act as chemical messengers, traveling through the bloodstream to target specific organs or tissues. Hormones play a crucial role in controlling blood flow, blood pressure, and other physiological responses affected by extrinsic regulation. 2. The Role of Extrinsic Regulation in Exercise Physiology: Exercise physiology is centered around understanding how our body adapts to the stress imposed during physical activity. Extrinsic regulation plays a significant role in maintaining optimal blood flow and blood pressure levels during exercise, ensuring that our muscles receive an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients. 2.1 Keeping Blood Flow in Check: During exercise, increased blood flow to the working muscles is essential for their proper functioning and energy production. Extrinsic regulation ensures that the blood vessels in the muscles dilate, optimizing the delivery of oxygen and nutrients while removing waste products such as carbon dioxide. This process is regulated by the sympathetic nervous system, which releases neurotransmitters and hormones that cause vasodilation. 2.2 Maintaining Blood Pressure: Extrinsic regulation is also responsible for adjusting blood pressure levels during physical activity. The sympathetic nervous system stimulates the release of epinephrine and norepinephrine, which increase heart rate and contractility, leading to an elevation in blood pressure. This response ensures that our muscles receive adequate blood supply and oxygenation during exercise. 2.3 Temperature Regulation: Extrinsic regulation plays a crucial role in maintaining body temperature during exercise. As our muscles generate heat, blood vessels near the skin dilate, allowing the release of excess heat through sweating and heat exchange with the environment. This process is orchestrated by the sympathetic nervous system and is essential for preventing overheating during physical activity. 3. Impact of Extrinsic Regulation on Health and Performance: Extrinsic regulation not only affects our body during exercise but also has a profound impact on our overall health and performance. Let's explore some key aspects in more detail: 3.1 Cardiovascular Health: The extrinsic regulation of blood flow and blood pressure is vital for maintaining cardiovascular health. Regular exercise and physical activity help optimize this regulation, improving heart function, reducing the risk of hypertension, and supporting healthy blood vessel function. By promoting efficient circulation, extrinsic regulation contributes to a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases in the long term. 3.2 Implications for Sports Performance: In the realm of sports performance, an optimal extrinsic regulation response is crucial. Athletes often aim to enhance their body's ability to regulate blood flow and blood pressure during exercise, as it can directly impact their endurance, stamina, and overall performance. Understanding and training this regulation can lead to improved athletic achievements and reduced fatigue during intense physical activity. 3.3 Metabolic Control: Extrinsic regulation is intricately linked with metabolic control. During exercise, the body relies on the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to fuel energy production. By fine-tuning blood flow and blood pressure, extrinsic regulation ensures the efficient supply of these essential resources, supporting optimal metabolic processes. Therefore, it is vital for individuals aiming to manage their weight, enhance muscle growth, or regulate hormonal imbalances. 4. FAQs: 4.1 How can I improve my body's extrinsic regulation response? There are several ways to enhance your body's response to extrinsic regulation. Regular exercise, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and reducing stress levels can all contribute to a more efficient autonomic nervous system and endocrine system function. 4.2 Can medications influence extrinsic regulation? In certain cases, medications can affect extrinsic regulation. Individuals on medications such as beta-blockers or vasodilators may experience altered blood flow and blood pressure responses during exercise. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional regarding any medications you are taking and their potential impact on extrinsic regulation. 4.3 Are there exercises specifically targeted at improving extrinsic regulation? While there are no exercises explicitly designed to improve extrinsic regulation, engaging in various forms of physical activity can enhance autonomic nervous system function. Cardiovascular exercises, such as running or cycling, and stress-reducing activities like yoga or meditation, can indirectly support optimal extrinsic regulation responses. Conclusion: Extrinsic regulation is a remarkable mechanism that enables our body to respond to external factors and maintain homeostasis. Through the coordination of the autonomic nervous system and endocrine system, our body adapts to changes in blood flow, blood pressure, and other vital functions during exercise. Understanding the significance of extrinsic regulation expands our knowledge of exercise physiology and its impact on overall health and performance. By optimizing extrinsic regulation through exercise, healthy lifestyle choices, and stress reduction techniques, we can harness its potential benefits and support our well-being.
A) Extrinsic Regulation Of Stem Cell Fate. B) The Use Of Material
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net regulation fate extrinsic scaffolds chemical
PPT - Cardiac Output, Blood Flow, And Blood Pressure PowerPoint
 Image Source : www.slideserve.com
Image Source : www.slideserve.com blood flow extrinsic pressure regulation cardiac output resistance peripheral total determines
Exercise Physiology
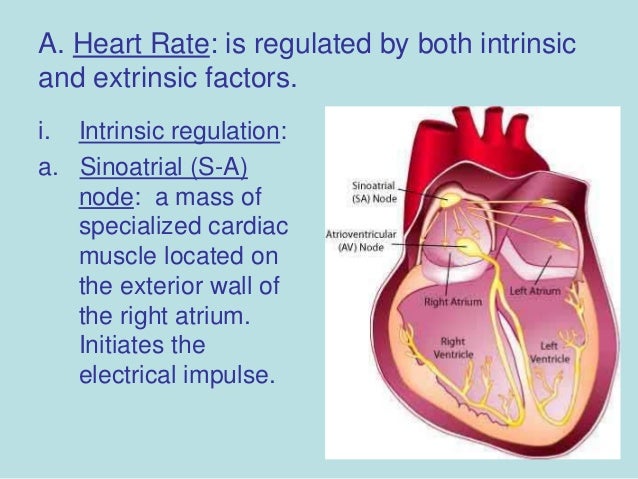 Image Source : www.slideshare.net
Image Source : www.slideshare.net regulation extrinsic physiology nervous
PPT - Cardiovascular Regulation PowerPoint Presentation, Free Download
 Image Source : www.slideserve.com
Image Source : www.slideserve.com regulation cardiovascular hr extrinsic parasympathetic acetylcholine epinephrine sympathetic neural norepinephrine
A) Extrinsic Regulation Of Stem Cell Fate. B) The Use Of Material
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net extrinsic scaffolds
Physiology: Extrinsic GFR Regulation: Sympathetic Nervous System | Draw
 Image Source : www.drawittoknowit.com
Image Source : www.drawittoknowit.com gfr regulation extrinsic sympathetic renal draw system know nervous mechanisms
PPT - CARDIAC REGULATION PowerPoint Presentation, Free Download - ID
 Image Source : www.slideserve.com
Image Source : www.slideserve.com regulation extrinsic heart presentation vessels cardiac slideserve
Examples Of Regulation Of The Extrinsic (caspase-8) And Intrinsic
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net caspase extrinsic intrinsic regulation pathways activation diagram
Extrinsic scaffolds. Exercise physiology. A) extrinsic regulation of stem cell fate. b) the use of material. Gfr regulation extrinsic sympathetic renal draw system know nervous mechanisms. Caspase extrinsic intrinsic regulation pathways activation diagram
 Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net  Image Source : www.slideshare.net
Image Source : www.slideshare.net  Image Source : www.slideserve.com
Image Source : www.slideserve.com  Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net  Image Source : www.drawittoknowit.com
Image Source : www.drawittoknowit.com  Image Source : www.slideserve.com
Image Source : www.slideserve.com  Image Source : www.researchgate.net
Image Source : www.researchgate.net